Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Indian Trade Union Act 1926
Încărcat de
bmdbmdbmd0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
35 vizualizări4 paginiindustrial engineering
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentindustrial engineering
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
35 vizualizări4 paginiIndian Trade Union Act 1926
Încărcat de
bmdbmdbmdindustrial engineering
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 4
THE TRADE UNIONS’ ACT, 1926
By: Mudit M. Saxena
Dept. of Mech. Engg.
• A trade union, trades union (British English) or labor union
(American English) is an organization of workers that have banded
together to achieve common goals such as better working
conditions.
• The trade union, through its leadership, bargains with the employer
on behalf of union members and negotiates labour contracts
(collective bargaining) with employers. This may include the
negotiation of wages, work rules, complaint procedures, rules
governing hiring, firing and promotion of workers, benefits,
workplace safety and policies.
• The agreements negotiated by the union leaders are binding on the
members and the employer and in some cases on other non-
member workers.
• Originating in Europe, trade unions became popular in
many countries during the Industrial Revolution, when
the lack of skill necessary to perform most jobs shifted
employment bargaining power almost completely to
the employers' side, causing many workers to be
mistreated and underpaid.
• Trade union organizations may be composed of
individual workers, professionals, past workers, or the
unemployed. The most common, but by no means
only, purpose of these organizations is "maintaining or
improving the conditions of their employment".[
• OBJECT: To provide for the registration of trade unions and to
define law relating to
• registered trade unions.
•
• APPLICABILITY: It extends to the whole of India.
•
• TRADE UNIONS: means any combination whether temporary or
permanent formed primarly for the purpose of regulating the
relations between workmen and employers for
• imposing restrictive conditions on the conduct of any trade or
business, and includes any
• federation of two or more trade unions.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- British Trade Unions Today: The Commonwealth and International Library: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionDe la EverandBritish Trade Unions Today: The Commonwealth and International Library: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labour Relations GuideDocument88 paginiLabour Relations Guiderhoda100% (1)
- Trade Unions: by Avantika MahajanDocument13 paginiTrade Unions: by Avantika MahajanAvantika MahajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Union, Is An: Organization of WorkersDocument34 paginiUnion, Is An: Organization of WorkersManish RajakÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Employer and the Employee: Your Legal Rights in WorkplaceDe la EverandThe Employer and the Employee: Your Legal Rights in WorkplaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organization of Workers: Rank and FileDocument16 paginiOrganization of Workers: Rank and FileManish RajakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial and Labor RelationsDocument42 paginiIndustrial and Labor RelationsEnjoy ChakmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade UnionsDocument36 paginiTrade Unionspankaj51281100% (1)
- Guide to Trade UnionsDocument26 paginiGuide to Trade UnionsPranay DabreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture TRADE UNION UpdatedDocument22 paginiLecture TRADE UNION UpdatedPrithibi IshrakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade UnionismDocument16 paginiTrade UnionismBhavika BaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade UnionDocument22 paginiTrade UnionEmilia Nkem Ohaegbuchi-Opara100% (1)
- Trade UnionsDocument38 paginiTrade Unionsshweta.gdp71% (7)
- Trade Union IntroductionDocument3 paginiTrade Union IntroductionBhanita BarmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labor Unions "Union Gives Strength" - AesopDocument19 paginiLabor Unions "Union Gives Strength" - AesopDhawal RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Collective Bargaining-NitiDocument15 paginiCollective Bargaining-NitiSimran JosanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IndustryDocument25 paginiIndustryAsres GizawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial RelationsDocument38 paginiIndustrial Relationsnetflixroom74Încă nu există evaluări
- Lec-5 Ll&irDocument12 paginiLec-5 Ll&irفیضان محبوبÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade UnionsDocument9 paginiTrade UnionsABDUR.RAFAY 12419Încă nu există evaluări
- Trade Union Act - DumpDocument41 paginiTrade Union Act - DumpjateelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 19 - Trade UnionsDocument20 paginiChapter 19 - Trade UnionsVCrockzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade Unions Explained: Their Functions and ObjectivesDocument80 paginiTrade Unions Explained: Their Functions and ObjectivesVISWANATHAN GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Collective Bargaining JSLDocument29 paginiCollective Bargaining JSLArunVermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit I: Trade UnionDocument18 paginiUnit I: Trade UnionNishanth NichuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics w3-TRADE UNIONSDocument7 paginiEconomics w3-TRADE UNIONSsaeed.hamidumohaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HRM 15Document27 paginiHRM 15Disal NimsaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade UnionsDocument21 paginiTrade UnionsFaizan AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labor RelationDocument13 paginiLabor RelationEamon awanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade Union: Shweta Chauhan Assistant Professor