Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
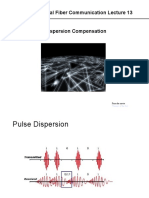
Dispersion Compensation
Încărcat de
srajalakshmiDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Dispersion Compensation
Încărcat de
srajalakshmiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
16.
711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
Today
Fiber modes
Fiber Losses
Dispersion in single-mode fibers
Dispersion induced limitations
Dispersion management
The Graded index fibers
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
Fiber modes --- single mode and multi-mode fibers
V-number
V
2a 2
2a 2
(n1 n22 )1/ 2 , Vcutoff
(n1 n22 )1/ 2 2.41,
Number of modes when V>>2.41
V2
M
,
2
Normalized propagation constant
b
2
neff
n22
n12 n22
b (1.1428 0.996 / V ) 2 , for V between 1.5 2.5.
Mode field diameter (MFD)
2 w 2a (1
1
),
V
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
Examples --- single mode and multi-mode fibers
1. Calculate the number of allowed modes in a multimode step index fiber, a = 100 m, core
index of 1.468 and a cladding index of 1.447 at the wavelength of 850nm.
Solution:
2a 2
V
(n1 n22 )1/ 2 91.44,
V2
M
4181,
2
2. What should be the core radius of a single mode fiber that has the core index of 1.468 and the
cladding index of 1.447 at the wavelength of 1.3m.
Solution:
2a 2
(n1 n22 )1/ 2 2.4, a < 2.1m
3. Calculate the mode field diameter of a single mode fiber that has the core index of 1.458 and
the cladding index of 1.452 at the wavelength of 1.3m.
Solution:
2 w0 2a (1 1 / V ) 10.1m,
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
Fiber loss
Material absorption
silica electron resonance <0.4m
OH vibrational resonance ~ 2.73 m
Harmonic and combination tones ~1.39 m
1.24 m, 0.95 m
Rayleigh scattering
Local microscopic fluctuations in density
C
,
4
C~ 0.8dB/km m4
0.14dB loss @ 1.55m
Bending loss and Bending radius
exp( R / Rc ), Rc
a
,
n12 n23
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
Dispersions in single mode fiber
Material dispersion
d
L
vg
| 0 , g ,
d
vg
d 2n
Dm ( 2 ),
c d
d
d 2n
( ) ( 2 ) ,
L
d
c d
g Dm L ,
Example --- material dispersion
Calculate the material dispersion effect for LED with line width of 100nm and a laser with a line
width of 2nm for a fiber with dispersion coefficient of Dm = 22pskm-1nm-1 at 1310nm.
Solution:
Dm L 2.2ns, for the LED
Dm L 44 ps,
for the Laser
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
Dispersions in single mode fiber
Waveguide dispersion
d
L
vg
| 0 , g ,
d
vg
d
n2 (n1 n2 ) d 2 (Vb)
( )
V
,
2
L
d
c
dV
1.984 N g 2
d
n2 (n1 n2 ) d 2 (Vb)
( )
, Dw
V
,
L
d
(2a) 2 2cn22
c
dV 2
g Dm L ,
Example --- waveguide dispersion
n2 = 1.48, and delta n = 0.2 percent. Calculate Dw at 1310nm.
Solution:
b (1.1428 0.996 / V ) 2 , for V between 1.5 2.5.
d 2 (Vb)
V
0.26,
dV 2
n2 (n1 n2 ) d 2 (Vb)
Dw
V
1.9 ps /( nm km),
c
dV 2
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
chromatic dispersion (material plus waveduide dispersion)
g
L
( Dm Dw ) ,
material dispersion is determined by
the material composition of a fiber.
waveguide dispersion is determined
by the waveguide index profile of a
fiber
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
Polarization mode dispersion
g
D p ,
L
fiber is not perfectly symmetric,
inhomogeneous.
refractive index is not isotropic.
