Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Presentation1 Deepali Raut 11
Încărcat de
Patricia JosephDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Presentation1 Deepali Raut 11
Încărcat de
Patricia JosephDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
R.
A College Washim
Department Of Zoology
Name :- Ku. Deepali Govindrao Raut
Class :- B.Sc III Year (Microbiology)
Seminar Topic :- Types Of Muscles
Types Of Muscle
There are three types of muscles which differ from each
physiologically and functionally.
Skeletal or striated muscles or voluntary muscles.
Smooth or non striated muscles or non-voluntary muscles
and
Cardiac or heart muscles
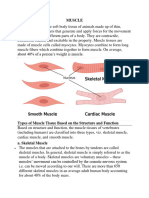
Skeletal muscles or Striated muscles
Skeletal muscles are those muscles which are attached to the bones and are
mainly responsible for the movement of the skeleton and therefore of the body
as a whole.
Each muscle cell is a long, straight and unbranched cylindrical fiber, 10-40
p.m in thickness and up to 1-40 El in length. It consists of a thin
outgr_limiting membrane, the sarcolemma, which encloses a cytoplasm
known as sarcoplasm. It is multinucleate and has well developed cross
striations. Each muscle fiber— is composed of fibrils or myofibrils,. having
characteristically alternate light and darluegions. It is also called asoluntary
musclsjbecause its contractile activities are under the control of central
nervous system rather than autonomic nervous system. They comprise about
40 % of the total body weight.
Smooth Muscles or Unstriated Muscles:
Smooth muscles are also called unstriated or involuntary muscles and
do not have s striations on their myofibrils .
Each muscle cell of the muscle fiber are elongated and spindle shaped
and sionally branched at the ends. It is about 18-200 it long and 3-8 11
thick. Each le fiber consists of a long cigar-shaped nucleus situated in
the widest part of the cell . The cytoplasm's homogenous andiMillikdite.d
with little or-I1-0-gr known as plasm. In it are found numerous fine
contractile threads, the myofibrils, which lie
lel to the long axis of the cell. The cytoplasm is bounded externally by a
thin cell brane. The sarcolemma 1_absent.
They are generally found in the walls of the internal organs, such as
digestive tract, iratory passages, urinary bladder, arteries, veins, etc.
They are slow in contraction are not under voluntary control. The
contraction and relaxation of smooth mus,-les directly controlled partly
by nervous system and partly by them.
Cardiac Muscles:
These muscles are found in the heart only. They are made up of
striated tinucleate fiber, thus resembling the skeletal muscles in
many respects. Functionally arc homologous to the unstriated
muscle. They contract rapidly rhythmically, lessly and endlessly.
The cardiac muscles are branched and form a network in the wall
of the heart. fibres are short cylindrical, branching and
anastomosing separated by loose ective tissue and richly
supplied with blood capillaries. The fibres are joined end to and
are interconnected by oblique bridges. The end of these fibres
form Zig-zag ions called intercalated discs. The sarcolemma is
absent. The sarcoplasm is more myofibrils are less. They are
uninucleated and nucleus is centrally located.
These muscles are specialized in the sense that stimulation of
cardiac muscle -es all the muscle fibers to respond initiating
rhythmic beats of the heart. They are 'ever, involuntary in
function and are innervated by autonomic nerves.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Wilkins Clinical Assessment in Respiratory Care 7th Edition by Heuer - Test BankDocument37 paginiWilkins Clinical Assessment in Respiratory Care 7th Edition by Heuer - Test Bankroseyoung0Încă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology 2 Lab ManualDocument129 paginiAnatomy and Physiology 2 Lab ManualMAJEETH மஜீத் TIRUNELVELIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscular SystemDocument26 paginiMuscular Systemlubnab75% (4)
- Muscular TissueDocument49 paginiMuscular TissueSteph VeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Muscular System NotesDocument32 paginiThe Muscular System NotesVivien Talavera0% (1)
- BIOLOGY Form 5 Chapter 1 TransportDocument42 paginiBIOLOGY Form 5 Chapter 1 TransportShephard Png91% (95)
- Grade 9 Science LASDocument73 paginiGrade 9 Science LASJezza May Tambauan100% (8)
- ACLS Practice TestDocument5 paginiACLS Practice Testprettynpink0867% (3)
- Tachyarrhythmia SDocument46 paginiTachyarrhythmia SAsif HameedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus NewDocument16 paginiPatent Ductus Arteriosus NewchelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Case Study - 1 - (Acs)Document32 paginiNursing Case Study - 1 - (Acs)nidhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care of Clients in Emergency Situation 2 MergedDocument234 paginiNursing Care of Clients in Emergency Situation 2 MergedDanica Franco100% (1)
- HDFC Bank Report MbaDocument82 paginiHDFC Bank Report Mba8542ish83% (18)
- Muscular TissueDocument5 paginiMuscular Tissuenitesh.th15005Încă nu există evaluări
- Zoology Notes: 011 Chapter 7Document4 paginiZoology Notes: 011 Chapter 7humanupgradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- READING MATERIAL - Muscular TissuesDocument2 paginiREADING MATERIAL - Muscular TissuescharuislostÎncă nu există evaluări
- Histology of Muscles: Learning ObjectivesDocument5 paginiHistology of Muscles: Learning ObjectivesLP BenozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCCC C CDocument16 paginiCCCC C CLennon Mars LamsinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise No. 6 Muscle TissueDocument10 paginiExercise No. 6 Muscle TissueRyan Aaron Cruz ParÎncă nu există evaluări
