Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
History of Atoms: From Democritus to Rutherford
Încărcat de
Jason Monteroso Tulod0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
70 vizualizări7 paginiThis document discusses the history and development of atomic theory from ancient Greek philosophers to the early 20th century. It describes Democritus' early idea that all matter is made of indivisible atoms. Later, John Dalton provided experimental evidence supporting Democritus' theory and developed the first atomic theory. J.J. Thomson discovered electrons and proposed the plum pudding model of the atom. However, Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed atoms have a small, dense nucleus surrounded by empty space, overturning Thomson's model and establishing Rutherford's nuclear model of the atom.
Descriere originală:
Atoms
Titlu original
History of Atoms
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThis document discusses the history and development of atomic theory from ancient Greek philosophers to the early 20th century. It describes Democritus' early idea that all matter is made of indivisible atoms. Later, John Dalton provided experimental evidence supporting Democritus' theory and developed the first atomic theory. J.J. Thomson discovered electrons and proposed the plum pudding model of the atom. However, Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed atoms have a small, dense nucleus surrounded by empty space, overturning Thomson's model and establishing Rutherford's nuclear model of the atom.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
70 vizualizări7 paginiHistory of Atoms: From Democritus to Rutherford
Încărcat de
Jason Monteroso TulodThis document discusses the history and development of atomic theory from ancient Greek philosophers to the early 20th century. It describes Democritus' early idea that all matter is made of indivisible atoms. Later, John Dalton provided experimental evidence supporting Democritus' theory and developed the first atomic theory. J.J. Thomson discovered electrons and proposed the plum pudding model of the atom. However, Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed atoms have a small, dense nucleus surrounded by empty space, overturning Thomson's model and establishing Rutherford's nuclear model of the atom.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 7
Made by : Shelly, Elyssa , Nour,
HISTORY OF ATOMS Bhavya
8-C
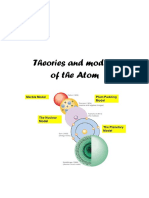
DEMOCRITUS’S IDEA
Democritus is a Greek philosopher who introduced his ideas about the atoms around
450 BC. He thought that everything was made up of tiny particles and that atoms
(also known as atomos) were indivisible and indestructible. He came up with this idea
when he was walking on the sand. As he walked on the sand, he thought of how the
sand used to be pebbles. These pebbles would’ve been broken down apart, forming
sand. He thought that sand would break down into bits of smaller pieces again and
again till it can’t break apart any further. The particle that would be left was the
smallest individual particle, in other words the atom. However, a Greek philosopher
Aristotle, rejected his ideas of atoms as it was lacking of evidence. Aristotle’s ideas
were accepted for more than 2000 years whereas his ideas were more or less
forgotten.
JOHN DALTON
Around 1800, a British chemist named John Dalton revived Democritus’s early ideas about the atom. He
made a living by teaching and just did research in his spare time. Nonetheless, from his research results,
he developed one of the most important theories in science. John Dalton did many experiments that
provided evidence for atoms. For example, he studied the pressure of gases, and also researched the
properties of compound. He showed that a compound always consists of the same elements in the same
ratio. On the other hand, different compounds always consist of different elements or ratios. This can
happen, Dalton reasoned, only if elements are made of tiny particles that can combine in an endless
variety of ways. From his research, Dalton developed a theory of the atom.
The atomic theory Dalton developed consists of these ideas:
• All substances are made of atoms. Atoms are the smallest particles of matter.
•They can’t be divided into smaller particles. They also can’t be created or destroyed.
•All atoms of the same element are alike and have the same mass. Atoms of different elements are
different and have different masses.
•Atoms join together to form compounds. A given compound always consists of the same kinds of atoms in
the same ratio.
J.J THOMSON
J.J Thomson discovered electrons and noticed that an atom can be divided. Also, he
concluded atoms are made of positive cores and negatively charged particles within
it. He developed the Plum Pudding Model before the atomic nucleus was discovered.
This model shows that the electrons are surrounded by a “pudding” of positive
charges to balance the negative charges.
RUTHERFORD & GOLD FOIL EXPERIMENT
In 1911 Rutherford was the first to discover that atoms have a small charged nucleus
surrounded by largely empty space, and are circled by tiny electrons, which became
known as the Rutherford model. Rutherford overturned Thomson’s model in 1911 with
his well-known gold foil experiment in which he demonstrated that the atom has a tiny
and heavy nucleus. Rutherford designed an experiment to use alpha particles emitted
by a radioactive element as probes to the unseen world of atomic structure. If
Thomson was correct, the beam would go straight through the gold foil. Most of the
beams went through the foil, but a few were reflected.