Shweta.j1525@cgc - Ac. in Bcom-6 SemDocument22 paginiTrade Union: Shweta Chauhan Assistant Professor Shweta.j1525@cgc - Ac. in Bcom-6 SemDhanraj DagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Relations (COM18304CR) UNIT-I (B) : Meaning & Nature of Trade UnionDocument13 paginiIndustrial Relations (COM18304CR) UNIT-I (B) : Meaning & Nature of Trade UnionMuslim RashidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labour EcoDocument20 paginiLabour EcoKamrul MozahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- L13 CollectiveBargainingandEmploymentRelationsDocument37 paginiL13 CollectiveBargainingandEmploymentRelationsChíi KiệttÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailed overview of All India Central Council of Trade Unions (AICCTUDocument6 paginiDetailed overview of All India Central Council of Trade Unions (AICCTUMohiuddin ansariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade UnionDocument14 paginiTrade UnionMansoor ChowdhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Function of Trade Uni ProjectDocument22 paginiFunction of Trade Uni Projectpratiksha lakdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Employer and Employee RelationsDocument23 paginiEmployer and Employee RelationssaminaJanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec-1 Ll&irDocument9 paginiLec-1 Ll&irفیضان محبوبÎncă nu există evaluări
- HR Chapter16 PDFDocument27 paginiHR Chapter16 PDFDee Wang100% (1)
- Collective BargainingDocument21 paginiCollective BargainingAbhishek BarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guided By: Mr. Pradeep MuragundiDocument27 paginiGuided By: Mr. Pradeep MuragundiWaqar MohsiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labour Law 1: PresentationDocument6 paginiLabour Law 1: PresentationTejas VenkatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade Union Evolution & ActivitiesDocument42 paginiTrade Union Evolution & ActivitiesLucky Xerox100% (2)
- International Human Resource Management (Vyshnav Es 19uhcmd122)Document10 paginiInternational Human Resource Management (Vyshnav Es 19uhcmd122)Vyshnav esÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iom3 Trade UnionsDocument12 paginiIom3 Trade UnionsSultan MorseanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade Labor UnionsDocument7 paginiTrade Labor UnionsJune BaytaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Industrial Relations and Collective Bargaining ProcessesDocument154 paginiUnderstanding Industrial Relations and Collective Bargaining ProcessesBhagyalaxmi sahooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Collective Bargaining: Its Relationship To StakeholdersDocument9 paginiCollective Bargaining: Its Relationship To StakeholdersyddubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade unionsDocument9 paginiTrade unionsTS shortsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade UnionsDocument37 paginiTrade UnionsRakesh MandalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sony GeorgeDocument119 paginiSony GeorgeKishan PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Relations ModifiedDocument16 paginiIndustrial Relations ModifiedsomechnitjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Relations and Labour LawsDocument15 paginiIndustrial Relations and Labour LawsMukesh Kumar YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labor LawDocument38 paginiLabor LawmegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labor Relations and Collective Bargaining - Group 5Document69 paginiLabor Relations and Collective Bargaining - Group 5Reichstein CaduaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument5 paginiUntitledaarti ghodeswarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Mentoring FormDocument3 paginiStudent Mentoring FormbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- REP - REM - Exam-CIE - Syllabus 2020-JULY - MATHEMATICS DEPT.-25-06-20Document3 paginiREP - REM - Exam-CIE - Syllabus 2020-JULY - MATHEMATICS DEPT.-25-06-20bmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
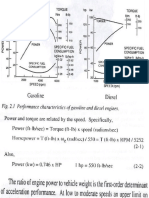
- Brief About Engine SystemDocument13 paginiBrief About Engine SystembmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- APDocument26 paginiAPbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mentor File: Department of Automobile Engieering Indus Institute of Technology & Research Indus UniversityDocument9 paginiMentor File: Department of Automobile Engieering Indus Institute of Technology & Research Indus UniversitybmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- AesDocument29 paginiAesbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Questions of PTMDocument1 paginăCommon Questions of PTMbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- OLD - Exam Schedule - RemedialDocument2 paginiOLD - Exam Schedule - RemedialbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Plan Format For StudentsDocument7 paginiCourse Plan Format For StudentsbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automobile Systems Design OptimizationDocument4 paginiAutomobile Systems Design OptimizationbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- APDocument26 paginiAPbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automobile Electrical Fundamentals: Prepared By: 110250102042Document42 paginiAutomobile Electrical Fundamentals: Prepared By: 110250102042bmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cim Test 1Document5 paginiCim Test 1bmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 08-09-2019Document2 paginiAssignment 08-09-2019bmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject Tribology SyllabusDocument3 paginiSubject Tribology SyllabusbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automobile Electrical Fundamentals: Prepared By: 110250102042Document42 paginiAutomobile Electrical Fundamentals: Prepared By: 110250102042bmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject Tribology SyllabusDocument3 paginiSubject Tribology SyllabusbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automobile Electrical Systems CourseDocument9 paginiAutomobile Electrical Systems CoursebmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject Production Techology SyllabusDocument3 paginiSubject Production Techology SyllabusbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject Production Techology SyllabusDocument3 paginiSubject Production Techology SyllabusbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- VDDocument9 paginiVDbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- BOS - New Exam SchmeDocument28 paginiBOS - New Exam SchmebmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Power Learning ObjectivesDocument40 paginiFluid Power Learning Objectivesbmdbmdbmd100% (1)
