Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Principles of Electronic Communication Systems
Încărcat de
mehul03ecTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Principles of Electronic Communication Systems
Încărcat de
mehul03ecDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1
Principles of Electronic
Communication Systems
Third Edition
Louis E. Frenzel, Jr.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
Chapter 23
Television
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
Topics Covered in Chapter 23
23-1: TV Signal
23-2: TV Receiver
Cable TV
Satellite TV
Digital Television
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
23-1: TV Signal
The TV signal occupies a significant amount of
spectrum space because it contains a great deal of
intelligence.
The TV signal consists of the sound and the picture.
The sound is stereo and the picture carries color
information as well as the synchronizing signals that
keep the receiver in step with the transmitter.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
23-1: TV Signal
Signal Bandwidth
The entire TV signal occupies a channel in the
spectrum with a bandwidth of 6 MHz.
There are two carriers, one each for the picture and the
sound.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
23-1: TV Signal
Figure 23-1: Spectrum of a broadcast TV signal.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
23-1: TV Signal
Signal Bandwidth: Audio Signal
The sound carrier is at the upper end of the spectrum.
Frequency modulation is used to impress the sound
signal on the carrier.
The audio bandwidth of the signal is 50 Hz to 15 kHz.
Stereo sound is also available in TV, and the
multiplexing method used to transmit two channels of
sound information is virtually identical to that used in
stereo transmission for FM broadcasting.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
23-1: TV Signal
Signal Bandwidth: Video Signal
The picture information is transmitted on a separate
carrier located 4.5 MHz lower in frequency than the
sound carrier.
The video signal derived from a camera is used to
amplitude-modulate the picture carrier.
The color information in a picture is transmitted by way
of frequency-division multiplexing techniques.
The video signal can contain frequency components up
to about 4.2 MHz.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
23-1: TV Signal
Signal Bandwidth: TV Spectrum Allocation
TV signals are assigned to frequencies in the VHF and
UHF range.
U.S. TV stations use the frequency range between 54
and 806 MHz.
Although TV is still transmitted by radio waves, most
viewers get their TV signals via a cable.
Over 80 percent of U.S. homes have cable TV that
carries the over-the-air TV channels as well as
premium and specialized channels of programming.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
10
23-1: TV Signal
Generating the Video Signal
The video signal is most often generated by a TV
camera, a very sophisticated electronic device that
incorporates lenses and light-sensitive transducers to
convert the scene or object to be viewed into an
electrical signal that modulates a carrier.
All visible scenes and objects are simply light that has
been reflected and absorbed and then transmitted to
our eyes.
The camera takes the light intensity and color details in
a scene and converts them into an electrical signal.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
11
23-1: TV Signal
Generating the Video Signal
In order to convert them into electrical signals, the
scene to be transmitted is collected and focused by a
lens upon a light-sensitive imaging device.
Both vacuum and semiconductor devices are used for
converting the light information into an electrical signal.
The scene is divided into smaller segments that can be
transmitted serially over a period of time.
The camera subdivides the scene in an orderly manner
so that an acceptable signal is developed.
This subdivision process is known as scanning.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
12
23-1: TV Signal
Generating the Video Signal: Principles of Scanning
Scanning is a technique that divides a rectangular
scene into individual lines.
The standard TV scene dimensions have an aspect
ratio of 4:3; that is, the scene width is 4 units for every 3
units of height.
To create a picture, the scene is subdivided into many
fine horizontal lines called scan lines.
Each line represents a very narrow portion of light
variations in the scene.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
13
23-1: TV Signal
Generating the Video Signal: Principles of Scanning
The greater the number of scan lines, the higher the
resolution and the greater the detail that can be
observed.
U.S. TV standards call for the scene to be divided into a
maximum of 525 horizontal lines.
The TV camera converts the scene into an electrical
signal by transmitting a voltage of 1V for black and 0V
for white.
The electrical signals derived from each scan line are
referred to as the video signal.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
14
23-1: TV Signal
Generating the Video Signal: Principles of Scanning
Shades of gray are represented by some voltage level
between the 0- and 1-V extremes represented by white
and black.
The resulting signal is known as the brightness, or
luminance, signal and is usually designated by Y.
One complete scanning of the scene is called a field.
The scene is scanned a second time in such a way that
its scan lines fall between those of the first field.
This produces what is known as interlaced scanning.
Interlaced scanning is used to reduce flicker.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
15
23-1: TV Signal
Figure 23-3: Simplified explanation of scanning.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
16
23-1: TV Signal
Figure 23-5: Interlaced scanning is used to minimize flicker.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
17
23-1: TV Signal
Generating the Video Signal: Relationship between
Resolution and Bandwidth
The resolution of the TV picture refers to the amount of
detail that can be shown.
Pictures with high resolution have excellent definition.
A picture lacking detail looks softer, or somewhat out of
focus.
The bandwidth of a video system determines the
resolution.
