Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Session 1 Overview of Sales ManagementSF
Încărcat de
Anshul Gupta0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
38 vizualizări35 paginisales management
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentsales management
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
38 vizualizări35 paginiSession 1 Overview of Sales ManagementSF
Încărcat de
Anshul Guptasales management
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 35
Business is many things, the least of which is
the Balance Sheet…
It’s a Fluid, Living, Ever-Changing Thing…
Sometimes Building to Great Peaks,
And Sometimes Falling to Crumbled
Lumps…
The Soul of Business is a Curious Alchemy of
Needs, Desires, Greed and Gratification..
Mixed Together with Selflessness, Sacrifices
and Personal Contribution far Beyond
Material Returns
It Serves the Aspirations of Hundreds of
Men and Women,
And is the Source of Physical security and
Well Being for All of Us…
The Process of Managing Business is
Fascinating, Demanding and Creative…
Worthy of Being Classed with the Higher
Arts,
Worthy of the Highest Personal
Commitment for Self and Society’
Harold Sydney Geneen
ITT
Strategic Dimensions
Organising the Sales Effort
Operational Dimension
Managing Sales Personnel
Controlling Sales Personnel
Tactical Dimension
Managing the Selling Process
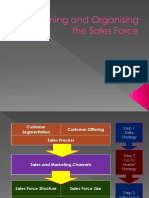
The Sales Organisation
Demand Forecasting
Product Decisions
Channel Decisions
Pricing Decisions
Sales Force Size Decisions
A success of any organisation depends
on its ability to acquire and retain the
right customers
The Sales Force is the most important
function which enables the organisation
to accomplishes this Goal
The Sales Force accounts for 10-20% of a
company’s total expense budget
A large Sales Force generates more
Revenues than a small one
An Organised, Trained, Motivated,
Knowledgeable Sales Force generates
more Revenues than one that is not
Not merely Communicating Value
But Creating Value
Managing Boundary Functions Between
Customer and Seller
The Sales Force has a Market Sensing
Role
It is the Primary Sensory Organ of the
Organisation
It contributes Significantly to the
Organisation’s Marketing Process
Who are the Customers
What value do they seek from the seller
What are their Priorities
What are their Purchase Processes
How the company’s Products are used
by the Customer
Who is involved in the Decision Making
process
What are the customer’s Evaluation
Criteria
How the Customer prefers to Acquire
Information about products they need
What Sales Channels do they Prefer
What are the Emerging Sales Channels
What Product Benefits and Features are
the Customers seeking
What is the Pre-Sales and Post Sales
support customers seek
Who are the Competitors
How do Customers view Competitors
What are their Strengths and Weaknesses
What Strategies and Tactics do
Competitors Use
Globally Co-ordinated Purchasing
Cost of Product In Use
New Industries
Industry Convergence
Customer Consolidation
Product Innovation
Channel Innovation
Aggressive Investment
Price Competition
Bankruptcy
Mergers
Economic Changes
Deregulation
Technology
Labour Market Shifts
New Product Launch
Merger
Selling Process Redesign
More Consultative
Less Transactional
New Channel Strategy
New Markets
Value Added Services
High Cost To Sales Ratio
Not Enough New Customer Acquisition
Complacency
Lack of Accountability
High Turnover
Inability to Handle Customer Diversity
Inability to Handle Product Diversity
The Sales Organisation
Demand Forecasting
Product Decisions
Channel Decisions
Pricing Decisions
Sales Force Size Decisions
Recruiting & Selecting Sales Personnel
Planning, Executing, Evaluating Sales
Training Programs
Managing Sales Person Performance
Motivating Sales Personnel
Evaluating & Supervising Sales Personnel
Compensating Sales Personnel
Establishing Performance Standards
Recording and Evaluating Performance
The Sales Budget
Quotas
Sales Territories
Sales Control and Cost Analysis
Strategy
Structure
Systems
Style Of Management
Skills - Corporate Strengths
Staff
Shared Values
A bias for action, active decision making
- 'getting on with it'.
Close to the customer - learning from the
people served by the business.
Autonomy and entrepreneurship -
fostering innovation and nurturing
'champions'.
Productivity through people - treating
rank and file employees as a source of
quality.
Hands-on, value-driven - management
philosophy that guides everyday
practice - management showing its
commitment.
Stick to the knitting - stay with the
business that you know.
Simple form, lean staff - some of the best
companies have minimal HQ staff.
