Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
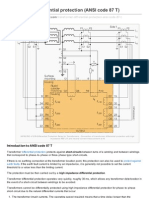
Differential and CB Failure Protection
Încărcat de
aalamz93_854917254Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Differential and CB Failure Protection
Încărcat de
aalamz93_854917254Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Differential Protection
A differential relay is one that operates when the vector difference of two or more
similar electrical quantities exceeds a predetermined amount.
Most differential-relay applications are of the current-differential type. The
simplest example of such an arrangement
Differential Protection
Differential Relay Settings
Line Charging Current Calculations
Maximum charging current IC = (2 x 3.142 x fN x CB' x s x Un)/1.732
Where;
Ic = Maximum charging current throughout the length (A)
UN= Nominal line voltage in V
fN = Rated frequency (Hz)
s = Length of the line in km
CB= Per unit line length service capacitance of the line in F/km
Differential Relay Settings
Dynamic Tripping threshold (87L Idyn)
We have done settings as per manual, which says that the value for dynamic pickup
threshold should be set as per below
It should be set to atleast 0.2 of the rated current
It should be larger than 2.5 to 3 times the capacitive charging current.
Dynamic Tripping threshold for Closing (87L Idyn close )
We have done calculations such that
the value for 87L Idyn (close) should be greater than or equal to 87L Idyn>, but it
should equal at least 3 times the value of capacitive charging current.
Differential Relay Settings
Static Tripping threshold (87L Isteady >)
The static tripping threshold should be set to a value that is larger than the rated current plus at
least 3 times the value of capacitive charging current. That is:
Selected value (1.3 * In+3 * Ic)
Trip Time Delay (87L Time Delay)
The trip time delay for 87L Isteady> is set in address 87L Trip Delay
Pickup Threshold (87L I min)
This value should at least corresponds to the settings of 87L I dyn> ,but not exceed the rated
current.
SI Time all CL
The Seal in time determines the activation for enabling protections following energization of the
line.
Transformer Differential Protection
The faults occur in the transformer inside the insulating oil can be detected by
Buchholz relay. But if any fault occurs in the transformer but not in oil then it can
not be detected by Buchholz relay.
Differential relays can detect such type of faults. Buchholz relay is also
provided in transformer for detecting any internal fault in the transformer but
Differential Protection scheme detects the same in more faster way.
Its working principle is similar to the one discussed in line differential protection
however for transformer some consideration must be kept in mind:
Transformer Differential Protection
A transformer has a turns ratio so the current in is not really equal to the current
out which causes an unbalance current in the operating coil of a transformer
differential relay.
Transformers require magnetising current. There will be a small current flow in
the transformer primary even if the secondary is open circuited.
In wye-delta connections there is a phase shift and difference in magnitude by
some 1.73 times between primary and secondary. Also a transformer has an
inrush current which tends to deviate from ideal behaviour.
Transformer Differential Protection
When transformers are first energized there is over-fluxing (saturation) of the core and
the large inrush energizing current has a distorted waveform. This waveform is
described as having high second harmonic content.
The transformer differential relays make use of this known fact and add in extra
restraint when it detects thissecond harmonic.
This extra feature prevents the transformer from tripping due to magnetizing current
when being energized, but does not add any time delay.
Because the differential relay will not operate with load current or faults outside the
protected zones (through faults), it can be set to operate at a low value of current
thereby giving rapid operation when a fault occurs.
Hence there is no need to time delay the operation of the relay and therefore a fast
acting type of relay can be used.
Transformer Differential Protection
For setting of such relays following calculations are performed
Rated Current
Differential Initial Setting I - Diff >
Differential Bias Slope Setting SLOPE 1
Differential Bias Slope Limit SLOPE 2
Differential Highest Setting I - Diff >>
Magnetising Inrush Restraint Level
Transformer Differential Protection
Load
Current:
The voltage corresponding to the average current of the regulated range.
The following applies:
Where Umax, Umin are the voltages at the limits of the regulated range.