The greater the bandwidth, the greater the amount of
definition and detail.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
18
23-1: TV Signal
Generating the Video Signal: Color Signal Generation
The color detail in the scene is represented by dividing
the light in each scan line into three separate signals,
each representing one of the three primary light colors,
red, green, or blue.
The light in any scene can also be divided into its three
basic color components by passing the light through
red, green, and blue filters.
The result is the generation of three simultaneous
signals (R, G, and B) during the scanning process by
the light-sensitive imaging devices.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
19
23-1: TV Signal
Figure 23-8: How the camera generates the color signals.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
20
23-1: TV Signal
Generating the Video Signal: Color Signal Generation
The R, G, and B signals also contain the basic
brightness or luminance information.
The color signals must be transmitted with the
luminance information in the same bandwidth allotted to
the TV signal.
This is done by a frequency-division multiplexing
technique that combines the three color signals into I
and Q color signals.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
21
23-1: TV Signal
Generating the Video Signal: Color Signal Generation
These signals comprise different proportions of the R,
G, and B signals:
I = 60 percent red, 28 percent green, 32 percent blue
Q = 21 percent red, 52 percent green, 31 percent blue
The I and Q signals are called chrominance signals.
To transmit them, they are phase-encoded; they
modulate a subcarrier which is mixed with the
luminance signal to form a complete video signal.
The resulting signal is called the NTSC composite
video signal.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
22
23-1: TV Signal
Figure 23-9: (a)
How the NTSC
composite video
signal is
generated. (b)
The chrominance
signals are
phase-encoded.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
23
23-1: TV Signal
Generating the Video Signal: Color Signal Generation
To demodulate the double-sided (DSB) AM signals, the
carrier must be reinserted at the receiver.
An oscillator in the receiver generates the subcarrier for
the balanced modulator-demodulator circuits.
For the color signals to be accurately recovered, the
subcarrier at the receiver must have a phase related to
the subcarrier at the transmitter.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
24
23-1: TV Signal
Generating the Video Signal: Color Signal Generation
To ensure the proper conditions at the receiver, a
sample of the 3.58-MHz subcarrier signal developed at
the transmitter is added to the composite video signal.
Eight to 12 cycles of the 3.58-MHz subcarrier are gated
and added to the horizontal sync and blanking pulse.
This is called the color burst, and it rides on what is
called the back porch of the horizontal sync pulse.
The receiver uses this signal to phase-synchronize the
internally generated subcarrier before it is used in the
demodulation process.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
25
23-2: TV Receiver
The process involved in receiving a TV signal and
recovering it to present the picture and sound outputs
in a high-quality manner is complex.
The TV set has evolved from a large vacuum tube unit
into a smaller and more reliable solid-state unit.
Today, most of the circuitry is incorporated in largescale ICs, however, the typical TV receiver still uses
many discrete component circuits.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
26
23-2: TV Receiver
Tuner
The signal from the antenna or the cable is connected
to the tuner, which consists of an RF amplifier, mixer,
and local oscillator.
The tuner is used to select which TV channel is to be
viewed and to convert the picture and sound carriers
plus their modulation to an intermediate frequency (IF).
Most TV set tuners are prepackaged in sealed and
shielded enclosures.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
27
23-2: TV Receiver
Tuner
TV set tuners are two tuners in one, one for the VHF
signals and another for the UHF signals.
The VHF tuner usually uses low-noise FETs for the RF
amplifier and the mixer.
UHF tuners use a diode mixer with no RF amplifier or a
GaAs FET RF amplifier and mixer.
Most modern tuners are single integrated circuits.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
28
23-2: TV Receiver
Tuner: Tuning Synthesizer
The local oscillators are phase-locked loop (PLL)
frequency synthesizers set to frequencies that will
convert the TV signals to the IF.
Tuning of the local oscillator is typically done digitally.
The PLL synthesizer is tuned by setting the feedback
frequency-division ratio.
Most TV sets are tuned by IR remote control.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
29
23-2: TV Receiver
Video Intermediate Frequency and Demodulation
The standard TV receiver IFs are 41.25 MHz for the
sound and 45.75 MHz for the picture.
Because the local oscillator frequency is above the
frequency of incoming signals, the relationship of the
picture and sound carriers is reversed at the
intermediate frequencies, the picture IF being 4.5 MHz
above the sound IF.
The IF signals are sent to the video IF amplifiers.
Selectivity is usually obtained with a surface acoustic
wave (SAW) filter.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
30
23-2: TV Receiver
Video Intermediate Frequency and Demodulation
The SAW IF filter greatly attenuates the sound IF to
prevent it from getting into the video circuits.
The IF signals are amplified by IC amplifiers.
The video (luminance) signal is recovered by an AM
demodulator.
In most modern sets, a synchronous balanced
modulator type of synchronous demodulator is used.
It is part of the IF amplifier IC.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
31
23-2: TV Receiver
Sound Intermediate Frequency and Demodulation
To recover the sound part of the TV signal, a separate
sound IF and detector section are used.
