Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Angelou Bello
Încărcat de
Christle PMD0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
33 vizualizări8 paginibeloo
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentbeloo
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
33 vizualizări8 paginiAngelou Bello
Încărcat de
Christle PMDbeloo
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 8
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Lesson 1 The Reading Process
Lesson 2 Metacognitive Reading Strategies
Lesson 3 Levels of Comprehension
Lesson 4 Translating Reading into Writing (Process
Approach)
Lesson 5 Unity, Coherence, and Cohesion in
Paragraph Writing
Lesson 1: The Reading Process
Reading is a process of translating letters and other
symbols into meaningful information for understanding
and use in everyday life. Readers use three schemas,
namely content schema, formal schema and linguistic
schema, in order to translate and understand text.
Schema Theory
Content Schema -
Formal Schema
Linguistic Schema
Lesson 2: Metacognitive Reading
Strategies
Metacognition is the awareness and knowledge of
ones mental processes such that one can monitor,
regulate, and direct them to a desired goal.
Metacognition Reading Strategies
Prereading (Planning)
While Reading (Monitoring)
Post-reading (Evaluating)
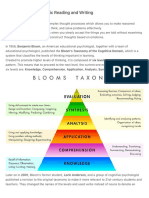
Lesson 3: Levels of Comprehension
Reading is thinking cued by written language. Effective readers
think within the text. Effective readers think beyond the text.
Effective readers think about the text.
Levels of Comprehension
Literal involves understanding of explicit ideas or identifying
main ideas and details used.
Interpretive the reader is able to make inferences, draw
conclusions, and predict outcomes from information not directly
stated.
Applied the reader is able to relate ones experiences to provide
an evaluation.
Lesson 4: Translating reading into
Writing
Writing is a mark of civilization
There is always a way out when you stumble
People live in a highly literate global society, which
involves reading and writing.
Process Approach
Prewriting Activities ( Brainstorming, Graphic
Organizers, Outlining)
Prewriting is the most important stage to break the
writers block. It involves BRAINSTORMING, LISTING,
CLUSTERING, INTERVIEWING, OR QUESTIONING,
FREEWRITING, AND LOOPING.
Lesson 5: Unity, Coherence and Cohesion in
Paragraph Writing
Unified, coherent and cohesion paragraphs make sense.
Good writers follow rules and standards.
Paragraph is a piece of writing that focuses on one topic or
idea. It usually consists of more than one sentence.
A single paragraph consists:
Topic Sentence the main point of the writer.
a) Topic what the paragraph is all about
b) Controlling idea expresses the writers opinion or attitude towards
the topic
Supporting details refers to the sentence that develop the main idea
of the paragraph. Writers usually use descriptions, examples and
explanations to support or prove the topic sentence.
Conclusion/ Concluding statement the final sentence of
the paragraph. The purpose is to summarize the ideas, provide
comments or suggestions, and give the paragraph proper
closure.
Unity refers to how the writer developed the controlling
idea through the supporting details. For as long as each
and every detail can prove or support the main idea, the
paragraph is considered unified.
Coherence is another vital characteristic of a well-
written paragraph. A paragraph is considered
incoherent if there are sentences that are misplaces or
in the wrong order.
Cohesion refers to the smooth flow of ideas in the
paragraph. It is achieved when the writer can smoothly
Cohesion in writing can be achieved through the following devices:
Lexical chains refers to the sequence of related words in writing sentences or
paragraphs. Example: The choir sang as the pianist played a series of familiar
Christmas carols, which created a melodious atmosphere inside the church
Cohesive nouns are single words that name an idea presented by the writer in the
preceding sentences. Example: Some families spend thousands of pesos during the
holiday season, Their expenses usually include food, gifts, and travels.
Pronoun reference another way to achieve cohesive writing, Basically, pronouns
are used to replace nouns. The word/ group of words that a pronoun are used to
replaces or refers to is called antecedent.
Ellipsis cohesive device. It is done by omitting a word or phrase and substituting
them with those dots. Example: Christine likes to go shopping during the Christmas
rush, but her best friend Anne hates to. (go shopping during Christmas rush)
Substitution it is achieved by replacing a word or an idea with a more general word.
Example: Students always look forward to a long, stress-free Christmas break. The
same as true to the working adults.
Conjunction - coordinators and subordinators which writers are able to connect ideas
logically.