Calculation of HV side and LV Side Currents:
In this step we have calculated the HV and LV side currents as well as
secondary current of CTs as IN1 and IN2
Transformer Differential Protection
Differential
Initial Setting I - DIFF >
Spill current calculation due to following Constant Errors:
Tap changer regulation
Magnetizing currents of CTs and Power transformer
Transformer Differential Protection
Other settings includes:
Differential Bias Slope Setting
Differential Highest Setting
Add-on stabilization I - ADD ON STAB
2nd Harmonic
Cross blocking for 2nd Harmonic
I - DIFF >>
Circuit Breaker Failure Protection
The circuit breaker failure protection provides rapid back-up clearance
of fault, in the event that the circuit breaker nearest to the fault fails to
respond to a trip command from the object protection.
The preset time of the breaker failure device is over, the breaker fail
trip command is released to trip all circuit breakers concerned with the
bus section to which the failed circuit breaker is connected.
CB Failure protection provides more reliability to the system and works
under the fail scenario of far CB.
CB Failure Protection Settings
The Substation has 5 number of bays with double bus bar system &
132kV gas insulated switchgears. These are configured as follows:
S.no
Circuit Breaker Description
CB no.
132kV Feeder (Civic Center)
E03
132kV Feeder (Gulshan)
E04
Bus-coupler
E05
Power Transformer
E06
Power Transformer
E07
CB Failure Protection Settings
CT Ratios and other system data:
System voltage = 132 / 11 kV
Power Transformers (E06 & E07)
200/1 A
Line Feeders (E03 & E04)
1600/1 A
Bus coupler (E05)
2500/1 A
Relay type
7UT6121-5EB22-1BA0
Relay rating
1A
Current detection setting range
to (steps 0.01IN)
Pick-up time
3 ms with measured quantities present
20ms after switch-on of measured
Reset/Drop-off time maximum
quantities
30 ms
Time setting range
0.00 to 60 s; infinite
CB Failure Protection Settings
132 kV Breaker Failure Protection
Relay Type: 7UT6121-5EB22-1BA0
System voltage
132 / 11 kV
CT Ratio
1600/ 1 A
Relay rating
1A
Setting range
Time setting range
&
Line Feeders: E03 & E04
The breaker failure protection switching
ON
Pick-up value of breaker failure protection
0.2 IN
current detector
Three pole trip repetition to the local feeder
0.120
circuit breaker
0.04In ~ 1.00In
2nd stage delay time for adjacent circuit
0.25 s
0.00 ~ 60.00 sec;
breakers, T2
Circuit breaker auxiliary contacts monitoring
Yes
Yes
CB Failure Protection Settings
132 kV Breaker Failure Protection
Relay Type: 7UT6121-5EB22-1BA0
Coupler
E05
System
voltage
132 / 11 kV
&
Bus
The breaker failure protection switching ON
Pick-up value of breaker failure
CT Ratio
2500/ 1 A
Relay rating
1A
Setting range
0.04In ~ 1.00In
Time setting range
0.00 ~ 60.00 sec;
0.2 IN
protection current detector
Three pole trip repetition to the local
0.120
feeder circuit breaker
2nd stage delay time for adjacent
0.25
circuit breakers, T2
Circuit breaker auxiliary contacts
Yes
monitoring Yes
CB Failure Protection Settings
132/11 kV Breaker Failure Protection
Relay Type: 7UT6121-5EB22-1BA0
System voltage
132 / 11 kV
&
20MVA Transformers
The breaker failure protection switching
ON
Pick-up value of breaker failure protection 0.2 IN
CT Ratio
200/ 1 A
Relay rating
1A
Setting range
0.04In ~ 1.00In
current detector
Three pole trip repetition to the local
0.120
feeder circuit breaker
2nd stage delay time for adjacent circuit
0.25 s
breakers, T2
Time setting range
0.00 ~ 60.00 sec;
Circuit breaker auxiliary contacts
monitoring
Yes
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Symmetrical Components: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionDe la EverandSymmetrical Components: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- High Volt Electric Defstan PDFDocument26 paginiHigh Volt Electric Defstan PDFMuhammad Jawwad Moeen AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Apostolov Requirements For Testing Power Swing Blocking Functions in Protection IEDs PDFDocument33 pagini3 Apostolov Requirements For Testing Power Swing Blocking Functions in Protection IEDs PDFqais652002100% (2)
- Test Instructions For Potential TransformerDocument4 paginiTest Instructions For Potential TransformerthegemishereÎncă nu există evaluări
