Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Process Valves: For Fluid Control
Încărcat de
Castañeda Valeria0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
13 vizualizări35 paginiThe document discusses different types of process valves used to control the flow of various fluids. It describes 2/2 valves which have two ports and two positions (open or closed), including direct solenoid, diaphragm seat, and piston seat valves. It also covers 3/2 valves which have three ports to control flow direction, such as direct solenoid actuated valves. The valves discussed can be used to control fluids across a wide range of operating conditions and industries.
Descriere originală:
..
Titlu original
ProcsV97
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThe document discusses different types of process valves used to control the flow of various fluids. It describes 2/2 valves which have two ports and two positions (open or closed), including direct solenoid, diaphragm seat, and piston seat valves. It also covers 3/2 valves which have three ports to control flow direction, such as direct solenoid actuated valves. The valves discussed can be used to control fluids across a wide range of operating conditions and industries.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
13 vizualizări35 paginiProcess Valves: For Fluid Control
Încărcat de
Castañeda ValeriaThe document discusses different types of process valves used to control the flow of various fluids. It describes 2/2 valves which have two ports and two positions (open or closed), including direct solenoid, diaphragm seat, and piston seat valves. It also covers 3/2 valves which have three ports to control flow direction, such as direct solenoid actuated valves. The valves discussed can be used to control fluids across a wide range of operating conditions and industries.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 35
Process Valves
For fluid control
Contents
Introduction
2/2 Valves
Direct solenoid
Diaphragm seat valves
Solenoid with force lifting
Piston seat valves
Pilot angle seat valves
3/2 Valves
NAMUR interface
Click the section to advance directly to it
Introduction
Process valves control a
wide variety of fluids
such as air, water,
nitrogen, food products,
carbon dioxide, acids,
alkalis, fuels, solvents,
superheated steam, dry
ice and many others
Valves are used to shut
off, distribute or combine
fluid flow for normal
processing and safety
functions
Introduction
Process valves control
the flow of many types of
fluid these can be:
Liquids
Gasses (including air)
Vapours
The fluids can be:
Neutral, (water or air)
Aggressive, (acids)
Hot or cold , (steam or
dry ice)
Operating conditions
Valves may be required to
operate in:
Sub zero refrigeration
units
Desert heat
Highly explosive
environments, for
example a flour mill
Radio-active zones in
nuclear plant
Operating conditions
To meet this wide range Body and seal material
of fluid types and Operating method, air or
environmental conditions, solenoid
valves can be selected Solenoid type and
from a variety of designs protection rating
and detail specifications:
2/2 Valve Types
2/2 Valves
2/2 valves have two ports
(inlet and outlet) and two
positions (open or
closed)
Typical valve types:
Direct acting solenoid
Diaphragm solenoid
pilot
Diaphragm solenoid
force lifting
Piston seat solenoid
force lifting
Seat valve pressure
operated
General purpose 2/2
For the on off control of
corrosive gases and
liquids
Stainless steel
construction
G1/8 and G1/4 ports
Orifice 2mm to 6mm
Operating pressures:
G1/8 0:30 bar (2mm)
0:8 bar (3mm)
G1/4 0:50 bar (2mm)
0:20 bar (3mm)
0:12 bar (4mm)
0:5 bar (6mm)
Direct solenoid actuation 2/2
For aggressive gases and
liquids
Plastic body PVDF
Maximum operating
pressure 1 to 7 bar
Orifice sizes 3 to 8 mm
G1/4 to G 3/8 ports
Sealed core tube with
PTFE bellows
Direct solenoid actuation 2/2
Stainless steel body for
use with aggressive
gasses and liquids
Maximum operating
pressure 1.5 to 10 bar
Orifice size 5 or 10mm
port sizes G1/4 or G1/2
Direct solenoid principle (NC)
2/2 valve has an inlet and
outlet port and two
positions, open or closed
Energise the coil to lift the
armature to open the
valve, for low pressures
the orifice can be large,
for high pressures it
needs to be smaller
When the coil is de-
energised a spring seals
the core against the
orifice (normally closed)
Wet core design
Click the illustration to start and stop animation