Transitional words a writer can link one sentence to another smoothly by using
this. Example: first, also, as a result, for example, similarly, in summary.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Come On Rain s1Document24 paginiCome On Rain s1api-259057314Încă nu există evaluări
- Properties of A Well-Written TextDocument8 paginiProperties of A Well-Written TextAmstrada Guieb Palomo-Tinte92% (13)
- Reviewer in RWSDocument3 paginiReviewer in RWSSali MonroeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer in RWSDocument6 paginiReviewer in RWSAbraham Del CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer in English For Q4Document13 paginiReviewer in English For Q4andrerupert9Încă nu există evaluări
- Quarter 4 - Lesson 1:: Clearly or in ConclusionDocument3 paginiQuarter 4 - Lesson 1:: Clearly or in ConclusionynobznÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Lesson 4 Cohesion and Coherence FINALDocument49 pagini4 Lesson 4 Cohesion and Coherence FINALreveriehale1210Încă nu există evaluări
- RWS Handout 3rd QuarterDocument4 paginiRWS Handout 3rd QuarterCharles DecenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theme-Rheme in Efl Learners Recount Text A Case Study By: Fitria DewiDocument5 paginiTheme-Rheme in Efl Learners Recount Text A Case Study By: Fitria DewiDeandra DayobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Content: Properties of A Well-Written Text Content StandardDocument6 paginiContent: Properties of A Well-Written Text Content StandardGladys Alejo PelotinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties of Well-Written TextsDocument35 paginiProperties of Well-Written TextsAbegail RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- RW Lesson 1-6Document3 paginiRW Lesson 1-6Hanna Mae AbreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading and Writing 3rd Grading NotesDocument3 paginiReading and Writing 3rd Grading NoteslanguidojaycÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading and Writing Lesson 1 9 ReviewerDocument4 paginiReading and Writing Lesson 1 9 ReviewersarahjoyjoveloÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Writing ProcessDocument26 paginiThe Writing ProcessJanice L. Langit100% (2)
- Reading and Writing Skills MODULE WEEK 3Document14 paginiReading and Writing Skills MODULE WEEK 3Hazel Mae HerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading and WritinghandoutDocument6 paginiReading and WritinghandoutRikki MeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conneted DiscourseDocument7 paginiConneted DiscourseBehappy 89Încă nu există evaluări
- Reading and Writing.Q3 Weeks 7 8Document11 paginiReading and Writing.Q3 Weeks 7 8Lawrenceglenn DeguzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Term ActiviyDocument8 paginiFinal Term ActiviyMichaela ParalejasÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 4-The ParagraphDocument5 paginiCHAPTER 4-The ParagraphNeil Henessy Casuncad CuareÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRẮC NGHIỆM-READING WRITINGDocument3 paginiTRẮC NGHIỆM-READING WRITINGSy Tam PhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- RW Lesson 1 2 3 4Document4 paginiRW Lesson 1 2 3 4Hanna Mae AbreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Effective Writing NotesDocument1 paginăPrinciples of Effective Writing NotesFretz AelÎncă nu există evaluări
- RW ReviewerDocument9 paginiRW ReviewermkfolaesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Reading Comprehension Skills For LPDocument4 pagini5 Reading Comprehension Skills For LPJoan PeridaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RNW ReviewerDocument5 paginiRNW ReviewerHakdogÎncă nu există evaluări
- RWS Lecture NotesDocument20 paginiRWS Lecture NotesArlene AstovezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties of A Well Written TextDocument5 paginiProperties of A Well Written TextJoy Villaspin25% (4)
- E App ReviewerDocument3 paginiE App Reviewerjoshua33Încă nu există evaluări
- Reading and Writing CGDocument18 paginiReading and Writing CGنجشو گحوشÎncă nu există evaluări
- Academic Writing The Big PictureDocument5 paginiAcademic Writing The Big PictureElija ChesainaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Handbook of RhetoricDocument111 paginiA Handbook of RhetoricSudeshna bhar100% (2)
- EAPP Reviewer 2Document9 paginiEAPP Reviewer 2Ysabelle RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer W&RDocument6 paginiReviewer W&RmarianoprintingshopÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties of A Well-Written TextDocument5 paginiProperties of A Well-Written TextDoris MondragonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading & Writing: Lesson 1: Text As A Connected DiscourseDocument10 paginiReading & Writing: Lesson 1: Text As A Connected DiscourseEndrina Jansen EricÎncă nu există evaluări
- RWS Lesson 3 HandoutDocument6 paginiRWS Lesson 3 HandoutReshelle DumayÎncă nu există evaluări
- EAPP Reviewer L1 L7Document15 paginiEAPP Reviewer L1 L7jeromemallorca10Încă nu există evaluări
- Pair of Shoes As A Sample Sentence Gives Us An Idea That Someone Wants ADocument5 paginiPair of Shoes As A Sample Sentence Gives Us An Idea That Someone Wants Aelmer bacabacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading and Writing CompositionDocument23 paginiReading and Writing CompositionChrystal Miles ComajigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading and WritingDocument23 paginiReading and WritingCHRYSTAL MILES COMAJIG100% (1)