- 220kV Busbar & Bus Coupler Control & Relay Panel - 07.09.18Document49 pagini220kV Busbar & Bus Coupler Control & Relay Panel - 07.09.18Guru Mishra100% (1)
- ProNautic ManualDocument9 paginiProNautic ManualJose CandedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- VTXDocument6 paginiVTXHari Krishna.MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scope: Transformer Winding Resistance MeterDocument4 paginiScope: Transformer Winding Resistance MeterL Adly100% (1)
- Transformer Protection-HosurDocument35 paginiTransformer Protection-HosurNaga BinduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applicatify REFDocument7 paginiApplicatify REFsupermannonÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Tap ChangerDocument42 paginiWhat Is Tap ChangerMatele de GilesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Inrush Current On Transformer ProtectionDocument27 paginiEffect of Inrush Current On Transformer ProtectiontusharlilaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short Circuit TestDocument1 paginăShort Circuit TestFatima MirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Testing Directional Overcurrent ProtectionDocument2 paginiTesting Directional Overcurrent ProtectionZokiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Restricted Earth Fault Relay-AHQDocument4 paginiRestricted Earth Fault Relay-AHQEnpak ArsalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1KHL020319 Aen Apn Note BBP Io enDocument40 pagini1KHL020319 Aen Apn Note BBP Io enhaichau199Încă nu există evaluări
- CT Class Very ImportantDocument6 paginiCT Class Very ImportantEngr Fahimuddin QureshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 87t ConnectionDocument20 pagini87t Connectionraul_bsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProtectionDocument157 paginiProtectionsivaepeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Omicron Test Method For DTPDocument17 paginiOmicron Test Method For DTPMohamed Wahid100% (1)
- Exercise - Setting An SEL-751A To Replace An Existing Electromechanical RelayDocument8 paginiExercise - Setting An SEL-751A To Replace An Existing Electromechanical RelayDavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnetizing CurrentDocument4 paginiMagnetizing CurrentSureshraja9977Încă nu există evaluări
- R5582E RELAY Selection GuideDocument14 paginiR5582E RELAY Selection GuideChandra Hamidi KautsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- OC SettingsDocument2 paginiOC Settingsdkandh0% (1)
- Differential Protection of Power Transformer in SubstationDocument4 paginiDifferential Protection of Power Transformer in SubstationEditor IJTSRDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auxiliary Classical Ancillary Equipment CatalogueDocument94 paginiAuxiliary Classical Ancillary Equipment CatalogueĐinh ĐạtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer Protection Relay IM30Document8 paginiTransformer Protection Relay IM30ashish_patel111Încă nu există evaluări
- In The Name of The Most Beneficent & The Most Merciful: Radio and TV Antenna 1Document42 paginiIn The Name of The Most Beneficent & The Most Merciful: Radio and TV Antenna 1Bhanu Prakash100% (1)
- CT RequirementsDocument5 paginiCT RequirementsShiva GourishettiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Substation Testing and Commissioning: High Impedence Busbar ProtectionDocument8 paginiSubstation Testing and Commissioning: High Impedence Busbar ProtectionThirumal100% (1)
- JVS Manual JRP 011Document12 paginiJVS Manual JRP 011Tamilventhan_sÎncă nu există evaluări
