Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Injury
Încărcat de
niraj_sd0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
23 vizualizări19 paginiInjury to brain
Titlu original
injury
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentInjury to brain
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
23 vizualizări19 paginiInjury
Încărcat de
niraj_sdInjury to brain
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 19
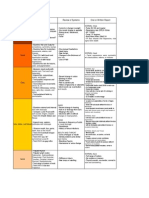
Injury to the brain.
Brain injuries may be caused by:
• Penetration by foreign object such as knife, bullet etc. or by
fragments of skull in a depressed fracture.
• By distortion of the skull. When a localised segment of the
skull undergoes deformation, shear strains may develop in the
brain tissue underlying the indentation, and a contusion may
be produced in the surface layers of the brain tissue. If a
fracture occurs , pieces of bone may penetrate the dura and
lacerate the brain.
• Due to movement of brain in relation to the skull
Cerebral contusion
• When a localised segment of the skull undergoes deformation
at the moment of impact. Shear strains may develop in the
brain tissue underlying the indentation, and a zone of
contusion may be produced in the surface layers of the brain.
• Most often they occur in cerebral and cerebellar cortices and
subcortical areas.
Post-traumatic CT scan of brain showing
bilateral contusion of frontal cerebral region:
Types:
• Intermediary coup contusions: Contusions found in deeper
structures of the brain along the line of impact.
• Fracture contusions : Contusions caused due to fracture of the
skull.
• Gliding contusions : Contusions in the cortex and white
matter of frontal and central convolutions.
• Herniation contusions : Contusions in the cerebellar tonsils
and the medulla oblongata.
Cerebral laceration
• They are traumatic lesions in the brain in which there is loss of
continuity of the substance of the brain.
• When the parenchyma is completely disorganised, it is
termed as pulpefaction.
• Lacerations are usually seen underneath skull fractures.
• All penetrating injuries produce laceration of brain.
• Laceration may also be produced without fracture of skull,
when they are usually found in regions where the brain is in
contact with projecting buttresses and ridges on the inner
surface of the skull.
Coup and Contrecoup lesions:
• Coup injury(Blow impact): It means that the injury is located
beneath the area of impact and results directly by the
impacting force
• Contrecoup injury : It means that the lesion is present in an
area opposite to the side of impact.
Contrecoup injuries are rare before the age of three.
Mechanism:
• Contrecoup injury is caused when the moving head is
decelerated suddenly by hitting a firm surface, eg., striking
the head on the ground during the fall, usually seen in traffic
accidents ( deceleration injury).
• Occipital injuries produce severe and extensive contrecoup
lesions in the frontal region. The irregular bony prominences,
especially of the orbital and cribriform plates, and the lesser
wings of the sphenoid, contuse or lacerate the base of the
frontal lobes and the tips of the temporal lobes.
• A blow to the head produces a coup contusion, while
contrecoup contusions are either small or absent.
• A fall on the head produces contrecoup contusions, while
coup contusions are small or absent.
Concussion of the brain
• Definition : concussion is a state of temporary
unconsciousness (due to partial or complete paralysis of
cerebral function), due to head injury, comes on immediately
after injury, is always followed by amnesia, and tends to
spontaneous recovery.
• Mechanism : it occurs due to acceleration or deceleration of
the head. Cerebral concussion may be produced by direct
violence to the head, or by indirect violence as a result of
violent fall upon the feet or buttocks, by an unexpected fall on
the ground in traffic or industrial accidents.
• Severe injuries occur in coronal head motion only.
• Medicolegal importance – in case of head injury, if the patient becomes
unconscious, in between he may become conscious, which again
terminates into unconsciousness. These periods of consciousness are
labelled as lucid interval.
• The person is responsible for acts done(civil or criminal) during lucid interval.
• ( The period of sanity in an insane person is also called lucid interval).
• Diffuse axonal injury (DAI) is a brain injury in which
extensive lesions in white matter tracts occur over a widespread area. DAI
is the result of traumatic shearing forces that occur when the head is
rapidly accelerated or decelerated, as may occur in car accidents, falls,
and assaults.Vehicle accidents are the most frequent cause of DAI.
• Immediate disconnection of axons could be observed in severe brain
injury, but the major damage of DAI is delayed secondary axon
disconnections slowly developed over an extended time course
Punch-Drunk syndrome (traumatic
encephalopathy/dementia pugilistica)
• It refers to the chronic changes in the brain of a boxer, which
usually manifest after many episodes of minor head injuries.
• There will be deterioration in speed and coordination in boxers. In
extreme cases, it is recognised by slurred speech, memory loss,
stiff limbs and outbursts of violence.
Punch-Drunk Syndrome.
Cerebral oedema.
• Cerebral oedema occurs due to a localised or diffuse abnormal
accumulation of water and sodium, which increases the
volume of the brain.
• It is caused due to the increase in the intravascular pressure ,
increased permeability of the cerebral vessels, and decrease in
plasma colloid osmotic pressure.
• Focal oedema is almost invariably associated with and
secondary to contusions and lacerations of the brain. Focal
oedema in the brainstem is usually fatal.
• Generalised cerebral oedema occurs with diffuse brain injury.