- Eapp ReviewerDocument7 paginiEapp ReviewerELOISA DELOS SANTOSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extensive Reading DoneDocument7 paginiExtensive Reading Donesuci apriliana pertiwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developmental Reading Final LectureDocument141 paginiDevelopmental Reading Final LectureDavid-Aragorn Peredo TelmoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Well Written TextDocument58 paginiWell Written TextMarilyn Ibay SuballaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RWS Lesson 1 2 3 4Document4 paginiRWS Lesson 1 2 3 4bobandrei42Încă nu există evaluări
- RWS Module 2 Lessons 1 3 1Document8 paginiRWS Module 2 Lessons 1 3 1jy6fybjr5bÎncă nu există evaluări
- Academic Reading and Writing NotesDocument60 paginiAcademic Reading and Writing NotesEljhon Steve SatsatÎncă nu există evaluări
- RW-Learning Activity Sheet 3Document4 paginiRW-Learning Activity Sheet 3William De VillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teaching ReadingDocument12 paginiTeaching ReadingDado Dodo100% (1)
- Course Outline For Efapp: UNIT 1.1 Fundamentals of Reading Academic Texts A. Four Macro Skills in English CommunicationDocument5 paginiCourse Outline For Efapp: UNIT 1.1 Fundamentals of Reading Academic Texts A. Four Macro Skills in English CommunicationKIM LABRADOR - GALENDEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Text As Connected Discourse: Lesson 1Document21 paginiText As Connected Discourse: Lesson 1JMay BuensalidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1-Lesson 4 (Properties of A Well-Written Text)Document50 paginiUnit 1-Lesson 4 (Properties of A Well-Written Text)Lennie Diaz60% (5)
- Reading and WritingDocument49 paginiReading and WritingIren Castor MabutinÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Essay HintsDocument7 paginiThe Essay HintssocmasterÎncă nu există evaluări
- CORE 001 3rd Quarter - Lesson 4Document13 paginiCORE 001 3rd Quarter - Lesson 4NatsumiGraceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Core Snapshot: Administrator's Guide to the Common CoreDe la EverandCommon Core Snapshot: Administrator's Guide to the Common CoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contract of AgreementDocument1 paginăContract of AgreementChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- By Laws - SparDocument2 paginiBy Laws - SparChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAMS, CES Promote Body Wellness Thru Outreach MissionDocument2 paginiCAMS, CES Promote Body Wellness Thru Outreach MissionChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis Topics - JD4Document1 paginăThesis Topics - JD4Christle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis Topics - JD4Document2 paginiThesis Topics - JD4Christle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guarantor FormDocument1 paginăGuarantor FormChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Article 3 - Bill of RightsDocument34 paginiArticle 3 - Bill of RightsChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ass 8 Case DigestDocument3 paginiAss 8 Case DigestChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtual On Line Frog Dissection Vs - Docx OcrDocument2 paginiVirtual On Line Frog Dissection Vs - Docx OcrChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Article 1806Document3 paginiArticle 1806Christle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ged101 SemisDocument6 paginiGed101 SemisChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtual On Line Frog Dissection Vs - Docx OcrDocument94 paginiVirtual On Line Frog Dissection Vs - Docx OcrChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Batangas State University: - 7. "Camille Is Hungry So She Ate in Her Favorite Restaurant."Document5 paginiBatangas State University: - 7. "Camille Is Hungry So She Ate in Her Favorite Restaurant."Christle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Article 1802Document4 paginiArticle 1802Christle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Big Three in One Ub, Lpu, Batstateu Tie Up For IndigentsDocument2 paginiBig Three in One Ub, Lpu, Batstateu Tie Up For IndigentsChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Article 1808Document4 paginiArticle 1808Christle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- BusLaw Group 4 HandoutDocument1 paginăBusLaw Group 4 HandoutWilliam Andrew Gutiera BulaqueñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- General PrinciplesDocument7 paginiGeneral PrinciplesChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- January Date Costumer Check No. Check DateDocument2 paginiJanuary Date Costumer Check No. Check DateChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- BusLaw Group 4 HandoutDocument1 paginăBusLaw Group 4 HandoutWilliam Andrew Gutiera BulaqueñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- General PrinciplesDocument137 paginiGeneral PrinciplesChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAMS, CES Promote Body Wellness Thru Outreach MissionDocument2 paginiCAMS, CES Promote Body Wellness Thru Outreach MissionChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Remrev CasesDocument1 paginăRemrev CasesChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Remrev