- P633 - Test - Tools Farhad Rev 01Document4 paginiP633 - Test - Tools Farhad Rev 01Mosa Elnaid ElnaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Worked ExamplesDocument9 paginiPower Worked Examplesbilawal shakirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differential Relay SlopeDocument6 paginiDifferential Relay SlopeNADEEM KHANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Universe Differential Module Application Note Example of Use Transformer ENUDocument16 paginiTest Universe Differential Module Application Note Example of Use Transformer ENUYasna SuárezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Restricted Earth Fault ProtectionDocument15 paginiRestricted Earth Fault ProtectionKuntal SatpathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mason-The Art & Science of Protective Relaying (002-010)Document9 paginiMason-The Art & Science of Protective Relaying (002-010)Marian ArjonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example Settings For Applying The SEL-487B To A Six-Breaker BusDocument24 paginiExample Settings For Applying The SEL-487B To A Six-Breaker Busu2andresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer Differential Protection ANSI Code 87 TDocument4 paginiTransformer Differential Protection ANSI Code 87 TFarooq KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculate Idmt PDFDocument6 paginiCalculate Idmt PDFShuvan MabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protection and Switchgear - by BakshiDocument397 paginiProtection and Switchgear - by BakshiAhmed Elaraby50% (2)
- CoordinationDocument18 paginiCoordinationKhaled Galal AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current TransformersDocument1 paginăCurrent Transformerswec11011Încă nu există evaluări
- 2H34 Application & Commisioning Manual Rev2 PDFDocument16 pagini2H34 Application & Commisioning Manual Rev2 PDFking_electricalÎncă nu există evaluări
- R Ratio in Circuit Breaker Short Circuit Duty EvaluationDocument6 paginiR Ratio in Circuit Breaker Short Circuit Duty EvaluationNASSERÎncă nu există evaluări
- LINEREV ProtectionDocument92 paginiLINEREV Protectionhafiz_hazreen100% (2)
- Overexcitation ProtectionDocument7 paginiOverexcitation ProtectionAnonymous zxtBoTT100% (1)
- REF ProtectionDocument13 paginiREF ProtectionAnonymous zxtBoTTÎncă nu există evaluări
- TJM Section3 ApplicationsDocument5 paginiTJM Section3 ApplicationsVishal PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer Differential Protection PrinciplesDocument3 paginiTransformer Differential Protection Principlesjob_pÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differential ProtectionDocument20 paginiDifferential ProtectionsherubdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Transformer GroundingDocument4 paginiCurrent Transformer GroundingReza MuhammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- P438 EN M R-b5-A 311 661 PDFDocument1.192 paginiP438 EN M R-b5-A 311 661 PDFAshutosh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes On Power System Load Flow Analysis Using An Excel WorkbookDocument20 paginiNotes On Power System Load Flow Analysis Using An Excel WorkbookkittuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Restricted Earth Fault Application GuideDocument12 paginiRestricted Earth Fault Application GuidementongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Connections of Overcurrent Relay (Part 2)Document4 paginiConnections of Overcurrent Relay (Part 2)Mahmoud AlshairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types and Applications of Overcurrent Relay (Part 1) - EEPDocument12 paginiTypes and Applications of Overcurrent Relay (Part 1) - EEPNeelakandan MasilamaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Transformer Protection PresentationDocument11 paginiPower Transformer Protection PresentationOmpa AcharyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knee Point Voltage Calculation: DataDocument1 paginăKnee Point Voltage Calculation: DataPRATHAM SARANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityDe la EverandKnowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Differential RelayingDocument115 paginiPrinciples of Differential RelayingelitesankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- B) Non-Unit Scheme:: Over Current Relay and Its CharacteristicsDocument6 paginiB) Non-Unit Scheme:: Over Current Relay and Its CharacteristicskarthikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distance Relay BasicsDocument58 paginiDistance Relay Basicsaalamz93_854917254100% (1)
- Electrical Power System Model On MATLAB SimulinkDocument2 paginiElectrical Power System Model On MATLAB Simulinkaalamz93_854917254Încă nu există evaluări