dispersion flattened fibers:
Use waveguide geometry and
index profiles to compensate
the material dispersion
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
Dispersion induced limitations
For RZ bit With no intersymbol interference
B
1
,
2 1/ 2
For NRZ bit With no intersymbol interference
1
B
,
1/ 2
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
Dispersion induced limitations
Optical and Electrical Bandwidth
1
,
2 1/ 2
f 3dB 0.7 B,
Bandwidth length product
BL
0.25
,
D
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
Dispersion induced limitations
Example --- bit rate and bandwidth
Calculate the bandwidth and length product for an optical fiber with chromatic dispersion
coefficient 8pskm-1nm-1 and optical bandwidth for 10km of this kind of fiber and linewidth of
2nm.
Solution:
1/ 2 / L D 16 pskm 1 ,
BL
0.25
36.9Gbs 1km,
D
f 3dB 0.7 B 2.8GHz,
Fiber limiting factor absorption or dispersion?
Loss 0.25dB 10km 2.5dB,
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
Dispersion Management
Pre compensation schemes
1.
Prechirp
Gaussian Pulse:
1 t
A(0, t ) A0 exp[ ( ) 2 ],
2 T0
2T02
~
2 1/ 2
A(0, ) A0 (2T0 ) exp(
),
2
dk
1 d 2k
k ( ) k 0
| ( 0 )
| ...,
d 0
2 d 2 0
k ( )
d
d 2
1
( )
0
| 0 ( 0 )
|
...
2 ( ) 2 ...,
0
1
2 0
c
d
d
2
i
~
~
A( z , ) A(0, ) exp( 2 z ),
2
A0
1 ~
i
1
A( z , t )
A
(
0
,
)
exp(
)
d
exp[
],
0
2
2
2
2
2
T
Q
(
z
)
Q( z )
0
Q( z ) 1
i 2 z
2 z 2 1/ 2
,
T
(
z
)
[
1
(
) ] T0 ,
T02
T02
1
,
T0
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
Dispersion Management
Pre compensation schemes
1.
Prechirp
Prechirped Gaussian Pulse:
2T02 1/ 2
2T02
~
A(0, ) A0 (
) exp(
),
1 iC
2(1 iC )
A(0, t ) A0 exp[
(1 iC ) t 2
( ) ],
2
T0
2
i
2T02 1/ 2
2T02
~
~
2
2 iCT0 2
A( z , ) A(0, ) exp( 2 z ) A0 (
) exp[
],
2
1 iC
2(1 C 2 )
(1 C 2 )
1
0 (1 C 2 )1/ 2 ,
T0
A( z , t )
1
2
Q( z ) 1
A0
i
1
~
A
(
0
,
)
exp(
)
d
exp[
],
0
2
2
2
2
T
Q
(
z
)
Q( z )
0
(C i ) 2 z
C 2 z 2 2 z 2 1 / 2
,
T
(
z
)
[(
1
) ( 2 ) ] T0 ,
2
2
T0
T0
T0
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
Dispersion Management
1.
Prechirp
With T1/T0 = sqrt(2), the transmission distance is:
C 1 2C 2
L
LD ,
1 C 2
LD T02 / 2 ,
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
Dispersion Management
Examples:
1. Whats the dispersion limited transmission distance for a 1.55m light wave system making
use of direct modulation at 10Gb/s? D = 17ps(km-nm). Assume that frequency chirping broadens
the guassian-shape by a factor of 6 from its transform limited width.
Solution:
1
5 10 11 ( s ), T0 TFWHM / 1.66 3 10 11 s,
2B
1
0 (1 C 2 )1/ 2 , C 5.9,
T0
2
2c
D 2 2 , 2 24 ps / km,
TFWHM
T ( z ) [(1
z 12km,
C 2 z 2 2 z 2 1 / 2
) ( 2 ) ] T0 T0 ,
2
T0
T0
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
Dispersion compensation fiber or dispersion shifted fiber
Why dispersion compensation fiber:
for long haul fiber optic communication.