The 4.5-MHz output of the sound detector is the sound
IF signal and contains both the AM picture and the FM
sound modulation.
It is passed to the sound IF amplifiers, which also
perform a clipping-limiting function that removes the
AM, leaving only the FM sound.
The audio is recovered with a quadrature detector or
differential peak detector.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
32
23-2: TV Receiver
Synchronizing Circuits
A major part of the TV receiver is dedicated to the
sweep and synchronizing functions that are unique to
TV receivers.
To display the picture on a picture tube, special sweep
circuits are needed to generate the voltages and
currents to operate the picture tube, and sync circuits
are needed to keep the sweep in step with the
transmitted signal.
The sweep and sync operations begin in the video
amplifier.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
33
23-2: TV Receiver
Synchronizing Circuits
The sync pulses are stripped off the video signal with a
sync separator circuit and fed to the sweep circuits.
The horizontal sync pulses are used to synchronize a
horizontal oscillator to 15,734 Hz.
This oscillator drives a horizontal output stage that
develops a sawtooth of current that drives magnetic
deflection coils in the picture tube yoke that sweep the
electron beams in the picture tube.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
34
23-2: TV Receiver
Synchronizing Circuits
The sync pulses are also fed to an IC that takes the
horizontal sync pulses during the vertical blanking
interval and integrates them into a 60-Hz sync pulse
that is used to synchronize a vertical sweep oscillator.
In most modern TV sets, the horizontal and vertical
oscillators are replaced by digital sync circuits.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
35
23-2: TV Receiver
Picture Tube
A picture tube is a vacuum tube called a cathode-ray
tube (CRT).
Monochrome (B&W) and color picture tubes are
available.
The CRT used in computer video monitors works like
the TV picture tube.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
36
23-2: TV Receiver
Picture Tube: Monochrome CRT
The tube is housed in a bell-shaped glass enclosure.
A filament heats a cathode that emits electrons, which
are attracted and accelerated by positive-bias voltages
on the elements in an electron gun assembly.
The electron gun focuses the electrons into a very
narrow beam.
A control grid controls the intensity of the electron beam
and the brightness of the spot it makes.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
37
23-2: TV Receiver
Picture Tube: Monochrome CRT
The beam is accelerated forward by a very high voltage
applied to an internal metallic coating called aquadag.
The face, or front, of the picture tube is coated internally
with a phosphor that glows and produces white light
when it is struck by the electron beam.
The magnetic field around the electron beam is
deflected by the magnetic field produced by the
deflection coils in the yoke.
Thus the electron beam is swept across the face of the
picture tube in the interlaced manner described earlier.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
38
23-2: TV Receiver
Picture Tube: Monochrome CRT
As the beam is being swept across the face of the tube
to trace out the scene, the intensity of the electron
beam is varied by the luminance, which is applied to the
cathode or the control grid.
By varying the grid voltage, the beam can be made
stronger or weaker, thereby varying the intensity of the
light spot produced by the beam when it strikes the
phosphor.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
39
23-2: TV Receiver
Picture Tube: Color CRT
To produce color, the inside of the picture tube is coated
with many tiny red, green, and blue phosphor dots
arranged in groups of three, called triads.
Some tubes use a pattern of red, green, and blue
stripes.
These dots or stripes are energized by three separate
cathodes and electron guns driven by the red, green,
and blue color signals.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
40
23-2: TV Receiver
Picture Tube: Color CRT
A metallic plate with holes for each dot triad called a
shadow mask is located between the guns and the
phosphor dots to ensure that the correct beam strikes
the correct color dot.
By varying the intensity of the color beams, the dot
triads can be made to produce any color.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
41
23-2: TV Receiver
Figure 23-16: (a) Basic construction and operation of a black-and-white (monochrome)
cathode-ray tube. (b) Details of color picture tube.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
42
23-2: TV Receiver
Other Screen Displays
While most TV sets still use a CRT for a display, in
recent years new display methods have been brought to
market, including liquid-crystal displays (LCDs), plasma,
projection, Digital Light Processing (DLP), and a few
others.
These new displays are more expensive than CRTs, but
they have brought two major benefits to TV displays.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
43
23-2: TV Receiver
Other Screen Displays
1. The displays are flat or thin. The typical depth of a
CRT is 18 to 24 in. LCD and plasma displays are
rarely more than 5 in thick.
2. These alternative displays can be made in much
larger sizes. The maximum CRT size made today is
36 in. Other displays can be made in sizes from
about 37- to 60-in diagonal measurement.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
44
23-2: TV Receiver
Other Screen Displays
Plasma: A plasma screen is made up of many tiny cells
filled with a special gas. When the gas is excited by an
electric signal, the gas ionizes and becomes a plasma
that glows brightly in shades of red, blue, and green.
The cells are organized to form triads that are mixed
and blended by your eye to form the picture.
