Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Investigative techniques and cell biology
Încărcat de
abbiechong0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
84 vizualizări13 pagini1) The syllabus document outlines topics for an investigative techniques course, dividing them into easier "Upper 6" topics and more difficult "Lower 6" topics that delve into areas like taxonomy, biodiversity, and quantitative ecology.
2) The basic chemicals in the cell section covers water, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, ions, and vitamins - focusing on water's roles as a solvent, transport medium, and moderator of temperature in living things due to its high specific heat capacity and hydrogen bonding.
3) Carbohydrates are classified based on their number of carbon atoms (triose, pentose, hexose) or functional groups. Monosaccharides can exist as chains or rings and undergo oxidation
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
1 Basic Chemicals in Cell
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest document1) The syllabus document outlines topics for an investigative techniques course, dividing them into easier "Upper 6" topics and more difficult "Lower 6" topics that delve into areas like taxonomy, biodiversity, and quantitative ecology.
2) The basic chemicals in the cell section covers water, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, ions, and vitamins - focusing on water's roles as a solvent, transport medium, and moderator of temperature in living things due to its high specific heat capacity and hydrogen bonding.
3) Carbohydrates are classified based on their number of carbon atoms (triose, pentose, hexose) or functional groups. Monosaccharides can exist as chains or rings and undergo oxidation
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
84 vizualizări13 paginiInvestigative techniques and cell biology
Încărcat de
abbiechong1) The syllabus document outlines topics for an investigative techniques course, dividing them into easier "Upper 6" topics and more difficult "Lower 6" topics that delve into areas like taxonomy, biodiversity, and quantitative ecology.
2) The basic chemicals in the cell section covers water, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, ions, and vitamins - focusing on water's roles as a solvent, transport medium, and moderator of temperature in living things due to its high specific heat capacity and hydrogen bonding.
3) Carbohydrates are classified based on their number of carbon atoms (triose, pentose, hexose) or functional groups. Monosaccharides can exist as chains or rings and undergo oxidation
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 13
SYLLABUS Investigative techniques
Upper 6 topics are easier 2) Cell & organelle structure—
than those of Lower 6: Types of tissue
LOWER 6 – 3) Control in cells
6) Taxonomy: Enzymes, DNA replication &
protein synthesis
Linnaean Binomial
classification system
B) Energetics
7) Biodiversity: 4) Photosynthesis:
Plantae, Insects, Light- & Dark reactions
Preservation C3, C4 & crassulacean plants,
8) Quantitative ecology: Limiting factors of
photosynthetic rate
Sampling techniques
5) Respiration:
A) cell & molecular Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle &
biology electron transport system
1) Basic chemicals in the 9) Nutrition
cell – water, carbs, 10) Gaseous exchange
proteins, lipids, ions, In animals & plants
vitamins 11) Transport: Cardiac cycle,
Movement across xylem & phloem
membranes
UPPER 6
12) Homeostasis: 19) Genetics:
Temperature, glucose regulation, Mendel’s laws, and their
liver, kidney, plants exceptions
13) Nervous System: Synapse, 20) Mutation:
muscle contraction, drugs Gene mutation & chromosomal
14) Endocrine system: amino & mutation
steroid Hormones, estrous cycle, 21) Population genetics:
phytohormones Hardy-Weinberg Law
15) Immunity: 22) Gene regulation &
Antibodies, lymphatic system, expression: Lactose operon
AIDS. 23) Biotechnology:
16) Reproduction: Cloning, recombinant DNA
Sexual & asexual 7) Biodiversity:
17) Development: Monera, Protoctista, Fungi,
Embryology, double fertilization Animalia.
& seed germination
24) Variation:
18) Growth:
Natural selection, Evolution
Measuring, growth curves, ecdysis 8) Ecology: Ecosystems, r & K
strategies
BASIC CHEMICALS IN THE CELL(1)
Human body :70 % water. Animals = 100% molecules bonded together
& plants = 65 – 95 %. at freezing point to become solid.
Physical properties : liquid at I) Hydrolysis :Breaks up other
ambient temperature. Boiling point substances --Breaking up bonds in
100 degrees C, freezing large molecules. E.g.