Direct solenoid actuation 2/2
For neutral gases and
liquids
Normally closed and
normally open versions
Maximum pressure 4 to
50 bar dependant on
orifice diameter
Suitable for vacuum
Orifice sizes 1.5mm to
6mm diameter
Options 24V dc,
24V 110V 230V ac
Brass body
Direct solenoid principle (NO)
2/2 valve normally open
has an inlet and outlet
port and two positions,
closed or open
Energise the coil to lift the
armature to allow the
sprung loaded poppet
seat to close
When the coil is de-
energised the sprung
loaded armature pushes
the seat open
Click the illustration to start and stop animation
Diaphragm seat valves 2/2
Solenoid pilot operated
diaphragm
Wide range of port sizes
G1/4 : G 2
Orifice sizes 8 mm : 50 mm
Extensively used for
water control and other
neutral liquids and gases
Standard coil options 24V
dc, 24V, 110V, 230V ac
Diaphragm operated 2/2
Solenoid pilot operated
for higher flow
The upstream pressure
(0.5 bar min) bleeds
through the diaphragm to
seal the valve closed
When the solenoid is ON
the fluid escapes to the
downstream side opening
the diaphragm
The solenoid is turned off
to re-establish the closed
state
Click the illustration to start and stop animation
Solenoid with force lifting 2/2
Stainless steel
construction for
moderately aggressive
gasses and liquids
Port sizes G 1/4 : G 1/2
Operating pressures 1 bar
: 10 bar
Standard coil options
dc 24V 12 W.
ac 24V, 110V, 230V 13 VA
Solenoid with force lifting 2/2
Solenoid performs a dual
function, pilot operation
and direct lifting of the
valve seat
Will operate at zero
pressure differential
Port sizes G1/4 : G1
Orifice size 8 : 25 mm
Max pressure 8 bar for dc
coils 16 bar for ac coils
Standard coil options 24V
dc 18 W. 24V, 110V, 230V
ac 35 VA
Solenoid with forced lifting
Two stage design suitable
for low to zero differential
pressures
When the armature lifts,
the pilot valve is opened
to allow the primary
pressure to open the
diaphragm
If the primary pressure is
very low, continued
movement of the
armature will directly lift
the diaphragm seat
Click the illustration to start and stop animation
Solenoid with force lifting 2/2
Piston seat for rugged
applications
For neutral gasses and
liquids
12mm : 50 mm orifice
G1/2 to G2 ports
0 to 25 bar operating
pressure
Standard coil options
dc 24V 22 W and 40 W.
ac 24V, 110V, 230V 25 VA
and 45 VA
Solenoid with force lifting 2/2
Stainless steel
construction for
moderately aggressive
gasses and liquids
Piston seat valve
10 mm : 50 mm orifice
G3/8 to G1 ports
0 to 25 bar operating
pressure
Standard coil options
dc 24V 22 W and 40 W.
ac 24V, 110V, 230V 25 VA
and 45 VA
Piston seat valve 2/2
Powerful solenoid with
forced lifting and piston
seat for heavy duty use
First stage opens pilot
orifice to release pressure
Second stage assists
fluid pressure to open
main seat
When the differential
between inlet and outlet
is low, the solenoid will
continue to lift the piston
to open the valve
Click the illustration to start and stop animation
Pressure pilot valves 2/2
For neutral gases and
liquids
Air operated, can be close
coupled with a 3/2
solenoid pilot valve
Orifice sizes 15 mm :50
mm
Port sizes G1/2 : G2
Pilot pressure 3.5 bar : 8
bar
Operating pressure from
90% vacuum to 16 bar
max depending on size
Pressure pilot valves 2/2
Stainless steel
construction for
aggressive gases and
liquids
Air operated
Orifice sizes 15 mm : 50
mm
Port sizes G1/2 : G2
Pilot pressure 3.5 bar : 8
bar
Operating pressure from
90% vacuum to 16 bar
max depending on size
Pilot operated 2/2 seat valve
Springs provide excellent
sealing in the normally
closed position
Air pilot signal lifts the
seat against the spring
In sizes G1/2 to G2 for
high flow
Suitable for vacuum to up
to 16 bar
Can be close connected
with a solenoid pilot valve
to generate the pilot
signal
Click the illustration to start and stop animation
Pilot valve 2/2
Pressure diaphragm
operated popet seat valve
Pilot fluid air, water, oil
hydraulic 3 bar : 8 bar
For neutral gasses and
liquids
Suitable for contaminated
fluids
Visual position indicator
Port sizes G1/4 : G 1/2
Operating pressure 0.9
bar to 6 bar
3/2 Valve Types
Direct solenoid actuation 3/2
The solenoid core
incorporates the main
sealing element to
directly control the fluid
Suitable for relatively low
flow applications 1.6 mm
orifice
Vacuum to 10 bar
Filtered air lubricated or
unlubricated
1-6 subplate mounted or
in line design
Plastic or brass body
Direct solenoid actuation 3/2
Pressure is permanently