Alloptical solution
D1 L1 D2 L2 0
Approaches
d 2n
Dm ( 2 ),
c d
longer wavelength has
a larger index.
make the waveguide
weakly guided so that
longer wavelength has a
lower index.
16.711 Lecture 3 Optical fibers
The Graded index fibers
n1[1 ( / a ) ];
n( )
d 2 1 dn
,
2
dz
n d
D1 L1 D2 L2 0
n1(1 ) n2 ;
a,
a,
0 cos( pz ) 0 ' sin( pz ),
Approaches
p (2 / a 2 )1/ 2 , z 2 / p,
Only valid for paraxial approximation
General case Intermode dispersion
n1
2 ,
20 3c
Calculate the BL product of a grade index filber of 50m core with refractive index of n1 =
1.480 and n2 = 1.460. At 1.3 m.
Solution:
n1
2 0.026ns,
20 3c
BL
0.25L
9.6Gbs 1km,
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 7.1.2 - Spectra - QUESTIONSDocument3 pagini7.1.2 - Spectra - QUESTIONSmalihaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SET4523 Final TutorialDocument60 paginiSET4523 Final TutorialHilmi MujahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved Problems of Laser Chapter 4 KeiserDocument35 paginiSolved Problems of Laser Chapter 4 Keisersohaib50% (2)
- Quiz - Radiation Safety On-LineDocument4 paginiQuiz - Radiation Safety On-LineManmik8252Încă nu există evaluări
- IB Physics HL Study GuideDocument233 paginiIB Physics HL Study GuideJosh Smith80% (5)
- Lecture3 16.711Document18 paginiLecture3 16.711Manveen KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Figure 3.1 The Structure of The Step-Index Optical FiberDocument12 paginiFigure 3.1 The Structure of The Step-Index Optical FiberMalakonda ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16.711 Lecture 3 Optical FibersDocument18 pagini16.711 Lecture 3 Optical FibersVijay JanyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16.711 Lecture 3 Optical FibersDocument18 pagini16.711 Lecture 3 Optical FibersVijay JanyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework Chapter 02Document8 paginiHomework Chapter 02Muzamil ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture3 16.711Document18 paginiLecture3 16.711sruharithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical FiberDocument16 paginiOptical FiberRinju DuttÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turowicz 1Document62 paginiTurowicz 1Saurav KauraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiber Pres 3Document24 paginiFiber Pres 3nomanashrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 02 - TTQ 2022ADocument73 paginiChapter 02 - TTQ 2022Ahai NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-1 and 2 OpticalDocument278 paginiUnit-1 and 2 OpticalGuru VelmathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Waveguides, 2 ND EditionDocument32 paginiOptical Waveguides, 2 ND EditionHammad SÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3320 Fiber-Optic CommunicationDocument32 pagini3320 Fiber-Optic CommunicationEdward FahmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loss in Fiber OpticsDocument23 paginiLoss in Fiber OpticsCeline Dian SitorusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Communication Systems: n n a V λ πDocument5 paginiOptical Communication Systems: n n a V λ πkutty_dineshÎncă nu există evaluări
- SIGNAL DISTORTION (Dispersi)Document38 paginiSIGNAL DISTORTION (Dispersi)Amay SubtoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 PropagationDocument29 pagini2 PropagationrazifhamzahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec.5-COMM 554 Optical Communication SystemsDocument17 paginiLec.5-COMM 554 Optical Communication SystemsMahmoud SayedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 4 StudentDocument15 paginiLecture 4 StudentJanine NaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Communication ? Significance of Guided and Unguided Communication Wireless / Mobile Communication Radio Propagation EffectsDocument61 paginiWhat Is Communication ? Significance of Guided and Unguided Communication Wireless / Mobile Communication Radio Propagation EffectsSrinath RavichandranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 13Document33 paginiLecture 13Pavan DeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 13: From The MovieDocument33 paginiEE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 13: From The MoviemofiwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Fibre CommunicationsDocument4 paginiOptical Fibre CommunicationsFetsum Lakew100% (1)
- Silicon Waveguide Polarization Rotator Sampled Bragg GratingDocument3 paginiSilicon Waveguide Polarization Rotator Sampled Bragg Grating鍾國方Încă nu există evaluări