Polysaccharide becomes simple
0o C. Occupies space in container, sugar. Speeded up by enzymes.
transparent, most dense at 4o C.
Low viscosity, universal solvent. II) Condensation- reaction that
Difficult to compress, poor produces water (reverse of
conductor of electricity, adhesion hydrolysis) Monosaccharide
to other molecules, cohesion to condenses to polysaccharide &
own molecules, Specific heat water.
capacity 1 calorie = 4184 J kg-1 oC- III) Photolysis : (water is broken
1 = to raise 1 kg water by 1oC. 3 up) light reaction
states : solid, liquid, gas. High Properties of water important as a
surface tension. component and medium of
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES: H2O : organisms.
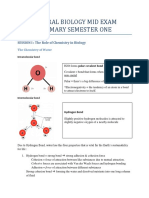
Hydrogen bonds, 3-D linkage. PHYSIOLOGICAL ROLES:
15% of molecules bound together. Good solvent : 1) Water molecule
Ambient temperature = liquid. Ice with poles (1450). Therefore, polar
solvent
Even though a lot of heat lost,
WATER (2) temperature only goes down a
little. A body of water has a
more or less constant
2) Universal solvent : Consists of temperature. So, suitable
polar molecules, easily dissolves medium for life.
other polar compounds. ii) Main component of
3) Ions & molecules free only if organisms : because of high
dissolved, cellular reactions only specific heat capacity. preserves
occur in an aqueous medium, so constant body temperature.
water is main component of 7) Surface tension : suitable
protoplasm.
medium for organisms – Small
4) 90% of blood plasma is water. ones supported and live on the
Materials dissolved in the plasma
can be transported throughout the surface, or stuck to the
body – water is important underside, e.g. water boatman.
constituent of living things. This property is important in
plants – brings water in narrow
xylem.
5) Gases and mineral salts can be
dissolved in water for aquatic life. 8)Density decreases with
So, it’s suitable as a medium for decreasing temperature.
them. Maximum at 40C. Water at 0oC
6) High specific heat capacity : freezes on the surface=
i) water absorbs a lot of heat to Insulation preventing freezing
raise a temperature slightly of the whole pond .
Why is the specific heat
(3)water & carbs capacity of water so high?
1) The heat energy disrupts H-
9) High latent heat of fusion and bonds, & then makes water
evaporation molecules move faster. As heat
A lot of heat needs to be lost from is absorbed when the bonds
water at 00C before it freezes. break, water absorbs and stores
Contents of cell and surrounding a large amount of heat while
water difficult to freeze. Water =
suitable medium and component of warming up only a few degrees.
cells. High heat of vaporization= 2) Conversely, when water is
transpiration effective for reducing cooled, more hydrogen bonds
heat. 10) Transparent: Aquatic form. Heat energy is released
plants can carry out photosynthesis. when the H-bonds form,
light can penetrate water to reach slowing the cooling process.
chlorophyll. Water moderates temperature
11) Low viscosity: Main by evaporative cooling. The
component of plasma. Particles molecules with the greatest
flow quickly in the body. Aquatic energy vaporize first.
organisms navigate smoothly.
Lubricant in the body. Movement Why is ice less dense than
of faeces in the rectum, reduces liquid water?
friction between joints. H-bonds in ice are stable, with
12) Adhesion and Cohesion: Sends each molecule bonded to 4
water & minerals up xylem vessels neighbours.
under pressure.
(4)
CARBOHYDRATES Can reduce
Basic formula: CnH2nOn (1:2:1) Benedict’s/Fehling’s solution.
Organic compound. Functions :
1) Energy source. 2) OXIDATION REDUCTION
Important component of nucleic
acid. 3) Cell structure – wall &
membrane
4) Defence & protection - chitin, Add oxygen Add hydrogen
thick gum 5) Storage
compound – energy.
3 types of sugar – 1) MONO (1
molecule) 2), di (2 molecules)
3) Poly (many molecules) Remove Remove
CLASSIFICATION OF hydrogen oxygen
MONOSACCHARIDES :
1) According to the number of C
atoms:
Triose (C3H603) = 3C, Pentose
Remove Add electrons
C5H1005 = 5C, Hexose(C6H1206) = electrons
6C.