connected to the inlet
port
Normally held closed by
the force from the
solenoid armature return
spring, outlet open to
exhaust through the seat
When the coil is
energized the armature
lifts the double poppet
seat to open the supply to
the outlet, exhaust closed
Click the illustration to start and stop animation
Direct solenoid actuation 3/2
For neutral gases and
liquids
Normally closed uni-
directional, normally open
uni-directional and bi-
directional versions
Maximum pressure 7 to
18 bar depending on
orifice size and solenoid
power
Orifice size 2 to 5mm
Port size G 1/4
Suitable for vacuum
Direct solenoid actuation 3/2
For neutral gases and
liquids
Maximum operating
pressure 9 to 10 bar
Orifice size 3 or 4mm
Direct solenoid actuation 3/2
Pressure is permanently
connected to the inlet
port
Normally held closed by
the force from the
solenoid armature return
spring, outlet open to
exhaust
When the coil is
energized the armature is
lifted and the spring
under the double poppet
seat opens the supply to
the outlet, exhaust closed
Click the illustration to start and stop animation
Valves with NAMUR Interface
NAMUR interface
An industry standard
interface pattern for
joining control valves
directly to process valve
actuators
Allows interchangeability
24mm
of valves and actuators Ports
from different product
brands
Devised by the NAMUR 32mm
committee formed from
control valve and valve M5
actuator manufacturers Location holes for dowel
End
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Guide BRF+ PDFDocument274 paginiGuide BRF+ PDFHiro Dm60% (5)
- Guide BRF+ PDFDocument274 paginiGuide BRF+ PDFHiro Dm60% (5)
- Basic Circuit Pneumatic From NorgrenDocument134 paginiBasic Circuit Pneumatic From NorgrenArief Wahyu Purwito100% (2)
- Prevention of Valve Fugitive Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryDe la EverandPrevention of Valve Fugitive Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nozzle Loads - Part 1 - Piping Engineering PDFDocument6 paginiNozzle Loads - Part 1 - Piping Engineering PDFkparthypanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation For Pneumatic ValvesDocument44 paginiPresentation For Pneumatic ValvesRajat SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumatic CircuitsDocument134 paginiPneumatic CircuitsChristopher Irvine100% (1)
- Allenair Catalog 4 Way ValvesDocument5 paginiAllenair Catalog 4 Way ValvesEddie WallsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumatic Valves: For Precision and ControlDocument45 paginiPneumatic Valves: For Precision and Controlm_alodat6144Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic Pneumatic Circuitry: For Control and AutomationDocument134 paginiBasic Pneumatic Circuitry: For Control and AutomationIpquisÎncă nu există evaluări
- ValvesDocument26 paginiValvesRajeshSahuÎncă nu există evaluări
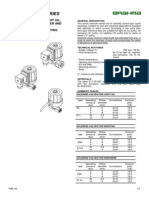
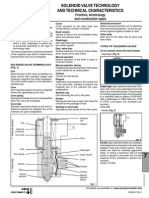
- Solenoid Valve TypesDocument6 paginiSolenoid Valve Typeschdi0% (1)
- Control Valve PresentDocument120 paginiControl Valve PresentShoeb Ali KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Queen: Two Way Solenoid Valves General PurposeDocument1 paginăQueen: Two Way Solenoid Valves General PurposeYDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumatic Valves: For Precision and ControlDocument104 paginiPneumatic Valves: For Precision and ControlVMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valves From NorgrenDocument104 paginiValves From NorgrenArief Wahyu PurwitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ValvesDocument31 paginiValvesJuber KhatibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generator CO2 Firefighting SystemDocument47 paginiGenerator CO2 Firefighting Systemrotimi olalekan fataiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MarusujufawoDocument3 paginiMarusujufawonileshnk2000Încă nu există evaluări
- ZTV ZTR PRSH enDocument4 paginiZTV ZTR PRSH enmustafa Al AsfourÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASCO 35-1 General Service 2-Way Valves PDFDocument37 paginiASCO 35-1 General Service 2-Way Valves PDFAndre SyahputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2way Ball CV - ShunFu China MakeDocument2 pagini2way Ball CV - ShunFu China MakeAnonymous 6hptH95Încă nu există evaluări