RUTHERFORD’S MODEL
Rutherford’s new model for the atom, based on the experimental results, contained
the new features of a relatively high central charge concentrated into a very small
volume in comparison to the rest of the atom and with this central volume also
containing the bulk of the atomic mass of the atom.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Manual of Standard Practice For Welded Wire Mesh ReinforcementDocument38 paginiManual of Standard Practice For Welded Wire Mesh Reinforcement970186csÎncă nu există evaluări
- Historical Timeline of The AtomDocument19 paginiHistorical Timeline of The AtomHisagi ShuheiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic ModelsDocument35 paginiAtomic Modelsrinlacer100% (1)
- Physical Science: Prepared By: Ms. Shaira G. SalardaDocument41 paginiPhysical Science: Prepared By: Ms. Shaira G. SalardaShaira SalardaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Sciences Lesson 2 The Atomic Structure and The Chemical ElementsDocument11 paginiPhysical Sciences Lesson 2 The Atomic Structure and The Chemical ElementsJustin Bird100% (1)
- Power Electronics and Drives Laboratory ManualDocument71 paginiPower Electronics and Drives Laboratory ManualSureshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic StructureDocument91 paginiAtomic StructureUmmu juraijÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atoms and Elements ExplainedDocument10 paginiAtoms and Elements ExplainedsleepyanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dalton's atomic theory and the discovery of subatomic particlesDocument13 paginiDalton's atomic theory and the discovery of subatomic particlesAlex Omunga100% (2)
- Everything Maths Grade 11 Trig GraphsDocument3 paginiEverything Maths Grade 11 Trig GraphsAmyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inertia BaseDocument2 paginiInertia BasePackiaraj KrishnasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 7: 7H Energy Stores and Transfers Notes and Resources Name: - FormDocument14 paginiYear 7: 7H Energy Stores and Transfers Notes and Resources Name: - FormJason Monteroso TulodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Models and TheoryDocument23 paginiAtomic Models and TheoryKhair TaupÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic ModelsDocument26 paginiAtomic ModelsFlitcher Diane PilotonÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEMO Roof Brochure en 2019Document27 paginiBEMO Roof Brochure en 2019Anonymous wzuyBcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gating System Design GuideDocument11 paginiGating System Design GuideAshok Pradhan100% (1)
- How The Ideas of The Atom, Along With The Idea of The Elements EvolvedDocument50 paginiHow The Ideas of The Atom, Along With The Idea of The Elements EvolvedChosen ExeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The History of The Atom Notes - CondensedDocument10 paginiThe History of The Atom Notes - CondensedWahyu Ervin SaputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of AtomsDocument9 paginiHistory of AtomsARGIEÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Evolution of The AtomDocument42 paginiThe Evolution of The Atomapi-380653744Încă nu există evaluări
- 1stQ.3.1 Atomic TheoryDocument35 pagini1stQ.3.1 Atomic TheoryRaiden Gabriel LontokÎncă nu există evaluări
- LESSON 2.1 Sir FahadDocument41 paginiLESSON 2.1 Sir FahadJeriel Edell ClaritoÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of The Atom: From: Regina Gargiulo Teacher: Alessandro Abbate Class: 8th GradeDocument17 paginiHistory of The Atom: From: Regina Gargiulo Teacher: Alessandro Abbate Class: 8th GradeRegina GargiuloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of The Atomic TheoryDocument2 paginiDevelopment of The Atomic TheoryJimmy gogoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Evolution of Atomic Theories from Democritus to RutherfordDocument5 paginiThe Evolution of Atomic Theories from Democritus to RutherfordTaufik Qodar RomadiansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of AtomDocument8 paginiHistory of AtomMohamadÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemocritusDocument58 paginiDemocritusKRISTEL JANE ALBISOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic History and Model SummaryDocument2 paginiAtomic History and Model SummarySherchen Antonio-CortesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atoms, Molecules & IonsDocument42 paginiAtoms, Molecules & Ionsja_QuinineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Science Timeline of Atomic Models July 202020 1Document33 paginiPhysical Science Timeline of Atomic Models July 202020 1Policarpio R Princess LynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Structure: By:-Abhinav Amol SomwanshiDocument33 paginiAtomic Structure: By:-Abhinav Amol SomwanshimadhurisdnyankunjÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4-Discovery of The Subatomic ParticlesDocument35 pagini4-Discovery of The Subatomic ParticlesEdchel Espeña100% (1)