2) According to the functional
group –aldehyde (H-C=0); carbonyl Increase Decrease
(C=0).
valency valency
Physical characteristics – soluble in
water. Sweet, small molecules, low
mass, can crystallize.
REDUCING SUGAR (5) ii)ring iii) Can exist in 2 isomers
(alpha, beta) same molecular
Produces disaccharide(poly-S) formula but different arrangement
through condensation. of atoms. E.g. glucose alpha –
CLASSIFICATION OF OH group jutting out below C no.1,
MONOSACCHARIDES : but glucose beta – OH jutting out
According to the number of C above
atoms, or functional group. FRUCTOSE : 3 forms – chain, 5C
E.g. - Functional group at Carbon ring (furanose), 6C ring (pyranose)
no. 1 = Aldehyde (Propanal), like Monosaccharide test:
Triose - glyceraldehyde ( an aldose 1. All monosaccharides and some
sugar) disaccharides are reducing sugars.-
Other aldose sugars:Pentose – Because of free functional group in
Ribose, and Hexose –Glucose. the molecule for donating electrons
Ketose sugars : Triose – in the reduction process.
dihydroxyiacetone, Pentose – 2. When a monosaccharide is
ribulose, and Hexose – fructose. boiled in Benedict’s solution,
Functional group = carbonyl copper ions(blue) become brick red
(propanon) precipitate(Cu20)
PENTOSE : Can exist in the form Disaccharides: 1. General formula
of a (i) chain(ribose) = C12H22011. 2. Formed by
(ii) ring (when dissolved in water) condensation. 3. Dehydration,
HEXOSE : I) chain (e.g. glucose) because water molecule is
removed.
4. Usually involves 2 monosaccharide
molecules(Hexose) Can happen to
ribose (pentose) also.
AMYLOSE (6)
Glucose alpha –glucose alpha POLYSACCHARIDES
(condensation) becomes maltose. 1) Consists of monosaccharide
Maltose(hydrolysis)becomes units. Condensed and linked by
glucose alpha glycosidic bonds.
NON-REDUCING SUGAR E.G. 2) GENERAL PROPERTIES
SUCROSE- hydrolyzed to glucose A) Not soluble, but forms colloid.
alpha and fructose beta. (By adding B) Not sweet C) Will not
dilute HCl). crystallize. D) High molecular
TESTS: Boiling sucrose with mass
Benedict’s/Fehling’s solution – E) can hydrolyze,
negative result. 3) Divided into 3 main groups:
Add hydrochloric acid. Neutralize Starch, glycogen and cellulose
with sodium bicarbonate
STARCH : consists of glucose
Add Benedict/Fehling and reboil. polymers. General formula =
Product = brick red precipitate. (C6H10O5)n n = 300 – 1000.
MAIN FUNCTIONS OF 2 polymers entwined together –
DISACCHARIDES: amylose and amylopectin.
1) Maltose – respiration substrate AMYLOSE : 1) Long straight chain
2) Sucrose – Extra carbohydrates of glucose alpha units joined with
transported in the form of sucrose glycosidic alpha 1,4 bonds.
because inactive & soluble. 2) Because of more hydroxide
Storage in sugar cane and beet. groups on a side chain, hydrogen
3) Lactose – CHO source for bonds between glucose sub-units
nursing babies. cause the amylose molecule to form
helix when suspended in water.
(7)
3) Spaces in the helix just big Structure same as amylopectin,
enough to trap iodine molecules and EXCEPT chains are shorter &
form dark blue complex. more branches. Functions: Animal
4) Dissolves in hot water and the food storage compound and energy
blue complex disappears because source.
the molecule has become straight. CELLULOSE
Blue again when cold.
General properties same as starch.