- Control ValveDocument23 paginiControl ValveRama ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operation Manual FOR SKT140 Series of Pneumatic Hydraulic Test-BedDocument12 paginiOperation Manual FOR SKT140 Series of Pneumatic Hydraulic Test-BedAlex RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proportional Reducing ValveDocument8 paginiProportional Reducing ValvediabalziabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dongguan Suncenter Fluid Control Equipment Co., LTDDocument10 paginiDongguan Suncenter Fluid Control Equipment Co., LTDJeisson DazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Be106-01 NDVDocument6 paginiBe106-01 NDVcodoik_050Încă nu există evaluări
- 2 Way IntroDocument2 pagini2 Way IntroKovit S. MoonlightÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flow SwitchDocument16 paginiFlow Switchsales1068100% (1)
- 3B - Inst - Control ValveDocument31 pagini3B - Inst - Control ValveMystic AamirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mobrayl Manual.4.2.09Document14 paginiMobrayl Manual.4.2.09svkraja007100% (3)
- PneumaticsDocument36 paginiPneumaticsTaku Teekay MatangiraÎncă nu există evaluări
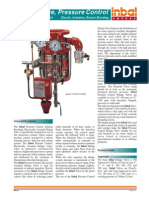
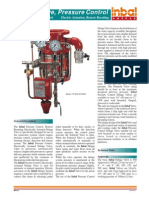
- Inbal - Deluge Valve Pressure Control 03 - 13 CR01Document4 paginiInbal - Deluge Valve Pressure Control 03 - 13 CR01gustavosalvatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrovalva E6-E11 SeriesDocument3 paginiElectrovalva E6-E11 SeriesMonica GrecuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valve Classification According To Port SizeDocument6 paginiValve Classification According To Port SizeMuhammad AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valve FunctionDocument7 paginiValve Functionرسول ناصر كريم خريبطÎncă nu există evaluări
- ValveDocument4 paginiValveshubh shahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumatic ValvesDocument100 paginiPneumatic Valvesdai83Încă nu există evaluări
- VT-BAYARD-Automatic Control Valves-FloatDocument8 paginiVT-BAYARD-Automatic Control Valves-Floatsiva ramakrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 06 Pneumatic Control SystemDocument49 pagini06 Pneumatic Control SystemFian RohmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- INBAL GeralDocument10 paginiINBAL GeralAlisson Gustavo KalilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Válvula SolenóideDocument3 paginiVálvula Solenóidecleiton260589Încă nu există evaluări
- Diaphragm ValveDocument10 paginiDiaphragm Valveshganesh81Încă nu există evaluări
- PARTIIOUTPUTDEVICEDocument333 paginiPARTIIOUTPUTDEVICEFiras BEN HMIDAÎncă nu există evaluări
- FunctionalSafety V7666Document12 paginiFunctionalSafety V7666rufino.perea.2Încă nu există evaluări
- Control Valve Accessories: - Samson KoshyDocument49 paginiControl Valve Accessories: - Samson KoshySamson KoshyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASCO Solenoid Engineering SpecsDocument26 paginiASCO Solenoid Engineering SpecsviruspoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- ValvesDocument44 paginiValvesأحمد محمد قدريÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Valve - Theory & SizingDocument29 paginiControl Valve - Theory & SizingSandeep KulathapallilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model 210 Digital Electro-Hydraulic Set Stop - PDF-, AttachmentDocument4 paginiModel 210 Digital Electro-Hydraulic Set Stop - PDF-, AttachmentMohd HassanudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regolatori Pressione IngleseDocument30 paginiRegolatori Pressione IngleseThanos KantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irrigation Solenoid ValveDocument1 paginăIrrigation Solenoid ValveAtul KalaskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inbal - Deluge Valve Pressure Control 03-13 CR01Document4 paginiInbal - Deluge Valve Pressure Control 03-13 CR01pvalverdea2014Încă nu există evaluări
- Asco Solenoid SpecificationsDocument2 paginiAsco Solenoid SpecificationsPrathamesh GangalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rotating Control Device Service ManualDocument24 paginiRotating Control Device Service ManualJeck MaxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumatic and Apm Liquid Level ControlDocument12 paginiPneumatic and Apm Liquid Level Controlyuri0527Încă nu există evaluări
- D 633 Series Valves eDocument16 paginiD 633 Series Valves ehaggÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Pneumatic CircuitsDocument81 paginiDesign of Pneumatic CircuitsNikhil PandharpatteÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileDe la EverandA Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitDe la EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryDe la EverandPrevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryÎncă nu există evaluări