Simultaneous loose-tight properties -
autonomy in shop-floor activities plus
centralised values.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Chap 013Document25 paginiChap 013Sadaf IftikharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 5 StrategyDocument18 paginiTopic 5 StrategyAnshul GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session 3.selling ProcessDocument68 paginiSession 3.selling ProcessAnshul GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session 3.sales Structure and RolesDocument98 paginiSession 3.sales Structure and RolesAnshul GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session 2 Sales StrategyDocument115 paginiSession 2 Sales StrategyAnshul GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Inventory Management and Control: Chapter-05Document5 paginiInventory Management and Control: Chapter-05Bijoy SalahuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comprehensive Illustration On PM of Profit Centers CH 5Document2 paginiComprehensive Illustration On PM of Profit Centers CH 5Tekalign MegersaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pratyush - CV Latest - 08-Jul-17 - 00 - 18 - 46Document4 paginiPratyush - CV Latest - 08-Jul-17 - 00 - 18 - 46PRATYUSH K YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11 Valuation Using MultiplesDocument22 paginiChapter 11 Valuation Using MultiplesUmar MansuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Winning+Trading+Strategy+4 0 PDFDocument22 paginiWinning+Trading+Strategy+4 0 PDFRemo100% (1)
- Indian Telecom IndustryDocument33 paginiIndian Telecom IndustryTarun Daga100% (4)
- LMV Holdings ProposalDocument1 paginăLMV Holdings Proposaldkjh8796nlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 16Document30 paginiChapter 16Jieun LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Needs, Wants, and DemandDocument4 paginiNeeds, Wants, and Demand7 KeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10-Slide Pitch Deck TemplateDocument16 pagini10-Slide Pitch Deck TemplateRahul Agnihotri100% (1)
- Lecture 5.2-General Cost Classifications (Problem 2)Document2 paginiLecture 5.2-General Cost Classifications (Problem 2)Nazmul-Hassan Sumon75% (4)
- Account Analysis and Time Allocation: Key To ProductivityDocument48 paginiAccount Analysis and Time Allocation: Key To ProductivitySheikh Muhammad Sadique SulemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advertising Class NotesDocument38 paginiAdvertising Class Notesyusuf1183100% (4)
- Chapter 25: Step by Step Murabaha Financing: Bank ClientDocument3 paginiChapter 25: Step by Step Murabaha Financing: Bank ClientAlton JurahÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECO603m.pricing Options Reviewer.3.2016-17Document4 paginiECO603m.pricing Options Reviewer.3.2016-17Neale CacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document39 paginiChapter 1Haaromsaa Taayyee TolasaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case3 KKDDocument4 paginiCase3 KKDvrenhays_xia039267Încă nu există evaluări
- MonaliDocument36 paginiMonaliNishu AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Submitted By: Bhakti Shelar SMBA - 2, Roll No - 08 ITM, ThaneDocument7 paginiSubmitted By: Bhakti Shelar SMBA - 2, Roll No - 08 ITM, ThaneBhakti ShelarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Price Action Bar Patterns You Must KnowDocument14 pagini10 Price Action Bar Patterns You Must Knowsal8471100% (2)
- StarbucksDocument18 paginiStarbucksemmett81Încă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Plan in Apple: Yubo Yang Xi Chen Sitong Lu Bosheng HuDocument20 paginiMarketing Plan in Apple: Yubo Yang Xi Chen Sitong Lu Bosheng HuYubo YangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing ProjectDocument5 paginiMarketing ProjectTamanna KotnalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLC - Analytics Problem StatementDocument13 paginiCLC - Analytics Problem StatementRana UsamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MINICOM Made in Rwanda PolicyDocument45 paginiMINICOM Made in Rwanda PolicyJ-Claude DougÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elabore en Ingles Un Mapa Conceptual Del Tema Visto en El Primer Material Complementario IndicadoDocument2 paginiElabore en Ingles Un Mapa Conceptual Del Tema Visto en El Primer Material Complementario IndicadoNatalia castellanosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Marketing StrategiesDocument11 paginiAdvanced Marketing Strategiesmena98989371Încă nu există evaluări
- Quiz UTSDocument7 paginiQuiz UTSRuth SoesantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- FINA3080 Assignment 1Document2 paginiFINA3080 Assignment 1Koon Sing ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soap Industries (FMCG)Document66 paginiSoap Industries (FMCG)Bhavin Patel55% (11)