AMYLOPECTIN :
Chemical properties : Enzymes can
I) Consists of branching glucose hydrolyze it into glucose beta units.
polymers. 600 – 6000 glucose sub-
units. (cf. why diabetics shouldn’t STRUCTURE : 1) A long straight
eat too much rice although not chain, with glucose beta units
sweet) II) Each branch is a linked in glycoside beta 1,4 bonds.
short glucose chain linked with 2) Neighbouring cellulose chains
glycosidic alpha 1,4. The branches cross linked by hydrogen bonds.
are linked by glycosidic 1,6 bonds. This type of bonding is possible as
GLYCOGEN cellulose chains is formed from
Molecular formula = (C6H1005)n glycoside-beta 1,4 bonds which
straighten the chain. The
N = 300 – 1000. hydroxide groups jut out in all
Chemical characteristics : I) Can be directions to form H bonds. Forms
hydrolyzed by the enzyme glycogen a stable & strong structure. Cell
phosphorylase to glucose, wall – 80 to 2000 chains bind to
II) or glucose –1-phosphate. form thin fibres.
Distribution = liver, brain, muscles,
cytoplasmic granules in plants.
Lipids (8) Needed by the body and which it
can synthesize, e.g. 0leic, stearic &
1) Consists of C,H & O : organic palmitic acids.
compound, with low oxygen ratio. 4) Known as ester alcohol, because
Olive oil = C57H114O6 formed from acid & alcohol.
2) Formed from fatty acids & glycerol. 5) Hydrophobic organic
A) Fatty acids : consist of compound: not soluble – avoid
carboxylic acid with long hydrocarbon water, but soluble in organic
chain ; 14 – 20 C atoms. Saturated solvents (acetone & chloro-
fatty acid: without double bond
between 2 C atoms. Unsaturated : l or form) TEST FOR LIPID
more double bonds. 1) Grease spot test
B) Glycerol : a type of alcohol known 2) Fat emulsion with alcohol test:
as propane-1,2,3-trid Usually, ethanol dissolves in water,
3) A) Essential fatty acids but if a little lipid dissolved in 2 ml
of ethanol, and the solution is
(i) needed by the body, but the body dropped into a test tube of water,
cannot synthesize it e.g. Linoleic acid an emulsion of lipid in water is
linolenic acid & arachinodic acid for formed. If the substance is not
the control of blood pressure & lipid, the ethanol just dissolves
clotting. without any emulsion.
(ii)Plants can synthesize linoleic and 6) 3 groups : a) Triglycerides
linolenic acids – source of fatty acid in
food. b) phospholipids c) steroids
B) Non-essential fatty acids :
PHOSPHOLIPID (9)
1) 1 ester (--O--) is formed from 1 II) Storage medium.
molecule of glycerol and 3 III) Forms plasma membrane : fat
molecules of fatty acid, by with phosphoric acid =
condensation/esterization. phospholipid. IV) Heat insulator
2) All fats & oils are triglycerides. –mechanical protection, bouyancy
3) Different types of oil/fat force V) Insulator of
formed from different fatty acids:- Electricity at myelin sheath.
a)saturated fatty acids – because VI) Water-proof layer on feathers.
packed arrangement, no empty Fatty acid (14 – 20C) becomes
space. functional group = COOH. triglyceride
stearic acid C17H35COOH.i) Solid PHOSPHOLIPID : 1) Triglyceride
at room temperature (ii) in which 1 of the fatty acid groups
Mostly animal fats. is replaced by another group that
b) Unsaturated – Oleic Acid : contains phosphorus through
C17H33COOH : i) liquid at room condensation of 1 molecule
temperature ii)Mostly plant fats glycerol and 2 molecules of fatty
acid and 1 molecule phosphoric
4) Distribution : in adipose tissue, acid
surface of heart, liver, alimentary
canal, eggs of birds & insects. 2) Its structure is a glycerol
molecule bound to ester with 2
5. Functions : I) as energy source – molecules of fatty acid & 1
respiratory substrate. molecule of phosphoric acid
residue
STEROIDS (10) 5. The usual phospholipid =
lechitin, i.e. main component of
3) Phosphoric acid residue on a cell membrane bi-layer.
molecule of phospholipid
bound to another molecule. 6. In aqueous medium, lechitin
E.g.Choline forms lechitin. molecules arrange themselves
spontaneously to form a bi-
4) Phospholipid distribution in layer, with hydrophobic tails
the middle of plasma and facing inwards, and
organelle fibres, and on hydrophilic to the outside. This
nerve,heart and kidney tissues. barrier retains water in the cell,
5) FUNCTIONS : which also becomes a living
1) structural component of cell unit, and enables exchange of
membrane materials with aqueous
2) Lechitin involved in environment.
formation of acetylcholine STEROIDS Structure = Large
transmitters and neurons. molecule which consists of 4 C
3)Transport of fat in the body : atom rings bound together, with
Lipids transported in the form R (a long variable side chain) =
of phospholipid because its Basic framework, different R’s
head is hydrophilic, being form different steroids.
soluble in water and able to be Examples: cholesterol,
transported by blood. testosterone.