CasesDocument64 paginiRemrev CasesChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal AFS RaeDocument2 paginiInternal AFS RaeChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Template CongratsDocument1 paginăTemplate CongratsChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAMS, CES Promote Body Wellness Thru Outreach MissionDocument2 paginiCAMS, CES Promote Body Wellness Thru Outreach MissionChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- January: Date Customer Check NumberDocument24 paginiJanuary: Date Customer Check NumberChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Big Three in One Ub, Lpu, Batstateu Tie Up For IndigentsDocument2 paginiBig Three in One Ub, Lpu, Batstateu Tie Up For IndigentsChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- SchedDocument1 paginăSchedChristle PMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wesley L SPED854 M5 Broken ArmDocument6 paginiWesley L SPED854 M5 Broken ArmLeah WesleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visual Information MediaDocument21 paginiVisual Information MediaDiana CabamonganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Nursing Theory TRANSESDocument2 paginiIntroduction To Nursing Theory TRANSESJoyce ElizaldeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frank Kessler Dispositif-NotesDocument19 paginiFrank Kessler Dispositif-NotesZelloff100% (1)
- The Generic Structures of Factual Report TextDocument4 paginiThe Generic Structures of Factual Report TextlanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epid Klinik 6 ValiduitasDocument71 paginiEpid Klinik 6 ValiduitasHalim SyahrilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intervention/Innovation: Research QuestionsDocument15 paginiIntervention/Innovation: Research Questionsapi-621535429Încă nu există evaluări
- Structural and Formal Disturbances of ThinkingDocument5 paginiStructural and Formal Disturbances of ThinkingAlex AthanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.technology Acceptance ModelDocument12 pagini4.technology Acceptance Modelkitii1701100% (2)
- 7 C's of Effective Communication - Talentedge PDFDocument1 pagină7 C's of Effective Communication - Talentedge PDFEngr Abdul QadeerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21st Cent LPDocument13 pagini21st Cent LPYelram FaelnarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Comparative Analysis of Nike and Adidas Commercials: A Multimodal Approach To Building Brand StrategiesDocument67 paginiA Comparative Analysis of Nike and Adidas Commercials: A Multimodal Approach To Building Brand StrategiesPrince Leō KiñgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sociology ReportingDocument9 paginiSociology ReportingMichelle UpodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cae Speaking ExpressionsDocument8 paginiCae Speaking ExpressionsVerónica CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Noun Phrase WorksheetDocument3 paginiNoun Phrase WorksheetTempat Menang 2Încă nu există evaluări
- Epse 437 Preferred Practice Final 590Document14 paginiEpse 437 Preferred Practice Final 590api-363225085Încă nu există evaluări
- The Difference Between Fichte's and Schelling's System of PhilosophyDocument250 paginiThe Difference Between Fichte's and Schelling's System of PhilosophyMavaddat Javid100% (2)
- A Review of Time Management LiteratureDocument24 paginiA Review of Time Management LiteratureStéfanie PaesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cse 304 Compiler DesignDocument6 paginiCse 304 Compiler DesignDustin ChangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neuro Fuzzy - Session 6Document21 paginiNeuro Fuzzy - Session 6Rohit Kumar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tet PGTRB Psychology Revision Test Model Question Papers Unit 456 English MediumDocument11 paginiTet PGTRB Psychology Revision Test Model Question Papers Unit 456 English MediumDhana CrushÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit #4 Grade Topic Title Subject(s) Unit Guiding Questions: Energize Me 6Document8 paginiUnit #4 Grade Topic Title Subject(s) Unit Guiding Questions: Energize Me 6shaneearlÎncă nu există evaluări
- SBFS1103 Thinking Skills & Problem Solving c2017 1-2Document47 paginiSBFS1103 Thinking Skills & Problem Solving c2017 1-2Kakra Kirk-MensahÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Guide For School LeadersDocument28 paginiA Guide For School LeadersIsam Al HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Hebrew Discourse - Patton & Putnam (2019)Document146 paginiBasics of Hebrew Discourse - Patton & Putnam (2019)Rob Cordopatri100% (6)
- Civil War Lesson PlanDocument3 paginiCivil War Lesson Planapi-335741528Încă nu există evaluări
- The Effect of Brain-Based Learning (BBL) Strategy On Students' Performance and Retention in ScienceDocument47 paginiThe Effect of Brain-Based Learning (BBL) Strategy On Students' Performance and Retention in ScienceFatmah BasherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evans Dual Processing 2008Document27 paginiEvans Dual Processing 2008PatrickBrown1100% (1)
- Teaching Philosophy 1Document2 paginiTeaching Philosophy 1Hessa Mohammed100% (2)
- Invitation To Interaction: Mary Cerutti, Lydia Guill, Cheri PiersonDocument5 paginiInvitation To Interaction: Mary Cerutti, Lydia Guill, Cheri PiersonSui Sing FengÎncă nu există evaluări