LCD. Liquid-crystal displays use special chemicals,
sandwiched between pieces of glass, that are designed
to be electrically activated so that they block light or
pass light. When a bright white light is placed behind
the screen, the red, blue, and green sections of the
screen pass the desired amount of light.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
45
23-2: TV Receiver
Other Screen Displays
Projection screens. A very bright light is passed
through a smaller LCD screen and then through a lens,
creating a picture from 40 to 60 in. diagonally.
Digital Light Processing (DLP): These chips are made
with microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), which
consist of thousands of tiny mirror segments, each of
whose tilt angle is controllable.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
46
23-3: Cable TV
Cable TV, sometimes called CATV, is a system of
delivering the TV signal to home receivers by way of a
coaxial cable rather than over the air by radio wave
propagation.
A cable TV company collects all the available signals
and programs and frequency-multiplexes them on a
single coaxial cable that is fed to the homes of
subscribers.
A cable decoder box is used to receive the cable
signals, select the desired channel, and feed the
signal to the TV set.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
47
23-3: Cable TV
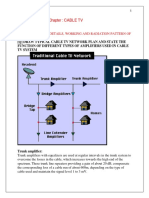
Modern Cable TV Systems
Cable TV companies collect signals and programs from
many sources, multiplex them, and distribute them to
subscribers.
The main building or facility is called the headend.
The antennas receive local TV stations and other
nearby stations plus the special cable channel signals
distributed by satellite.
The cable companies use parabolic dishes to pick up
the so-called premium cable channels.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
48
23-3: Cable TV
Modern Cable TV Systems
A cable TV company uses many TV antennas and
receivers to pick up the stations whose programming it
will redistribute.
These signals are processed and combined or
frequency-multiplexed onto a single cable.
The main output cable is called the trunk cable.
In older systems is was large, low-loss coaxial cable.
Newer systems use a fiber-optic cable.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
49
23-3: Cable TV
Modern Cable TV Systems
The trunk cable is usually buried and extended to
surrounding areas.
A junction box containing amplifiers takes the signal and
redistributes it to smaller cables called feeders, which
go to specific areas and neighborhoods.
From there the signals are again rejuvenated with
amplifiers and sent to individual homes by coaxial
cables called drops.
The overall system is referred to as a hybrid fiber
cable (HFC) system.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
50
23-3: Cable TV
Figure 23-18: The modern cable TV system.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
51
23-3: Cable TV
Signal Processing
The TV signals to be redistributed by the cable
company usually undergo some kind of processing
before they are put on the cable to the TV set.
Amplification and impedance matching are the main
processes involved in sending the signal to remote
locations.
At the headend, other types of processes are involved.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
52
23-3: Cable TV
Signal Processing
Straight-through processing is a process in which
local stations signals are picked up and amplified
before being multiplexed onto the main cable.
Amplifiers called strip amplifiers and tuned to the
received channels pass the desired TV signal to the
combiner.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
53
23-3: Cable TV
Signal Processing
Heterodyne processing translates the incoming TV
signal to a different frequency.
The cable company uses modules called heterodyne
processors to translate the received signals to the
desired channel.
All signals on their final channel assignments are sent
to a combiner, which is a large special-purpose linear
mixer.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
54
23-3: Cable TV
Digital Cable
In the newest cable TV systems, the audio and video
are transmitted in digital form in one or more of the
regular 6-MHz-bandwidth analog channels to the cable
box.
A video compression technique is used to make the
signal fit the available channel bandwidth.
Digital modulation methods are used, mainly multilevel
QAM.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
55
23-3: Cable TV
Digital Cable
The cable box at the receiving end contains digital
demodulator and decompression circuits and D/A
converters to put the signals into analog form for
presentation on the still-analog TV set.
The primary benefits of digital cable are that more
channels can be carried and the picture quality is
somewhat better.
Cable TV systems with digital cable continue to support
the older analog TV system since it is less expensive.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
56
23-4: Satellite TV
One of the most common methods of TV signal
distribution is via communication satellite.
A communication satellite orbits around the equator
about 22,300 miles out in space.
It rotates in synchronism with the earth and therefore
appears to be stationary.
The satellite is used as a radio relay station.
The TV signal to be distributed is used to frequencymodulate a microwave carrier, and then is transmitted
to the satellite.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
57
23-4: Satellite TV
The path from earth to the satellite is called the
uplink.
The satellite translates the signal to another frequency
and then retransmits it back to earth, which is called
the downlink.
A receive site such as a cable company or individual
consumer picks up the signal.
Satellites are widely used by the TV networks, the
premium channel companies, and the cable TV
industry for distributing their signals nationally.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
58
23-4: Satellite TV
Figure 23-22: Satellite TV distribution.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
59
23-4: Satellite TV
With direct broadcast satellite (DBS) TV, the system
is designed for consumer reception directly from the
satellite.
The new DBS systems feature digitally encoded video
and audio signals, which make transmission and
reception more reliable and provide outstanding picture
and sound quality.