4) Damaged tissue – Properties : 1)Insoluble in
phospholipid helps in clotting water..
of blood by producing platelets.
10B
2) Soluble in non-polar solvents, like Cholesterol (saturated fat from
ether. animals)
A) Cholesterol : most important Too much = arteriosclerosis
component of cell membrane, ( deposits on arterial wall),
especially of nerves, besides Coronary thrombosis (deposits
phospholipid. Precursor = raw on wall of coronary artery)
material for synthesis of other lipids.
Testosterone = drug (anabolic
B) Testosterone : Reproductive steroid) – fat-soluble, diffuses
hormone of male mammal. through cell membrane to nucleus–
C) Estrogen & progesterone : quickens transcription of genes
Reproductive hormones of female that control synthesis of myofibril
mammal. proteins (actin and myosin) =
D) Adreno-cortical hormones : muscle tissue increases.
synthesized in the adrenal cortex Abuse = damaged liver, sterility,
gland for definite responses. death,
E) Bile acids – emulsifier for fats. Women = male characteristics.
F) Calciferol : (Vit. D) helps
absorption of Ca2+ and PO43 - from the
small intestine.
G) Ecdysone : the hormone that causes
ecdysis (moulting) of arthropods
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 2.1-2.6 Biology Review 1Document21 pagini2.1-2.6 Biology Review 1Victoria FinolÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMGBS-Bio 11. U.2 NoteDocument77 paginiEMGBS-Bio 11. U.2 Notenafhire2021Încă nu există evaluări
- Properties of WaterDocument154 paginiProperties of WaterGayathri AnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Notes BiologyDocument117 paginiUnit 1 Notes BiologyTwaiba AdmaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1 2.2 Metabolism+and+Water 2021 Science 10 IBDocument20 pagini2.1 2.2 Metabolism+and+Water 2021 Science 10 IBNexExplosiveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molecular BiologyDocument17 paginiMolecular BiologySapreen KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology NotesDocument161 paginiBiology NotesBlohsh KeenenÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntroDocument3 paginiIntroMary Rose AllinegÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1.2 Biology Ocr ADocument16 pagini2.1.2 Biology Ocr AFatima AfifiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peperiksaan Pra-STPM Penggal 1 2018 (Marking Scheme)Document6 paginiPeperiksaan Pra-STPM Penggal 1 2018 (Marking Scheme)Viola Voon Li WeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obj. 1.1-1.9 - BiomoleculesDocument26 paginiObj. 1.1-1.9 - BiomoleculesRecee josephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Molecules AS Bio 2022Document20 paginiBiological Molecules AS Bio 2022MrTechnomasterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1: Biological Molecules: WaterDocument15 paginiChapter 1: Biological Molecules: WaterChong Hyen100% (1)
- Revision Lecture Notes Biological Molecules: Chapter No-2Document17 paginiRevision Lecture Notes Biological Molecules: Chapter No-2Ãrêêbã ÅsĦfåqÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 WaterDocument15 pagini1.1 Waterjennymarimuthu3Încă nu există evaluări
- Updated Biochemistry Notes 2022Document17 paginiUpdated Biochemistry Notes 2022vandytommy308Încă nu există evaluări
- Cholesterol Proteins Glycocalyx/carbohydrates: Phospholipid BilayerDocument11 paginiCholesterol Proteins Glycocalyx/carbohydrates: Phospholipid BilayerGreenard Imperial GualbertoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biologically Important Molecules ExplainedDocument27 paginiBiologically Important Molecules ExplainedKargboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Composition Elements and CompoundsDocument22 paginiBody Composition Elements and CompoundsSophia RoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- MC2Introduction To BiochemistryDocument38 paginiMC2Introduction To BiochemistryKimberly SalarzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Substances of The CellDocument28 paginiChemical Substances of The Cellorkid_ijaÎncă nu există evaluări