- Kumpulan Soal SKODocument12 paginiKumpulan Soal SKOChrisna Fiddin IÎncă nu există evaluări
- ON Expt4Document10 paginiON Expt4Shubh ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mod I ProblemsDocument2 paginiMod I ProblemsMeera S NairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiber Optics Communications SystemDocument73 paginiFiber Optics Communications SystemKim Brian CarboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optelec2 PDFDocument114 paginiOptelec2 PDFafifeh ghaemniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment-1: Introduction To Optical Fiber CommunicationDocument37 paginiExperiment-1: Introduction To Optical Fiber CommunicationPallav KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- WDM Concept and Components-1Document66 paginiWDM Concept and Components-1UDDALAKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optoelectronics: Chapter #3 Transmission Characteristics of Optical FiberDocument61 paginiOptoelectronics: Chapter #3 Transmission Characteristics of Optical FiberMehroz FatimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document2 paginiAssignment 1rzbrzbÎncă nu există evaluări
- LinkPower BudgetDocument29 paginiLinkPower BudgetDevLaxmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 1-Ch 7Document13 paginiCH 1-Ch 7Eligius MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec8701 Optical CommunicationDocument2 paginiEc8701 Optical CommunicationSaranya GunasekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study and Optimization of High-Bit Rate Optical FiDocument11 paginiStudy and Optimization of High-Bit Rate Optical FiMostafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wideband Dual Posts Waveguide Band Pass FilterDocument7 paginiWideband Dual Posts Waveguide Band Pass FilterAmador Garcia IIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waveguide DispersionDocument4 paginiWaveguide DispersionBesondere06Încă nu există evaluări
- OFC - An IntroductionDocument26 paginiOFC - An IntroductionRaman KhullarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved Problems of Laser Chapter 4 KeiserDocument35 paginiSolved Problems of Laser Chapter 4 KeiserAamir khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec5 Optical FiberDocument22 paginiSec5 Optical Fiberaelsheikh834Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 4 2021-Second Semester Exams 2Document3 paginiYear 4 2021-Second Semester Exams 2Melsougly BryceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of Soliton Propagation in A Directional CouplerDocument97 paginiSimulation of Soliton Propagation in A Directional Couplerr2b2mÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture #1 Optical FibersDocument59 paginiLecture #1 Optical Fibersjeddo2005Încă nu există evaluări
- Ece477 3Document45 paginiEce477 3Abhijeet RaghuwanshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ofc Optical Fiber Communication Pune UniversityDocument7 paginiOfc Optical Fiber Communication Pune UniversityJohnathon Horton100% (1)
- Assignment For LecturesDocument16 paginiAssignment For LecturesDeepak JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fibers From The View of Geometrical Optics: EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 2Document21 paginiFibers From The View of Geometrical Optics: EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 2mofiwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signal Degradation in Optical FibersDocument23 paginiSignal Degradation in Optical FibersSanjayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psisdg 6770 1 67700H 1Document9 paginiPsisdg 6770 1 67700H 1Carlos Morales CarbajalÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 9: Light SourcesDocument36 paginiEE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 9: Light SourcesmofiwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light Scattered Short Length of Fiber Compare It With The Total Optical PowerDocument22 paginiLight Scattered Short Length of Fiber Compare It With The Total Optical PowervardhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment5 SimulationStudyDocument12 paginiExperiment5 SimulationStudyRishikant KashyapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transmission Characteristics of Optical FibersDocument45 paginiTransmission Characteristics of Optical FibersDr Ravi Kumar A VÎncă nu există evaluări