By using higher-frequency microwaves, higher-power
satellite transponders, and very low-noise GaAs FETs in
the receiver, the customers satellite dish can be made
very small.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
60
23-4: Satellite TV
Direct Broadcast Satellite Systems
The new DBS system uses compressed digital video to
lower the data rate and improve the reliability of
transmission.
Once the video signals have been put into digital form,
they are processed by DSP circuits.
The compressed serial digital signal is then used to
modulate the uplinked carrier using BPSK.
The DBS satellite uses the band Ku band with a
frequency range of 11 to 14 GHz.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
61
23-4: Satellite TV
Direct Broadcast Satellite Systems
The advantage of using the Ku band is that the receiving
antennas may be smaller for a given amount of gain.
The biggest problem is the increased attenuation of the
downlink signal caused by rain.
Any type of weather involving rain or water vapor can
seriously reduce the received signal because the
wavelength of Ku band signals is near that of water
vapor. Therefore, the water vapor absorbs the signal.
The digital signal is transmitted from the satellite to the
receiver using circular polarization.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
62
23-4: Satellite TV
DBS Receivers
The receiver subsystem begins with the horn antenna,
which picks up the Ku band signal and translates the
entire 500-MHz band down to the 950- to 1450-MHz
range.
The RF signal from the antenna is sent by coaxial cable
to the receiver.
The received signal is passed through another mixer
with a variable-frequency local oscillator to provide
channel selection.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
63
23-4: Satellite TV
DBS Receivers
The digital signal at the second IF is demodulated to
recover the original digital signal, which is passed
through a forward error correction (FEC) circuit.
The resulting error-corrected signals are sent to the
audio and video decompression circuits.
The signal is decoded to separate it into both the video
and the audio portions.
Finally, the signals are sent to D/A converters that
modulate the RF modulator which sends the signals to
the TV set antenna terminals
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
64
23-5: Digital Television
Digital TV (DTV), also known as high-definition TV
(HDTV), was designed to replace the National
Television Standards Committee (NTSC) system.
The goal of HDTV is to greatly improve the picture and
sound quality.
The HDTV system is an extremely complex collection
of digital, communication, and computer techniques.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
65
23-5: Digital Television
HDTV Standards
HDTV uses the scanning concept to present a picture
on the CRT.
The HDTV screen is made up of thousands of tiny dots
of light called pixels.
The greater the number of pixels on the screen, the
greater the resolution and the finer the detail that can be
represented.
HDTV uses progressive line scanning, in which each
line is scanned one at a time from top to bottom.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
66
23-5: Digital Television
HDTV Transmission Concepts
In HDTV both the video and the audio signals must be
digitized by A/D converters and transmitted serially to
the receiver.
Because of the very high frequency of video signals,
special techniques must be used to transmit the video
signal over a standard 6-MHz bandwidth TV channel.
Multiplexing techniques must be used because both
video and audio must be transmitted over the same
channel.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
67
23-5: Digital Television
HDTV Transmission Concepts: HDTV Transmitter
In an HDTV transmitter, the video from the camera
consists of the R, G, and B signals that are converted to
the luminance and chrominance signals.
These are digitized by A/D converters.
The resulting signals are serialized and sent to a data
compressor.
MPEG-2 is the data compression method used in
HDTV.
The signal is next sent to a data randomizer.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
68
23-5: Digital Television
HDTV Transmission Concepts: HDTV Transmitter
The random serial signal is passed through a Reed
Solomon (RS) error detection and correction circuit.
The signal is next fed to a trellis encoder.
Each audio channel is sampled at a 48-kbps rate.
The video and audio data streams are packetized.
The packets are multiplexed with some synchronizing
signals to form the final signal to be transmitted.
The modulation scheme used in HDTV is 8-VSB.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
69
23-5: Digital Television
HDTV Transmission Concepts: HDTV Transmitter
The modulated signal is up-converted by a mixer to the
final transmission frequency, which is one of the
standard TV channels in the VHF or UHF range.
A linear power amplifier is used to boost the signal level
prior to transmission by the antenna.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
70
23-5: Digital Television
Figure 23-27: HDTV transmitter.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
71
23-5: Digital Television
HDTV Transmission Concepts: HDTV Receiver
In an HDTV receiver, the tuner and IF systems are
similar to those in a standard TV receiver.
The 8-VSB signal is demodulated into the original bit
stream.
The signal then passes through an NTSC filter and an
equalizer circuit.
The signals are demultiplexed into the video and audio
bit streams.
The trellis decoder and RS decoder correct any errors.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
72
23-5: Digital Television
HDTV Transmission Concepts: HDTV Receiver
The signal is descrambled and decompressed.
The video signal is converted back to the digital signals
that will drive the D/A converters that, in turn, drive the
red, green, and blue electron guns in the CRT.
The audio signal is demultiplexed and fed to AC-3
decoders.