- To The Point New Ch1,2Document7 paginiTo The Point New Ch1,2m.mansoor3377Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2Document12 paginiUnit 2Yitbarek TesfayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molecules of Life Chapter 1Document41 paginiMolecules of Life Chapter 1saidatul atirahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 26 Inorganic and Organic CompoundsDocument6 pagini26 Inorganic and Organic CompoundsMark Allein AguinaldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Molecules Chapter on Water and CarbohydratesDocument30 paginiBiological Molecules Chapter on Water and CarbohydratesAlicia LamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Revision 2017Document62 paginiBiology Revision 2017Katherine O'Neill-RobinsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Lec2 (Chemistry of The CellDocument38 pagini(Lec2 (Chemistry of The Cellبلسم محمود شاكرÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochemistry Review MCATDocument92 paginiBiochemistry Review MCATSamuel JayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemicals of Life-1-1Document29 paginiChemicals of Life-1-1kaziba stephenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology 10th 2021-22 Reduced Portion 1Document45 paginiBiology 10th 2021-22 Reduced Portion 1Job VacancyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Photosynthesis Lect 1Document72 paginiPhotosynthesis Lect 1Nam GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1. Revision Notes in Accordance With Syllabus SpecificationsDocument50 paginiUnit 1. Revision Notes in Accordance With Syllabus SpecificationslucyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological ChemistryDocument62 paginiBiological ChemistryCapital AceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology NotesDocument4 paginiBiology Noteshaaayanna100% (1)
- Walang MakakaseethisDocument3 paginiWalang MakakaseethisAlissa YangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Photosynthesis: The Process That Sustains LifeDocument33 paginiPhotosynthesis: The Process That Sustains LifeKlara EmperadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological MoleculesDocument38 paginiBiological MoleculesmuzammalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Reactions Part II: Week 7: Organic ChemistryDocument24 paginiChemical Reactions Part II: Week 7: Organic Chemistrymia kris quiatchonÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Biology Mid Exam Summary Semester OneDocument26 paginiGeneral Biology Mid Exam Summary Semester OneDeborah ShirleenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Molecules Revision NotesDocument49 paginiBiological Molecules Revision NotesAyaz Nasih88% (8)
- AP Biology Notebook PDFDocument105 paginiAP Biology Notebook PDFعمر gamerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel Biology Unit 1 NotesDocument74 paginiEdexcel Biology Unit 1 NotesBene Bin100% (2)
- CampbellEssentialBiology4th CH - NotesDocument43 paginiCampbellEssentialBiology4th CH - Notescasper911caÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Test 1 Study Guide: Atoms Molecules MacromoleculeDocument11 paginiBiology Test 1 Study Guide: Atoms Molecules Macromoleculeюрий локтионовÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Notes Unit 1Document40 paginiBiology Notes Unit 1MirzaAteeqAhmedBaigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fe ConceptDocument177 paginiFe ConceptIvan MaximusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1: Module 1 - Cellular and Molecular Biology: General ObjectivesDocument180 paginiUnit 1: Module 1 - Cellular and Molecular Biology: General ObjectivesKashim AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water and PHDocument10 paginiWater and PHKristine VillanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam One: BiologyDocument16 paginiExam One: BiologyCecilia HansonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agri Science 302 Advanced Biochemistry: (9 Hours Lecture Per Week For 6 Weeks)Document8 paginiAgri Science 302 Advanced Biochemistry: (9 Hours Lecture Per Week For 6 Weeks)j8m8l8Încă nu există evaluări
- Mibi Midterm Review Lec 1: Overview of Microbial Life. 1. What Are Microorganisms?Document6 paginiMibi Midterm Review Lec 1: Overview of Microbial Life. 1. What Are Microorganisms?Hồ Thanh MaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology STPM Lower 6 Chapter 1Document9 paginiBiology STPM Lower 6 Chapter 1kmbej91% (11)
- MolBiol HL (2.1, 2.2,2.3.2.4,7.3) BookletDocument37 paginiMolBiol HL (2.1, 2.2,2.3.2.4,7.3) BookletSeo Young YOONÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiologyStudyGuide-1 2Document29 paginiBiologyStudyGuide-1 2melissagfreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAP 2Document19 paginiCAP 2Francesca PrevitaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDe la EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)