- Models of The Atom: Particle Model of MatterDocument16 paginiModels of The Atom: Particle Model of MatterEdison OrgilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baladad Richelle 11 ABM-B Physical ScienceDocument4 paginiBaladad Richelle 11 ABM-B Physical ScienceIvy Jane R AlarconÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Theory 2Document17 paginiAtomic Theory 2Liz EvermoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Democritus' Atomic ModelDocument7 paginiDemocritus' Atomic Modelkarla callejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theoretical Concept of AtomDocument2 paginiTheoretical Concept of AtomZayra Melgar AtreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Theory Worksheet - AnsweredDocument3 paginiAtomic Theory Worksheet - AnsweredMaleek HolderÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Atomic IntroDocument34 pagini1 Atomic Introapi-273966469Încă nu există evaluări
- History of Atomic TheoryDocument38 paginiHistory of Atomic TheorylovelyshaneibrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- History in The Developmet of The Structure of Atom: Different Contributions of ScientistDocument4 paginiHistory in The Developmet of The Structure of Atom: Different Contributions of ScientistJin09 GappalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic TheoryDocument2 paginiAtomic Theorybinaroth03Încă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Structure History and ModelsDocument44 paginiAtomic Structure History and ModelsLu NaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atoms and PeriodiciDocument19 paginiAtoms and PeriodiciAbhishek SivanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matter and Atomic Theories Through HistoryDocument10 paginiMatter and Atomic Theories Through Historycasey lÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contributions To The Development of Atomic ModelDocument12 paginiContributions To The Development of Atomic ModelHadif Darwish BadrulhishamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atoms 3rd TopicDocument36 paginiAtoms 3rd TopicReynalie BotonÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Evolution of the Atomic ModelDocument17 paginiThe Evolution of the Atomic ModelMaulana YusufÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic TheoryDocument5 paginiAtomic Theoryclarkefinlay68Încă nu există evaluări
- Atoms History (What's The Matter)Document17 paginiAtoms History (What's The Matter)qcsrjj9d4dÎncă nu există evaluări
- AtomDocument32 paginiAtomAdarsh TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- A History of The AtomDocument4 paginiA History of The AtomKeith Kevin ChuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AtomDocument13 paginiAtomronalyn madesÎncă nu există evaluări
- AtomsDocument26 paginiAtomsJhul Mhel SonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- From The Eyes of Philosophers and ScientistsDocument56 paginiFrom The Eyes of Philosophers and ScientistsMarielle GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept of Atom From Ancient Greek To PresentDocument59 paginiConcept of Atom From Ancient Greek To PresentJheniel Villa AgustinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of Atomic Theory and Structure Jan 4Document64 paginiDevelopment of Atomic Theory and Structure Jan 4Roseman TumaliuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChristianDocument21 paginiChristianAdrian John ManalotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic ModelsDocument5 paginiAtomic ModelsTikoÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-3-Lesson-10-for-CHEM-1-FINALDocument29 paginiUNIT-3-Lesson-10-for-CHEM-1-FINALSherlynMaeBasalatanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contributions To The Atomic TheoryDocument7 paginiContributions To The Atomic Theoryadios7897Încă nu există evaluări
- History of The Development of Atomic TheoryDocument26 paginiHistory of The Development of Atomic TheoryRohan lallÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reporting Physical ScienceDocument21 paginiReporting Physical ScienceDrezele CalantinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- It Was Around 440 BCE That Democritus First Proposed That Everything in The World Was Made Up of Tiny Particles Surrounded by Empty SpaceDocument5 paginiIt Was Around 440 BCE That Democritus First Proposed That Everything in The World Was Made Up of Tiny Particles Surrounded by Empty SpaceRonnel PilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aristotle Atomic TheoryDocument3 paginiAristotle Atomic TheoryEva DewsburyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bazinga 3Document2 paginiBazinga 3api-327712007Încă nu există evaluări