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGDe la EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Risks You Can't ForeseeDocument15 paginiThe Risks You Can't ForeseeCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bubble Column ReactorsDocument22 paginiBubble Column ReactorsCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crafting A Job Revisioning Employees As Active CraDocument25 paginiCrafting A Job Revisioning Employees As Active CraCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crafting Task and Cognitive Job Boundaries To EnhaDocument9 paginiCrafting Task and Cognitive Job Boundaries To EnhaCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retencion de Gas y Coeficientes de Transferencia de Materia en Columnas de Burbujeo. I. Difusores Placas PorosasDocument2 paginiRetencion de Gas y Coeficientes de Transferencia de Materia en Columnas de Burbujeo. I. Difusores Placas PorosasCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crafting Task and Cognitive Job Boundaries To EnhaDocument9 paginiCrafting Task and Cognitive Job Boundaries To EnhaCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BergWrzesniewskiDutton 2010 JOBDocument30 paginiBergWrzesniewskiDutton 2010 JOBCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retencion de Gas y Coeficientes de Transferencia de Materia en Columnas de Burbujeo. II. Difusores Placas Perforadas y Orificio SimpleDocument2 paginiRetencion de Gas y Coeficientes de Transferencia de Materia en Columnas de Burbujeo. II. Difusores Placas Perforadas y Orificio SimpleCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of Gas-Liquid Flow in Packed-Bed Contactors: J. M. de Santos, T. R. Melli, and L. E. ScrivenDocument29 paginiMechanics of Gas-Liquid Flow in Packed-Bed Contactors: J. M. de Santos, T. R. Melli, and L. E. ScrivenCarlos Jaramillo100% (1)
- Respiratory Protective Equipment - Non-Powered Air-Purifying Particle RespiratorDocument14 paginiRespiratory Protective Equipment - Non-Powered Air-Purifying Particle RespiratorCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Holdup in A Gasliquid Up Flow Bubble Column in The Presence of Double Cone Promoter PDFDocument8 paginiGas Holdup in A Gasliquid Up Flow Bubble Column in The Presence of Double Cone Promoter PDFCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GB 2626 - 2006 Respiratory Protective Equipment Non-Powered Air-Purifying Particle RespiratorDocument22 paginiGB 2626 - 2006 Respiratory Protective Equipment Non-Powered Air-Purifying Particle RespiratorCastañeda Valeria100% (1)
- 13 Iq 1990 1 PDFDocument2 pagini13 Iq 1990 1 PDFCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCF2017 No 170Document11 paginiRCF2017 No 170Castañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LV MaxSonar EZ - DatasheetDocument13 paginiLV MaxSonar EZ - DatasheetAlstein EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Holdup in A Gasliquid Up Flow Bubble Column in The Presence of Double Cone Promoter PDFDocument8 paginiGas Holdup in A Gasliquid Up Flow Bubble Column in The Presence of Double Cone Promoter PDFCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 Iq 1990 1 PDFDocument2 pagini13 Iq 1990 1 PDFCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensor UltrasonicDocument6 paginiSensor UltrasonicCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Line Equipment: For Quality Compressed AirDocument114 paginiAir Line Equipment: For Quality Compressed AirCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Facts and Theory of Air: For Industrial PneumaticsDocument74 paginiFacts and Theory of Air: For Industrial PneumaticspfalencarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mote User's Guide: 2015-2016 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001808BDocument33 paginiMote User's Guide: 2015-2016 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001808BCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materi Saklar Da Sensor Pneumatic - NorgrenDocument24 paginiMateri Saklar Da Sensor Pneumatic - NorgrenArief Wahyu PurwitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- UnidadDocument6 paginiUnidadCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fieldbus: For Central ControlDocument85 paginiFieldbus: For Central ControlCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 63 554173 PDFDocument9 pagini63 554173 PDFCastañeda ValeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab ReportDocument6 paginiLab ReportNero SwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Relief SystemsDocument30 paginiPressure Relief SystemsBibek MerÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASME 2286-2 Alternative Rules For Determining Allowable External PressureDocument16 paginiASME 2286-2 Alternative Rules For Determining Allowable External PressureMike Dukas100% (1)