- A-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDe la EverandA-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (2)
- Chemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2De la EverandChemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideDe la EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (2)
- Piping and Valves Trim MaterialsDocument2 paginiPiping and Valves Trim MaterialsDmitriy RybakovÎncă nu există evaluări
- QCVN 162019BXD National Technical Regulation On Products, Goods of Building Materials (Eng)Document41 paginiQCVN 162019BXD National Technical Regulation On Products, Goods of Building Materials (Eng)lwin_oo2435Încă nu există evaluări
- Brand Mgt. StarbucksDocument3 paginiBrand Mgt. StarbucksPrashansa SumanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 MoldingDocument46 paginiChapter 4 MoldingTamirat NemomsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- All About VapingREALDocument8 paginiAll About VapingREALKatherine CroweÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 4 Part 1 PDFDocument11 paginiLecture 4 Part 1 PDFBashar AntriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deutz-Fahr Workshop Manual for AGROTRON MK3 ModelsDocument50 paginiDeutz-Fahr Workshop Manual for AGROTRON MK3 Modelstukasai100% (1)
- TADO Smart Thermostat ManualDocument16 paginiTADO Smart Thermostat ManualMark WillisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Analysis of Mineral Constituents of Ethanol Leaf and SeedDocument9 paginiComparative Analysis of Mineral Constituents of Ethanol Leaf and SeedKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norris Claire White Paper Liftware PDFDocument14 paginiNorris Claire White Paper Liftware PDFmeysam NaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Filipino Nurses' Deep Faith and Cultural Attitudes in HealthcareDocument41 paginiFilipino Nurses' Deep Faith and Cultural Attitudes in HealthcareKeziah Marie Chua Santa-AnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessDocument8 paginiIntegrated Management of Childhood IllnessSehar162Încă nu există evaluări
- New Accreditation ToolsDocument52 paginiNew Accreditation ToolsLyle Guion Paguio100% (1)
- Product BrochureDocument2 paginiProduct BrochureNoel RodríguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAUTI Surveillance FormDocument2 paginiCAUTI Surveillance FormJiansong ChangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Making your own Agar PlateDocument8 paginiMaking your own Agar PlateCheska EngadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fem 3202-1 IntroductionDocument29 paginiFem 3202-1 IntroductionRon ChongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Steam Turbine VibrationDocument30 paginiUnderstanding Steam Turbine VibrationkatibraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 PROT4xx PowerSystemFaults r4Document84 pagini01 PROT4xx PowerSystemFaults r4Raul MistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan The Food: TH THDocument8 paginiLesson Plan The Food: TH THFeraru FlorinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neonatal Resuscitation: Dr. (Col) C.G.Wilson Professor& H.O.D (Paed)Document38 paginiNeonatal Resuscitation: Dr. (Col) C.G.Wilson Professor& H.O.D (Paed)shaharuddin_yahayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Job's Method of Continuous VariationDocument11 paginiJob's Method of Continuous Variationalex3bkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Butonal NS 175 TDSDocument2 paginiButonal NS 175 TDSPT. PITAGORAS KONSULTANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ate-U2 - Steam Boilers - PPT - Session 3Document13 paginiAte-U2 - Steam Boilers - PPT - Session 3MANJU R BÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Lesson Design in HELE 6 Chapter 2Document6 paginiA Lesson Design in HELE 6 Chapter 2Jestoni Paragsa100% (5)
- HemophiliaDocument62 paginiHemophiliamuhirwa Samuel100% (1)
- 30 Natural Ways To Help Treat Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDocument12 pagini30 Natural Ways To Help Treat Polycystic Ovary SyndromeArun AchalamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effects of Climate Change and Global WarmingDocument14 paginiEffects of Climate Change and Global WarmingSwetal SosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventilation SystemDocument13 paginiVentilation SystemSaru BashaÎncă nu există evaluări