The resulting digital signals are fed to D/A converters
that create the analog audio for each of the six audio
channels.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
73
23-5: Digital Television
The State of Digital TV
Most over-the-air television is still the original analog
NTSC programming, although satellite TV is all digital,
and cable TV companies are offering a growing amount
of digital TV.
The declining prices of large-screen plasma, LCD, and
projection sets with HDTV capability have had the
greatest impact in creating growth.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
74
23-5: Digital Television
The State of Digital TV
The U.S. government is anxious to initiate a complete
switch to digital by February 2009.
The governments desire to reclaim a large portion of
the UHF TV spectrum is driving this initiative.
The reclaimed spectrum will be auctioned off to cell
phone companies for expanded growth.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
75
23-5: Digital Television
The State of Digital TV
Spectrum is also needed for new communications
services and equipment that should help resolve the
incompatibility of radio services among the various city
police, fire, and public services.
The goal is to create fully interoperable radios for all
government, military, and other agencies to allow them
to communicate reliably during disasters.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
76
23-5: Digital Television
The State of Digital TV
In 2009, all current NTSC analog transmission will
cease and everyone will have to switch to HDTV.
For those who cannot afford a new TV set, the
government will subsidize special converter boxes that
will receive the HDTV signals and convert them to
standard analog output for older sets.
IPTV (Internet Protocol TV) will be transmitted over
high-speed Internet connections.
DVB-H is a special form of TV now being developed for
use on cell phones and other small-screen devices.
2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Components of TV SystemDocument16 paginiComponents of TV SystemRaja RÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELX 121 - Digital Television MultiplexingDocument22 paginiELX 121 - Digital Television MultiplexingClark Linogao FelisildaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eltr 303Document21 paginiEltr 303UmairSaeed33% (3)
- CD I DVD Mediji: Seminarski RadDocument17 paginiCD I DVD Mediji: Seminarski RadReronoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 6 (Chapter 6: Video) : C. NTSC - JapanDocument2 paginiExercise 6 (Chapter 6: Video) : C. NTSC - JapanNurul Aini Mohd ZamriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Electronic Communication Systems: © 2008 The Mcgraw-Hill CompaniesDocument76 paginiPrinciples of Electronic Communication Systems: © 2008 The Mcgraw-Hill CompaniesSaurabh ChardeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter23 TelevisionDocument37 paginiChapter23 TelevisionEsh WaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- TV BroadcastingDocument124 paginiTV BroadcastingKenneth Casuela100% (1)
- Week 13 - Digital TVDocument28 paginiWeek 13 - Digital TVHans Christian MacasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital TelevisionDocument27 paginiDigital TelevisionHans Christian MacasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TV Broadcasting (ECE 421)Document17 paginiTV Broadcasting (ECE 421)Jay-r De GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Television and DisplayDocument36 paginiTelevision and DisplayEbenezer HauleÎncă nu există evaluări
- AVE Labmanual 2023-24Document68 paginiAVE Labmanual 2023-2421ecuog059Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is Television: Basic Working of TV ReceiverDocument33 paginiWhat Is Television: Basic Working of TV ReceiverThs TeekoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doordarshan Summer Training ReportDocument36 paginiDoordarshan Summer Training Reportsmriti0% (1)
- Ifa LM 1823 An-391Document16 paginiIfa LM 1823 An-391Titis PrasetyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monochrome Picture TubeDocument5 paginiMonochrome Picture TubeNeeraj RanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modern Television: TV StandardsDocument5 paginiModern Television: TV StandardsNurul Syafiqah Jaafar SidekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doordarshan Seminar ReportDocument48 paginiDoordarshan Seminar ReportHimanshu Mahajan100% (1)
- Analog Television, Wimax and DVB-H On The Same Soc PlatformDocument5 paginiAnalog Television, Wimax and DVB-H On The Same Soc PlatformHồ TínÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 9 - TV Broadcast StandardsDocument12 paginiLesson 9 - TV Broadcast StandardsYousef BobadillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Television, Bernard GrobDocument15 paginiBasic Television, Bernard GrobaledieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study of Nec TransmitterDocument31 paginiStudy of Nec TransmitterSri HarshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Television and Video Engineering Lab Manual PDFDocument77 paginiTelevision and Video Engineering Lab Manual PDFtariq76100% (2)