- Calculating Weight Worksheet T1Document1 paginăCalculating Weight Worksheet T1Jason Monteroso TulodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculating Weight Worksheet T3Document1 paginăCalculating Weight Worksheet T3Jason Monteroso TulodÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Weight Equation Homework WorksheetDocument1 paginăThe Weight Equation Homework WorksheetJason Monteroso TulodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculating Weight Worksheet T2Document1 paginăCalculating Weight Worksheet T2Jason Monteroso TulodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 5 9th Week Day3Document12 paginiMath 5 9th Week Day3Jason Monteroso TulodÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7H Energy Transfer Student Notes and ResourcesDocument4 pagini7H Energy Transfer Student Notes and ResourcesJason Monteroso TulodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analyzing How Mass and Velocity Affect MomentumDocument12 paginiAnalyzing How Mass and Velocity Affect MomentumPauling ChiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequency and AmplitudeDocument12 paginiFrequency and AmplitudeJason Monteroso TulodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planets DisplayDocument11 paginiPlanets DisplayJason Monteroso TulodÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 14D 13 PDFDocument17 pagini6 14D 13 PDFRiyon Sanjaya IrmalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment # 4 MomentsDocument9 paginiAssignment # 4 MomentsKalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHM 2045 Exam 2 Form Code ADocument2 paginiCHM 2045 Exam 2 Form Code ABritanny NelsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circle TheoryDocument8 paginiCircle Theoryapi-278074538100% (3)
- AAnalyst 800 Detection Limits-Chromium DataDocument2 paginiAAnalyst 800 Detection Limits-Chromium DataЂорђе РадојичићÎncă nu există evaluări
- JR Engg WAPDA (Civil)Document16 paginiJR Engg WAPDA (Civil)Hamza MujahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rabin CryptosystemDocument41 paginiRabin CryptosystemArkadev GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC3-611 Rack Controller and ECD-000 Display UnitDocument8 paginiEC3-611 Rack Controller and ECD-000 Display UnitMaria DazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of The Light J 3 Mesons in QCD Sum RulesDocument11 paginiAnalysis of The Light J 3 Mesons in QCD Sum Rulesubik59Încă nu există evaluări
- Intensive and Extensive Properties Crowther-Robitaille 2019Document6 paginiIntensive and Extensive Properties Crowther-Robitaille 2019provocator74Încă nu există evaluări
- MODEL QUESTIONS (Lasers and Optical Fibers) Oct-2023Document2 paginiMODEL QUESTIONS (Lasers and Optical Fibers) Oct-2023shettysohan79Încă nu există evaluări
- The PA Bible Addn 13 The Electric Guitar Loudspeaker PDFDocument3 paginiThe PA Bible Addn 13 The Electric Guitar Loudspeaker PDFjosiasns5257Încă nu există evaluări
- Ageing of Zinc Alloys: January 2011Document23 paginiAgeing of Zinc Alloys: January 2011Alicia Jara ChavezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm d6218-00Document19 paginiAstm d6218-00Francisco DelgadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semester 1 Examinations 2018/2019: Programme (S)Document6 paginiSemester 1 Examinations 2018/2019: Programme (S)fuckoffmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- POLE FOUNDATION ANALYSISDocument2 paginiPOLE FOUNDATION ANALYSISPrabuVijayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sorvall MTX 150 Micro-Ultracentrifuges - Instruction Manual - Thermo Fisher ScientificDocument114 paginiSorvall MTX 150 Micro-Ultracentrifuges - Instruction Manual - Thermo Fisher Scientificluroguita-1100% (1)
- 23 Electronic TheodolitesDocument4 pagini23 Electronic TheodolitesEmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Providing Optimized Alignment & Automatic Interchange Design Software TutorialDocument11 paginiProviding Optimized Alignment & Automatic Interchange Design Software Tutorialadera1Încă nu există evaluări
- Tda 2170Document8 paginiTda 2170ricdem11_42047Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesoon PHI 20188 Lesson NotesDocument77 paginiLesoon PHI 20188 Lesson NotesGlennÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.15.MP75 CVL 015 STRL Des CriteriaDocument27 pagini4.15.MP75 CVL 015 STRL Des CriteriaLandon MitchellÎncă nu există evaluări
- TDS - Micro-Air 120Document3 paginiTDS - Micro-Air 120aahtagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metals and AlloysDocument34 paginiMetals and AlloyszenrockÎncă nu există evaluări