- Electric Power Generation Through Tidal Energy: Energy Conversion (EE-454) Presentation AssignmentDocument10 paginiElectric Power Generation Through Tidal Energy: Energy Conversion (EE-454) Presentation Assignmentaalamz93_854917254Încă nu există evaluări
- Nespak PresentationDocument116 paginiNespak Presentationaalamz93_8549172540% (1)
- NESPAK Internship ReportDocument21 paginiNESPAK Internship Reportaalamz93_85491725450% (2)
- What Is An Inverter?: Classification of InvertersDocument11 paginiWhat Is An Inverter?: Classification of Invertersayash mohantyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chris Rhodes - What Happens When The Oil Runs OutDocument44 paginiChris Rhodes - What Happens When The Oil Runs OutOnTheWightNewsÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIT6 701S10 Notes by Marc BaldoDocument261 paginiMIT6 701S10 Notes by Marc BaldoAlfredo Rico GuzmánÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solar Powered Charging StationDocument2 paginiSolar Powered Charging Stationarshid aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sunpower T0 Tracker: BenefitsDocument2 paginiSunpower T0 Tracker: BenefitsSaikumar NemalikantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Busbar ProtectionDocument23 paginiBusbar ProtectionJayamkondanÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Tneb 01july-2023 OnwardsDocument1 paginăNew Tneb 01july-2023 Onwardsreddyrajashekar100% (2)
- Project Report Power Generation Using Speed BreakerDocument16 paginiProject Report Power Generation Using Speed Breakersoham thumbreÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Exam ELT 22Document4 paginiEnglish Exam ELT 22rayane LouizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Axpert KING PYLONDocument59 paginiManual Axpert KING PYLONEllis BergmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Happens When We Charge Our Mobile With 5V 2A Rated Charger Instead of 5V 1A Rated Charger Will Charging Faster Damage TheDocument1 paginăWhat Happens When We Charge Our Mobile With 5V 2A Rated Charger Instead of 5V 1A Rated Charger Will Charging Faster Damage TheMalik AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Balance CalculationDocument2 paginiEnergy Balance CalculationSzelee KuekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan: Combined Science (Biology)Document3 paginiLesson Plan: Combined Science (Biology)mainaim2003Încă nu există evaluări
- SHP Power Contracted by MSEDCL As On 31.10.2020Document1 paginăSHP Power Contracted by MSEDCL As On 31.10.2020Om ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Load ComputationDocument12 paginiSample Load ComputationEric MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WEG w21 Aluminium Multimounting Three Phase Electric Motor 50035487 Brochure EnglishDocument24 paginiWEG w21 Aluminium Multimounting Three Phase Electric Motor 50035487 Brochure EnglishLeo Espinoza100% (1)
- Liebert GXT MT CX User Manual PDFDocument21 paginiLiebert GXT MT CX User Manual PDFBrian Boyle100% (2)
- Need of Solar EnergyDocument27 paginiNeed of Solar EnergyadityascribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC135 Classic B1 R06EN 10 - Electrical System.22911.2020 11 03.printableDocument76 paginiEC135 Classic B1 R06EN 10 - Electrical System.22911.2020 11 03.printableTitou GoltzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Otis Regenerative DrivesDocument2 paginiOtis Regenerative Drivestan0314Încă nu există evaluări
- 45 - 60055 - EE512 - 2015 - 5 - 2 - 1 - Experiment 2 PLC PDFDocument7 pagini45 - 60055 - EE512 - 2015 - 5 - 2 - 1 - Experiment 2 PLC PDFkrishnandrkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pilot Oil Supply: Type: MHSTE5G L1X/350 MHSTE5G L1X/100Document9 paginiPilot Oil Supply: Type: MHSTE5G L1X/350 MHSTE5G L1X/100anandsubbiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Training ISO 50008Document48 paginiTraining ISO 50008Ricardo AndresÎncă nu există evaluări
- T8 Linear Bypass Series: Led LampsDocument2 paginiT8 Linear Bypass Series: Led LampsJon GosnellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Looksfam EngineersDocument70 paginiLooksfam EngineersJohn PingkianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual EE1251 PDFDocument35 paginiLab Manual EE1251 PDFHitesh VijayÎncă nu există evaluări