- WINSEM2020-21 ECE4010 TH VL2020210503189 Reference Material I 02-Jun-2021 Direct TV-newDocument20 paginiWINSEM2020-21 ECE4010 TH VL2020210503189 Reference Material I 02-Jun-2021 Direct TV-newAryan VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Terrestrial TVDocument23 paginiDigital Terrestrial TVSatty_boyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Communication Systems All QuizDocument5 paginiPrinciples of Communication Systems All QuizPaulo Miguel TabuenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paytv System Development BackgroundDocument4 paginiPaytv System Development Backgroundnomatters_evenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amit Kumar Singh Anand Kumar Anita Bhavana KeshwaniDocument40 paginiAmit Kumar Singh Anand Kumar Anita Bhavana KeshwaniAjit BabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color Television ReceiverDocument42 paginiColor Television ReceiverTesfaye Mengistie ZewdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- TV Transmitter TutorialsDocument39 paginiTV Transmitter TutorialsSri HarshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DVB-T OFDM Modulation System: József Biró, Endre BorbélyDocument6 paginiDVB-T OFDM Modulation System: József Biró, Endre BorbélyFlower LandÎncă nu există evaluări
- DTH Direct To HomeDocument22 paginiDTH Direct To HomeKONA NAGENDRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Broadcasting and Cable TV SystemsDocument25 paginiBroadcasting and Cable TV SystemsTrina Ritchell AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doordashan Training ReportDocument38 paginiDoordashan Training ReportRanjeet pratap singh bhadoriya50% (4)
- Introduction To CATVDocument10 paginiIntroduction To CATVBello Taofeeq OladayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The ComponentsDocument5 paginiThe Componentslng_babie19Încă nu există evaluări
- ELX 121 - Digital Television MultiplexingDocument22 paginiELX 121 - Digital Television MultiplexingClark Linogao FelisildaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 590 Direct Satellite Television BroadcastingDocument13 pagini590 Direct Satellite Television BroadcastingKedhar MallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fast Guide To DTVDocument6 paginiFast Guide To DTVnsilverguyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Video A Multimedia ComponentDocument41 paginiVideo A Multimedia ComponentR. JhansiraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite Communication Lab ManualDocument3 paginiSatellite Communication Lab ManualJagadeesh Samudrala100% (2)
- TV System and Transmission MohitDocument19 paginiTV System and Transmission MohitKaran Maan100% (1)
- TELEVISIONDocument44 paginiTELEVISIONDeepanshu GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications of AM, SSB, VSBDocument24 paginiApplications of AM, SSB, VSBKirthi Rk100% (1)
- Principles of Digital Video Broadcasting "Terrestrial" DVB-TDocument6 paginiPrinciples of Digital Video Broadcasting "Terrestrial" DVB-TTorkia HadjazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Television Simplified TV SystemDocument18 paginiTelevision Simplified TV Systememmanuel wambuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multimedia Systems Chapter 5Document6 paginiMultimedia Systems Chapter 5Sanyogita ShindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Television: Receiving AntennasDocument9 paginiTelevision: Receiving AntennashunnbajajÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10.SN and CNDocument12 pagini10.SN and CNAnume123Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter: CABLE TV: Constructional Details, Working and Radiation Pattern of Dish AntennaDocument19 paginiChapter: CABLE TV: Constructional Details, Working and Radiation Pattern of Dish AntennaDivya KrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter02-1 Amplitude ModulationDocument43 paginiChapter02-1 Amplitude Modulationcreed60Încă nu există evaluări
- Terrestrial Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB-T) Coverage Planning For Adama StationDocument14 paginiTerrestrial Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB-T) Coverage Planning For Adama StationTeferi LemmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Definition TV: Audio-Video SystemsDocument4 paginiHigh Definition TV: Audio-Video SystemsAtit PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analog TV BroadcastingDocument26 paginiAnalog TV BroadcastingVinceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catv Block DiagramDocument7 paginiCatv Block DiagramJenny Babe Lindugan-Lopez0% (1)
- How TV WorksDocument17 paginiHow TV WorksSarita Madwal KargetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TV TrainingDocument33 paginiTV TrainingTesfaye Mengistie ZewdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1: Principles of Transmission: Part B: Television TheoryDocument20 paginiChapter 1: Principles of Transmission: Part B: Television Theorynestor martourezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analog TV BroadcastingDocument26 paginiAnalog TV BroadcastingVinceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ofdm Based Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB-T) Tecnique AnalysisDocument4 paginiOfdm Based Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB-T) Tecnique AnalysisseventhsensegroupÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gain To Frequency: Assume Carrier ofDocument10 paginiGain To Frequency: Assume Carrier ofmehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz QuestionsDocument2 paginiQuiz Questionsmehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Your Single Window To Invest In: IndiaDocument9 paginiYour Single Window To Invest In: Indiamehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 paginiGujarat Technological Universitymehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite Communication: Mikita Gandhi AditDocument41 paginiSatellite Communication: Mikita Gandhi Aditmehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite Navigation SystemDocument9 paginiSatellite Navigation Systemmehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- PinDocument2 paginiPinmehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semianr