- Opt Com Prob Set EntireDocument12 paginiOpt Com Prob Set EntirePallaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 8-Electrooptic Devices PDFDocument34 paginiCH 8-Electrooptic Devices PDFMahavir ChavdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To SpectrophotometryDocument26 paginiIntroduction To Spectrophotometryiryasti2yudistiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lanigan - 2000 - Lasers in DermatologyDocument115 paginiLanigan - 2000 - Lasers in DermatologyNicolás FarkasÎncă nu există evaluări
- A MATLAB-Based Application For Modeling and Simulation of Solar Slurry Photocatalytic Reactors For Environmental ApplicationsDocument17 paginiA MATLAB-Based Application For Modeling and Simulation of Solar Slurry Photocatalytic Reactors For Environmental ApplicationsMiume MewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 5.3 LightDocument10 paginiLesson 5.3 LightRais RahimiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter # 20 Nuclear RadiationDocument6 paginiChapter # 20 Nuclear RadiationSIR USMAN KHANÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP 2 Module 4Document39 paginiAP 2 Module 4Anshuman NandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 1 - Getting Started On EnergyPlus - 20120618 - 0Document28 paginiTutorial 1 - Getting Started On EnergyPlus - 20120618 - 0PaulaErikaMAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Components of Nuclear ReactorDocument17 paginiComponents of Nuclear ReactormrinalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post Task - Final Activity: Cristian VillegasDocument19 paginiPost Task - Final Activity: Cristian VillegasCristian VillegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronics Communication Engineering Optical Fiber Communication Fiber Couplers and Connectors NotesDocument15 paginiElectronics Communication Engineering Optical Fiber Communication Fiber Couplers and Connectors Notesroshan meharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Optics: 18 March 2021Document37 paginiPhysical Optics: 18 March 2021Luo MarkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irradiation in Food ProcessingDocument32 paginiIrradiation in Food ProcessingKishan KoyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- (166 Marks) : (1 Mark)Document32 pagini(166 Marks) : (1 Mark)Divit RayÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7H7773 - POC ITX 560 - UserGuide-enDocument192 pagini7H7773 - POC ITX 560 - UserGuide-ensaDÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCSE Physics: Electromagnetic Waves - 1Document4 paginiGCSE Physics: Electromagnetic Waves - 1Mr. SuitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics 295 Solutions To Problems in Chapter 37Document2 paginiPhysics 295 Solutions To Problems in Chapter 37HawJingZhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3c X Ray DiffractionDocument57 paginiChapter 3c X Ray DiffractionarulmuruguÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bruker Tracer and Artax XRF Raw Spectrum Analysis User Guide DraftDocument53 paginiBruker Tracer and Artax XRF Raw Spectrum Analysis User Guide DraftTimothy Benson100% (1)
- Iso 23603-2005Document28 paginiIso 23603-2005Chris AngelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 The Charactristics of Lens MaterialsDocument14 pagini01 The Charactristics of Lens MaterialsSayoki ghosgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Imaging in Conservation: SPRING 2017Document32 paginiImaging in Conservation: SPRING 2017OpticoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No. 1 ME-595 Solar Energy Utilization: Course Instructor: Asst. Prof. Dr. Muhammad AsifDocument7 paginiAssignment No. 1 ME-595 Solar Energy Utilization: Course Instructor: Asst. Prof. Dr. Muhammad AsifjawadÎncă nu există evaluări
- X-Ray Diffraction: Dr. Mukesh KumarDocument31 paginiX-Ray Diffraction: Dr. Mukesh Kumarhimanshu singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Wave Optics MCQDocument3 paginiPhysics Wave Optics MCQManjunath Sripathy100% (4)
- Physics Tir (Total Internal ReflectionDocument7 paginiPhysics Tir (Total Internal ReflectionHarsheet ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 5: Modern Physics Lecture 24: PHOTONS: ObjectivesDocument8 paginiModule 5: Modern Physics Lecture 24: PHOTONS: Objectivesprakhar vermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RPP Study MaterialDocument14 paginiRPP Study MaterialKartik SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări