Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Enzymes b2.3
Încărcat de
tahamid0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
14 vizualizări21 paginiNotes olvl enzyme
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentNotes olvl enzyme
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
14 vizualizări21 paginiEnzymes b2.3
Încărcat de
tahamidNotes olvl enzyme
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 21
Proteins
Made of long chains of
amino acids
The shape depends on its function. Proteins can be:
Catalyst
Antibodies
Tissues e.g. muscle
Hormones
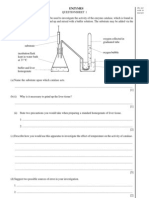
Enzymes + Catalysts
Chemical reactions in cells controlled by proteins called enzymes
BIOLOGICAL CATAYLSTS
Enzymes are large proteins, with shape vital for function,
place where molecules fit – ACTIVE SITE
SUBSTRATE - material/ chemical on which an enzyme acts
The substrate in a reaction held in active site
+ either connected to another molecule or broken down
Types of reaction
controlled by enzymes
Builds large molecules from small molecules
Changes one molecule to another
Breaks down large molecules into smaller molecules
Factors affecting enzymes?
Reaction faster when warmer
At higher temps molecules move around more quickly so
collide more often (in given time) + with more energy.
Too hot – enzymes stop working as active site changes shape –
enzyme denatured
Particular pH some best in alkaline, neutral or acid conditions
If too pH wrong for enzyme, active site changes shape –
enzyme denatured
Enzymes in Digestion
1. Digestive enzymes are made by glands in the
digestive system
2. Digestive enzymes work outside body cells
3. Digestion – breakdown of large, insoluble
molecules into smaller soluble molecules
4. Specific enzymes digest particular food types
Digestive enzymes to learn
Produced by Catalases the Where
Amylase Salivary glands Digestion of starch Mouth
(a carbohydrase) Pancreas Small intestine
Small intestine into sugars
Protease Stomach Breakdown of proteins Stomach
Pancreas Small intestine
Small intestine into amino acids
Lipase Pancreas Breakdown of lipids (fats + oils)
Small intestine
to fatty acids and glycerol
Speeding up digestion
Protease enzymes in stomach work best in acid so
glands in stomach wall produce hydrochloric acid
Amylase + lipase work in small intestine in slightly
alkaline conditions
Liver produces bile that us stored in the gall bladder
Alkaline bile squirted into small intestine to
neutralize stomach acid
Bile makes conditions in small intestine slightly
alkaline
Uses of enzymes
Microorganisms produce enzymes the we can
use, but are costly to produce
Biological detergents contain proteases + lipases that can digest food stains.
They work a low temps than ordinary washing powders
So saves energy + money spent on electricity
Proteases used to pre-digest proteins in baby foods
Isomerase used to convert glucose syrup into fructose syrup.
Fructose syrup much sweeter, so less needed in foods, so food less fattening
Carbohydrases used to convert starch into sugar syrup for food
In industry, enzymes allow reactions to occur at normal temps + pressures.
Traditional chemical processes need costly equipment and lots of energy to
produce high temps + pressures.
Using enzymes: advantages
In biological washing powders they are very
effective at removing stains
Biological washing powders can be used at lower
temps so saves energy and reduces costs
Some enzymes used in medicine to diagnose, control
or cure disease
In industry, costs of equipment + energy are reduced
Using enzymes:
disadvantages
✘ People misuse washing powders, may have allergic
reactions, enzymes are enclosed in capsules, once
powered is dissolved hands can’t be placed in water
✘ May enter waterways via sewage
✘ Industrial enzymes costly to produce
✘ They denature at high temps needed to kill
pathogens in washing
✘ Fabrics like wool will be digested by proteases.
Aerobic Respiration
Release of energy from food when oxygen is available.
Glucose + oxygen CO2 + water + energy
Takes place continuously in plants + animals
= inside mitochondria + controlled by enzymes
Anaerobic Respiration
During exercise:
Muscles need more energy
Muscles store glucose as glycogen which is converted back
If not enough oxygen reaching muscles they respire
anaerobically to get oxygen and become fatigued:
Anaerobic respiration is incomplete breakdown of glucose
+ produces lactic acid instead of water + CO2
The extra oxygen needed known as ‘oxygen debt’
If you are fitter, you pay off oxygen debt quicker
Questions
① What does do the terms ‘aerobic’ + ‘anaerobic’ mean?
② What do muscle cells need more of during exercise?
③ What are the 2 waste products of aerobic respiration?
④ What substance is stored in the muscles + can be converted to glucose?
⑤ Aerobic respiration word equation?
⑥ Why do muscles become fatigued (tired) during vigorous exercise?
⑦ What changes occur to the breathing and heart rate during exercise?
⑧ Why do blood vessels in muscles dilate during exercise?
⑨ What is meant by oxygen debt?
Answers
① Using oxygen + respiration without oxygen
② Energy
③ Carbon dioxide + water
④ Glycogen
⑤ Glucose + oxygen CO2 + water + energy
⑥ Lactic acid builds up in the muscles
⑦ Breathing + heart rate increase
⑧ Allows increased blood supply to muscle cells to provide oxygen + glucose
more quickly + to remove carbon dioxide faster
⑨ The amount of oxygen needed to breakdown the lactic acid in anaerobic
respiration
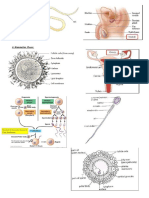
BODY CELLS DIVIDE FOR
GROWTH + REPAIR
Mitosis cell division – produces 2 identical new cells
(Making identical two)
Allele: a version of a particular gene
Chromosomes: contain genetic info (alleles)
Meiosis produces gametes (sex cells) – each gamete has
only one chromosome from original pair so all cells are
diff from each other and parent cells (Making eggs)
Stem cells, found in bone marrow – unspecialized – can
change into diff types of body cell – differentiation
A gene is a small section of DNA
Each gene codes for a particular combination of amino
acids – which make a specific protein
Chromosomes are made up of large molecules of DNA
which has a double helix structure
Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, one pair are sex cells
boy XY, girl XX
If the allele (gene controlling the same characteristic) masks
the effect of another it is said to be ‘dominant’, the allele
where the effect is masked is said to be ‘recessive’
Phenotype – physical appearance of the characteristic –
dimples
Genotype – the genetic make up - Which alleles does the
individual inherit? DD, Dd, dd
Homozygous both alleles are same DD (dominant) or dd
(recessive)
Heterozygous – 2 alleles are different Dd
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- This Study Resource Was: Drosophila Simulation - Patterns of HeredityDocument8 paginiThis Study Resource Was: Drosophila Simulation - Patterns of HeredityFUN PHYSICS FOR NEET67% (3)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- Breeding PDFDocument24 paginiBreeding PDFromnick0% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- CSEC Biology June 2005 P1 PDFDocument11 paginiCSEC Biology June 2005 P1 PDFCarl Agape Davis100% (7)
- Enzymes QuestionsDocument21 paginiEnzymes QuestionsJordan WanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enzymes QuestionsDocument21 paginiEnzymes QuestionsJordan WanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Centogene Indonesia CME 190830Document49 paginiCentogene Indonesia CME 190830Arshiya Nayara AvanishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSC Biology Paper 1 PDFDocument29 paginiHSC Biology Paper 1 PDFdgkulkarniÎncă nu există evaluări
- STRATEGIES TO ENHANCE FOOD PRODUCTIONDocument50 paginiSTRATEGIES TO ENHANCE FOOD PRODUCTIONgayatriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rhesus FactorDocument2 paginiRhesus FactormoneechoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Quiz 1 Questions Bio2296 Spring 2017Document5 paginiLab Quiz 1 Questions Bio2296 Spring 2017Nijo JacobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mastermind Biology Teacher Contact and Class SchedulesDocument12 paginiMastermind Biology Teacher Contact and Class SchedulestahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mastermind: Mock Examination (April 2019)Document1 paginăMastermind: Mock Examination (April 2019)tahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manejo Listas ArchivosDocument4 paginiManejo Listas Archivosqueperrito9314Încă nu există evaluări
- Note Approval For 50%Document1 paginăNote Approval For 50%tahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 QPDocument21 paginiUnit 1 QPtahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tahamid Bhuiya ResumeDocument2 paginiTahamid Bhuiya ResumetahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model A Mark Scheme P-1 & 2Document6 paginiModel A Mark Scheme P-1 & 2tahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Admission Information - As'levelDocument14 paginiAdmission Information - As'leveltahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Admission Information - A2'levelDocument10 paginiAdmission Information - A2'leveltahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fertilization FiguresDocument4 paginiFertilization FigurestahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- C1 W6 L1Document27 paginiC1 W6 L1tahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jan 19 MS PDFDocument26 paginiJan 19 MS PDFtahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 3Document4 paginiQuiz 3tahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 7 Lectures on TP53 Alignment and miRNA BindingDocument20 paginiWeek 7 Lectures on TP53 Alignment and miRNA BindingtahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIE As Practice Sheet 1Document3 paginiCIE As Practice Sheet 1tahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- WBI01 01 Pef 20180815Document56 paginiWBI01 01 Pef 20180815tahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enzyme Action - Testing Catalase ActivityDocument7 paginiEnzyme Action - Testing Catalase ActivitytahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investigate The Conditions Needed For The Growth of Plant Cells Using Tissue Culture TechniquesDocument20 paginiInvestigate The Conditions Needed For The Growth of Plant Cells Using Tissue Culture TechniquestahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel AS Worksheet - 3 - Nucleic AcidsDocument2 paginiEdexcel AS Worksheet - 3 - Nucleic AcidstahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 QPDocument21 paginiUnit 1 QPtahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- As SNAB Revision NotesDocument49 paginiAs SNAB Revision NotesXneo KMeng 茗茗 ~Încă nu există evaluări