THANK YOU.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Forensic PsychiatryDocument15 paginiForensic Psychiatryniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Responsibilities of A Mentally Ill PersonDocument13 paginiResponsibilities of A Mentally Ill Personniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Sexual OffencesDocument21 paginiSexual Offencesniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- IdentificationDocument41 paginiIdentificationniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Interjections in Dialogue Tom Sawyer PDFDocument2 paginiInterjections in Dialogue Tom Sawyer PDFniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viscera PreservationDocument15 paginiViscera Preservationniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- AbortionDocument92 paginiAbortionniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Post Mortem ArtefactsDocument35 paginiPost Mortem Artefactsniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- PM Changes MuscularDocument26 paginiPM Changes Muscularniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Causes of Death in BurnsDocument9 paginiCauses of Death in Burnsniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Antidotes Are Substances Which Counteract or Neutralise The Effects of Poisons Without Itself Being Harmful To The BodyDocument16 paginiAntidotes Are Substances Which Counteract or Neutralise The Effects of Poisons Without Itself Being Harmful To The Bodyniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Death and Changes After DeathDocument23 paginiDeath and Changes After Deathniraj_sd100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- DactylographyDocument14 paginiDactylographyniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algorithms - BermanDocument20 paginiAlgorithms - Bermanniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Vegetable IrritantsDocument50 paginiVegetable Irritantsniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- HomicideDocument22 paginiHomicideniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Quorom PDFDocument2 paginiQuorom PDFniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Examination of Long BonesDocument30 paginiExamination of Long Bonesniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Forensic SciencesDocument28 paginiForensic Sciencesniraj_sd100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Deliriant PoisonsDocument97 paginiDeliriant Poisonsniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Intersex & Sex DeterminationDocument37 paginiIntersex & Sex Determinationniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preservation of VicceraDocument21 paginiPreservation of Vicceraniraj_sd100% (1)
- Doctor in Witness BoxDocument22 paginiDoctor in Witness Boxniraj_sdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Text CDocument1.100 paginiText CAli NofalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Euthanasia ThesisDocument11 paginiEuthanasia ThesisAyush MathurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Renal Failure: A. DefinitionsDocument28 paginiChronic Renal Failure: A. Definitionssharu4291Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Critical Care Nursing 7th Edition Sole Test BankDocument11 paginiIntroduction To Critical Care Nursing 7th Edition Sole Test BankRoyBartonnidcf100% (15)
- The Physical Exam, Review of Systems, and ReportsDocument2 paginiThe Physical Exam, Review of Systems, and ReportsJuan DeSantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 360 MedSpa Client Information FormDocument3 pagini360 MedSpa Client Information FormV Thomas PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Complications of IV TherapyDocument16 paginiComplications of IV TherapyFayeTolentinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teknik Anestesi UmumDocument128 paginiTeknik Anestesi UmumAkmalNourÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vision TestDocument93 paginiVision TestAr JayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal Spiritual 2 PDFDocument20 paginiJurnal Spiritual 2 PDFYoan Rahmah ApriliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care of The DyingDocument4 paginiCare of The Dyingprokuno89% (9)
- Pharmaceutical Sales & Marketing Legal and Ethical ConsiderationsDocument41 paginiPharmaceutical Sales & Marketing Legal and Ethical ConsiderationsqmnwebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oncology NotesDocument9 paginiOncology NotesmyrkÎncă nu există evaluări
- JDPS 2 120 11Document3 paginiJDPS 2 120 11Hello BiacthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter1Questions and SolutionsDocument3 paginiChapter1Questions and SolutionsMohammed NajibÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF SMR OperationDocument64 paginiPDF SMR OperationRizqulloh Taufiqul Hakim BarsahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Communication and Ethics in Pharmacy Practice: What Is To BeDocument23 paginiCommunication and Ethics in Pharmacy Practice: What Is To BeMuhammad RezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Goldman-Cecil Medicine 25th 2015Document39 paginiGoldman-Cecil Medicine 25th 2015Dumitru HarsenieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carefusion CannulasDocument8 paginiCarefusion Cannulasrubenr25Încă nu există evaluări
- GAT NCP Surgery WardDocument4 paginiGAT NCP Surgery WardDon Richard0% (1)
- Senior Citizens Act - Frequently Asked Questions 30-09-2013 09.05.50 (Selectable PDF)Document5 paginiSenior Citizens Act - Frequently Asked Questions 30-09-2013 09.05.50 (Selectable PDF)lazylawstudentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 10 - Time & Stress Management NotesDocument6 paginiGroup 10 - Time & Stress Management NotesMimi Lizada BhattiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2-d Echo With Doppler: Prepared by Kurfessa, AbdisaDocument7 pagini2-d Echo With Doppler: Prepared by Kurfessa, AbdisaAb Staholic BoiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus ClosureDocument7 paginiPatent Ductus Arteriosus ClosureDard TongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlansDocument31 paginiNursing Care PlansCyril Jane Caanyagan AcutÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Perspective in Accelerated Orthodontics With Aligner Treatment 2017 Seminars in OrthodonticsDocument7 paginiA Perspective in Accelerated Orthodontics With Aligner Treatment 2017 Seminars in Orthodonticsdruzair007Încă nu există evaluări
- Closing Statement PlaintiffDocument3 paginiClosing Statement PlaintiffJosh HughesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proses Persalinan Normal Eb1Document43 paginiProses Persalinan Normal Eb1Cici RahmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Who en enDocument307 paginiWho en enAafreen ShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- N Tees 2013Document2 paginiN Tees 2013api-2477290330% (2)