- Fracture Toughness Properties of High-StrengthDocument10 paginiFracture Toughness Properties of High-StrengthEngels OchoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EGF316 Compound Cylinders - NotesDocument9 paginiEGF316 Compound Cylinders - NotesSakthivel ThangavelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plastic Theory of Bending - Materials - Engg Reference With Worked ExamplesDocument9 paginiPlastic Theory of Bending - Materials - Engg Reference With Worked ExampleshoojzteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monin and Obukhov 1954Document30 paginiMonin and Obukhov 1954Nikolay ZavgorodniyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experimental Testing of Conventional HSS Slotted Tube-to-GussetDocument10 paginiExperimental Testing of Conventional HSS Slotted Tube-to-Gussetadnan53Încă nu există evaluări
- Non Linear Pushover AnalysisDocument10 paginiNon Linear Pushover AnalysisyibungoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCPP 2 Thermal Audit Report PDFDocument61 paginiCCPP 2 Thermal Audit Report PDFRagesh JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 2019 Scheme S4 Syllabus Ktustudents - inDocument91 paginiMECHANICAL ENGINEERING 2019 Scheme S4 Syllabus Ktustudents - inashnbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5 HvacDocument42 paginiLecture 5 HvacJohn Bennett100% (2)
- Galgotias College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument19 paginiGalgotias College of Engineering and TechnologyJv100% (1)
- Chapter 1. Introduction On Fluid Mechanics BookDocument70 paginiChapter 1. Introduction On Fluid Mechanics BookMubarekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Space Frame 2019-Torque-Force 25.4X1.6Document24 paginiSpace Frame 2019-Torque-Force 25.4X1.6luis nunezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plate Design For Fixed BaseDocument59 paginiBase Plate Design For Fixed Basemoneoffice100% (2)
- PumpsDocument80 paginiPumpsMuhammad Nursalam100% (1)
- Texture Profile AnalysisDocument7 paginiTexture Profile AnalysisMariel OliverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study of Hydrodynamics and Upscaling of Immiscible Fluid Stirred Tank Using Computational Fluid Dynamics SimulationDocument19 paginiStudy of Hydrodynamics and Upscaling of Immiscible Fluid Stirred Tank Using Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulationเอกฤกษ์ พุ่มนกÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numerical Modeling of Rock Slopes in Siwalik Hills Near Manali Region: A Case StudyDocument21 paginiNumerical Modeling of Rock Slopes in Siwalik Hills Near Manali Region: A Case Studywidayat81Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - Bed Load EstimationDocument25 paginiChapter 3 - Bed Load EstimationTesfaye NegasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CA3632.Assignment 1 Questions. 2017 PDFDocument5 paginiCA3632.Assignment 1 Questions. 2017 PDFwilson604Încă nu există evaluări
- 2EF 2022 Test QuestionsOnlyDocument2 pagini2EF 2022 Test QuestionsOnlybhilacarlos10Încă nu există evaluări
- Pump CalculationDocument5 paginiPump CalculationrkobeissiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE140 AbcdefDocument39 paginiCE140 AbcdefJeo Jenson GalisimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Importance of Transport Phenomena? AnsDocument3 paginiImportance of Transport Phenomena? AnsRohit Bansode100% (1)
- Mass EnergyDocument64 paginiMass EnergyhlvijaykumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excel Program To Facilitate The Estimation of Critical Properties Using Group Contribution MethodsDocument2 paginiExcel Program To Facilitate The Estimation of Critical Properties Using Group Contribution MethodsElbahi DjaalabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airflow in Batch Fluid Bed ProcessingDocument11 paginiAirflow in Batch Fluid Bed ProcessingjokishÎncă nu există evaluări