ScheduleDocument1 paginăSemianr Schedulemehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite CommunicationDocument19 paginiSatellite Communicationmehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Go To Simulation Project Select "All Block As 3D Model" (Shown Below)Document6 paginiGo To Simulation Project Select "All Block As 3D Model" (Shown Below)mehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEC703 - Microwave EngineeringDocument168 paginiBEC703 - Microwave Engineeringmehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- PointersDocument6 paginiPointersmehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communication 6 May 2017Document33 paginiCommunication 6 May 2017mehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- NMMTM MD M: - 2 2 KumnceDocument8 paginiNMMTM MD M: - 2 2 Kumncemehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class Time Table 14-12-2016Document4 paginiClass Time Table 14-12-2016mehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network ParametersDocument55 paginiNetwork Parametersmehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annual Day From ECDocument1 paginăAnnual Day From ECmehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gujarat Technological University: Electronics and Communication Engineering Subject Code: B.E. 8 SemesterDocument4 paginiGujarat Technological University: Electronics and Communication Engineering Subject Code: B.E. 8 Semestermehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPU (2110003) EC Division Assignment 4 Note: Deadline To Submit This Assignment Is 4-1-17Document1 paginăCPU (2110003) EC Division Assignment 4 Note: Deadline To Submit This Assignment Is 4-1-17mehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Programming Utilization (2110003) EC Division: Assignment - 2Document2 paginiComputer Programming Utilization (2110003) EC Division: Assignment - 2mehul03ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Researchpioneers 150120224510 Conversion Gate02Document86 paginiResearchpioneers 150120224510 Conversion Gate02mehul03ec100% (1)
- CQ tv190Document48 paginiCQ tv190RahulChampÎncă nu există evaluări
- 40LV933Document3 pagini40LV933biibicusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radio and Television Written ReportDocument13 paginiRadio and Television Written ReportAlleah Jayzel GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RadioDocument10 paginiRadioNicolaescu EugenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liteon LVW-5002 & 5006 DVR User ManualDocument37 paginiLiteon LVW-5002 & 5006 DVR User ManualBenjamin Dover100% (1)
- Danish Television Drama Series: A Sunday Evening PhenomenonDocument18 paginiDanish Television Drama Series: A Sunday Evening PhenomenonFernando EgertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Htz131dvdDocument85 paginiManual Htz131dvdErnesto Rodriguez S.Încă nu există evaluări
- Aoc L32W961Document222 paginiAoc L32W961Angel ArebaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- TV ReviewsDocument2 paginiTV ReviewsAsitAgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bluray ReportDocument21 paginiBluray ReportTarachandSainÎncă nu există evaluări
- RapidMoviez - Latest MoviesDocument18 paginiRapidMoviez - Latest MoviesUSR SuceavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LCD TV ManualDocument9 paginiLCD TV ManualtanviriubdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yuki Yuna Op Akatsuki No Yona Ed2 Punch Line Op Nisekoi Op Etotama Op Ed Akame Ga Kill Op 2Document12 paginiYuki Yuna Op Akatsuki No Yona Ed2 Punch Line Op Nisekoi Op Etotama Op Ed Akame Ga Kill Op 2ekaputra2710Încă nu există evaluări
- Television FilmDocument6 paginiTelevision FilmnelsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- NSBC - A Dumped Raws: All The Files Are Gone For Good!! Go To THE !!Document116 paginiNSBC - A Dumped Raws: All The Files Are Gone For Good!! Go To THE !!teampayaman2029Încă nu există evaluări
- Professional Videography Unit2 Session1Document30 paginiProfessional Videography Unit2 Session1Vikram Aditya ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual de Servicio 4 Philips TVDocument44 paginiManual de Servicio 4 Philips TVabrahamcho8Încă nu există evaluări
- AllDocument1.229 paginiAllSaid MananiÎncă nu există evaluări
- LG l1919s SFDocument2 paginiLG l1919s SFaluislimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Canal Posição 150 Canais MEO Total 200 Canais PremiumDocument6 paginiCanal Posição 150 Canais MEO Total 200 Canais PremiumHugo FerreiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamental Concepts in VideoDocument4 paginiFundamental Concepts in VideoMerga G KewetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10-Bit, Integrated, Multiformat SDTV/HDTV Video Decoder and RGB Graphics Digitizer ADV7181CDocument20 pagini10-Bit, Integrated, Multiformat SDTV/HDTV Video Decoder and RGB Graphics Digitizer ADV7181Cbarukula_ramesh7376Încă nu există evaluări
- Samsung Ud6400 Ud6500 Ud6900Document74 paginiSamsung Ud6400 Ud6500 Ud6900edsel72Încă nu există evaluări
- Caption Maker - InstructionsDocument8 paginiCaption Maker - InstructionsrberioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lista Na Kanali SMDocument1 paginăLista Na Kanali SMZdravko RadulovićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genex 4009 9 Cam MultiplexerDocument2 paginiGenex 4009 9 Cam MultiplexerstadawgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lista Magic Kids TVDocument5 paginiLista Magic Kids TVLu AlmzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week of June 7 Basic Cable Ranker (Total Viewers)Document1 paginăWeek of June 7 Basic Cable Ranker (Total Viewers)AdweekÎncă nu există evaluări