- SonuDocument10 paginiSonubmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factors Affecting Plant Location & Layout, Production Planning, Quality ControlDocument7 paginiFactors Affecting Plant Location & Layout, Production Planning, Quality ControlbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPV Question BankDocument2 paginiSPV Question BankbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intake and Exhaoust SystemDocument21 paginiIntake and Exhaoust SystembmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Power Learning ObjectivesDocument40 paginiFluid Power Learning Objectivesbmdbmdbmd100% (1)
- Classification of Vehicles - LayoutDocument41 paginiClassification of Vehicles - LayoutbmdbmdbmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- ControllingDocument8 paginiControllingAnjo Pasiolco Canicosa100% (2)
- CFA三级百题 答案Document163 paginiCFA三级百题 答案vxm9pctmrrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ramesh Dargond Shine Commerce Classes NotesDocument11 paginiRamesh Dargond Shine Commerce Classes NotesRajath KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metatron AustraliaDocument11 paginiMetatron AustraliaMetatron AustraliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 Test A Test (Z Widoczną Punktacją)Document4 paginiUnit 3 Test A Test (Z Widoczną Punktacją)Kinga WojtasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chinnamasta Sadhana PDFDocument1 paginăChinnamasta Sadhana PDFSayan Majumdar100% (2)
- Short EssayDocument3 paginiShort EssayBlue PuppyÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Over AgainDocument583 paginiAll Over AgainJamie Kris MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Business Development PlanDocument90 paginiA Business Development PlanRishabh Sarawagi100% (1)
- Direct InstructionDocument1 paginăDirect Instructionapi-189549713Încă nu există evaluări
- Promotion From Associate Professor To ProfessorDocument21 paginiPromotion From Associate Professor To ProfessorKamal KishoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Download Test Bank For Macroeconomics 11th Edition Arnold PDF Full ChapterDocument36 paginiFull Download Test Bank For Macroeconomics 11th Edition Arnold PDF Full Chaptervitalizefoothook.x05r100% (17)
- ESS 4104 AssignmentDocument9 paginiESS 4104 AssignmentSamlall RabindranauthÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSE Inc. V CA G.R. No. 125469, Oct 27, 1997Document7 paginiPSE Inc. V CA G.R. No. 125469, Oct 27, 1997mae ann rodolfoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concepts of Cavity Prep PDFDocument92 paginiConcepts of Cavity Prep PDFChaithra Shree0% (1)
- Life Stories and Travel UnitDocument3 paginiLife Stories and Travel UnitSamuel MatsinheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Write The Missing Words of The Verb To Be (Affirmative Form)Document1 paginăWrite The Missing Words of The Verb To Be (Affirmative Form)Daa NnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Method Statement For Wall Panels InstallationDocument11 paginiMethod Statement For Wall Panels InstallationChristos LoutrakisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dwnload Full Fundamentals of Human Neuropsychology 7th Edition Kolb Test Bank PDFDocument12 paginiDwnload Full Fundamentals of Human Neuropsychology 7th Edition Kolb Test Bank PDFprindivillemaloriefx100% (12)
- Review Activity For The Final Test - 6 Level: 1. Match Phrasal Verbs and Match To The MeaningDocument3 paginiReview Activity For The Final Test - 6 Level: 1. Match Phrasal Verbs and Match To The MeaningGabrielle CostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GRADE 8 English Lesson on Indian LiteratureDocument3 paginiGRADE 8 English Lesson on Indian LiteratureErold TarvinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Paper 1 Eng Lang StudiesDocument4 paginiResearch Paper 1 Eng Lang Studiessastra damarÎncă nu există evaluări
- EDU101 Solution FileDocument2 paginiEDU101 Solution FileTahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modification of Core Beliefs in Cognitive TherapyDocument19 paginiModification of Core Beliefs in Cognitive TherapysalalepeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Challan Form OEC App Fee 500 PDFDocument1 paginăChallan Form OEC App Fee 500 PDFsaleem_hazim100% (1)
- Eun 9e International Financial Management PPT CH01 AccessibleDocument29 paginiEun 9e International Financial Management PPT CH01 AccessibleDao Dang Khoa FUG CTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creating Early Learning Environments PDFDocument25 paginiCreating Early Learning Environments PDFkrisnahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding electromagnetic waves and radioactivityDocument7 paginiUnderstanding electromagnetic waves and radioactivityJayesh VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multigrade Teaching NotesDocument4 paginiMultigrade Teaching Notesqw938Încă nu există evaluări
- Fact-Sheet Pupils With Asperger SyndromeDocument4 paginiFact-Sheet Pupils With Asperger SyndromeAnonymous Pj6OdjÎncă nu există evaluări