- Enzyme Disc Lab Instrucitons by DawnDocument4 paginiEnzyme Disc Lab Instrucitons by DawntahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plants and SensitivityDocument15 paginiPlants and SensitivitytahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plants and SensitivityDocument15 paginiPlants and SensitivitytahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global Warming First Emerged As A Cause of Global Concern in The 1980's, A Result of The Apparent Rise inDocument4 paginiGlobal Warming First Emerged As A Cause of Global Concern in The 1980's, A Result of The Apparent Rise intahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2. How Bonding and Structure Are Related To The Properties of Substances PDFDocument3 pagini2.2. How Bonding and Structure Are Related To The Properties of Substances PDFtahamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0708 Global WarmingDocument36 pagini0708 Global Warmingరాజా రావు చామర్తిÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology: Pearson EdexcelDocument24 paginiBiology: Pearson EdexcelMahmoudAboAlSamenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 9 Science Part 2 - Inheritance PatternsDocument4 paginiGrade 9 Science Part 2 - Inheritance PatternsMom GieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology QuestionsDocument41 paginiBiology QuestionsB.srihariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hardy-Weinberg ReviewDocument6 paginiHardy-Weinberg ReviewR A Y S U N S H I N EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction Basic GeneticsDocument6 paginiIntroduction Basic GeneticscsamarinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mirna 146 and Its Association With Autoimmune DseasesDocument7 paginiMirna 146 and Its Association With Autoimmune DseasesIJAR JOURNALÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Environmental Changes Can Lead to Species ExtinctionDocument8 paginiHow Environmental Changes Can Lead to Species ExtinctionEricha SolomonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Paper-3, Biology (2021-22)Document12 paginiPractice Paper-3, Biology (2021-22)Himani BudhirajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Problem Set AnalysisDocument6 paginiGenetics Problem Set AnalysisKunvarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 2: Heredity: Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument26 paginiScience: Quarter 1 - Module 2: Heredity: Non-Mendelian GeneticsShawee Gucor SaquilabonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Androgenic HaploidsDocument9 paginiAndrogenic HaploidsBasa SwaminathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mendel's Laws of Inheritance IndexDocument19 paginiMendel's Laws of Inheritance IndexVaishakhi MuraliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skin Health and Disease - 2021 - Zirn - Rothmund Thomson Syndrome Type 1 Caused by Biallelic ANAPC1 Gene MutationsDocument4 paginiSkin Health and Disease - 2021 - Zirn - Rothmund Thomson Syndrome Type 1 Caused by Biallelic ANAPC1 Gene MutationsEfren BalsecaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mendelian & Modern Genetics: General Biology 2Document51 paginiMendelian & Modern Genetics: General Biology 2sannsannÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Exploration: Hardy-Weinberg EquilibriumDocument6 paginiStudent Exploration: Hardy-Weinberg EquilibriumEmilyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Selangor 2007Document17 paginiMark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Selangor 2007hasimahazitÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAASOTA 56th Life Sciences OlympiadDocument20 paginiSAASOTA 56th Life Sciences OlympiadOsborn AgyemangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Exploring The Diversity of Life Canadian 3Rd Edition Russell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument22 paginiBiology Exploring The Diversity of Life Canadian 3Rd Edition Russell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFbierbalkgeorge3f17100% (13)
- Cells and Organelles Structure and Function Biology Standard 1.1Document26 paginiCells and Organelles Structure and Function Biology Standard 1.1Hithe60% (5)
- Genetics Lab NotesDocument4 paginiGenetics Lab NotesJayar AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Genetic Inheritance Sb015Document124 paginiChapter 4 Genetic Inheritance Sb015Muhammad IzuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IBO 2021 OnlineDocument35 paginiIBO 2021 OnlineFabian “TheLeviathan”Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology - Essential Maths Skills AnswersDocument47 paginiBiology - Essential Maths Skills AnswersTelman ResidovÎncă nu există evaluări