- MUSCLE and NERVOUSHISTOLOGYDocument78 paginiMUSCLE and NERVOUSHISTOLOGYAerielle De GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hadba University CollegeتقريرDocument11 paginiHadba University Collegeتقريرtaha1995irqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscular Tissues: Skeletal MusclesDocument3 paginiMuscular Tissues: Skeletal Musclesalimsaadun alimsaadunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sir FayyazDocument49 paginiSir FayyazSara ZaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscular TissuDocument3 paginiMuscular Tissunikifarnaz8Încă nu există evaluări
- The Muscular TissueDocument23 paginiThe Muscular TissueMuhammad Salisu IliyasuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faculty of Medicine: Practical Work No. 9Document3 paginiFaculty of Medicine: Practical Work No. 9Andrei TimofteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscular SystemDocument5 paginiMuscular SystemadequateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscle TissueDocument10 paginiMuscle TissueHesbone AneneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscle Tissue - HistologyDocument35 paginiMuscle Tissue - HistologyjabirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skeletal MuscleDocument32 paginiSkeletal MuscleArfiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Modifications and TissuesDocument4 paginiCell Modifications and TissuesElla PascuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscular TissueDocument6 paginiMuscular TissueChezkaMayC.OliverosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscular SystemDocument23 paginiMuscular SystemAland BakrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscle TissueDocument33 paginiMuscle TissueFady FadyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Physiology Chapter 4 - EndDocument172 paginiHuman Physiology Chapter 4 - EndEmebet DebissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 5 Muscular SystemDocument8 paginiLesson 5 Muscular SystemRodrigo SeriozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument27 paginiUntitledOtencianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embryology: Abdulrahman Uday AbdulfatahDocument27 paginiEmbryology: Abdulrahman Uday AbdulfatahAbdulrahman UdayÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015Document34 pagini3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015yigermalamanuel32Încă nu există evaluări
- UNIT 3 (Muscular System)Document7 paginiUNIT 3 (Muscular System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- MYOLOGYDocument20 paginiMYOLOGYNatty ChikumbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANA205 Muscular Tissue: Lecture Notes by Dr. Taiwo-OlaDocument31 paginiANA205 Muscular Tissue: Lecture Notes by Dr. Taiwo-OlaIbrahim BabatundeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2-Muscle StructureDocument33 pagini2-Muscle Structureasaad AseeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- TissuesDocument6 paginiTissuesvaidika.soni12009Încă nu există evaluări
- Cds Day1Document15 paginiCds Day1Rajkamal ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscular SystemDocument8 paginiMuscular SystemZoological science classesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscular SyastemDocument28 paginiMuscular SyastemKaizen Science AcademyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Anatomy (Lec 7)Document32 paginiIntroduction To Anatomy (Lec 7)ehtshamulhaq06Încă nu există evaluări
- Muscular TissueDocument37 paginiMuscular Tissueمؤمل عدنان الشمخيÎncă nu există evaluări
- MUSCLE B.Sc-IIDocument13 paginiMUSCLE B.Sc-IIAjinkya BansodeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMDocument20 paginiModule 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMMisha WilliamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscle TissueDocument31 paginiMuscle Tissueaimi BatrisyiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresDocument58 paginiLesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresPhoenixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells: Skeletal Muscle Is A Form of Striated Muscle Tissue Existing Under Control of The SomaticDocument11 paginiCells: Skeletal Muscle Is A Form of Striated Muscle Tissue Existing Under Control of The SomaticbloodythornÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 MuscleDocument3 pagini5 MuscleNicolePorsueloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscle Tissue SummaryDocument2 paginiMuscle Tissue SummaryLindenScholesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscle Histology: Assoc. Prof Dr. Karim Al-Jashamy IMS 2009Document35 paginiMuscle Histology: Assoc. Prof Dr. Karim Al-Jashamy IMS 2009Maniventhan NachimuthuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Proper For Week 9Document5 paginiLesson Proper For Week 9Merlyn NavarroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ilovepdf Merged 1 13Document13 paginiIlovepdf Merged 1 13Abdulrahman UdayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 7 Muscular SystemDocument7 paginiTopic 7 Muscular SystemMary Ann Morillo TenederoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Exercise - MuscleDocument3 paginiLaboratory Exercise - MuscleJohn Henry G. Gabriel IVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscle TissueDocument30 paginiMuscle Tissued20231107667Încă nu există evaluări
- Muscle Tissue: Lecturer Reham M.M. Almosawi Medical MicrobiologyDocument10 paginiMuscle Tissue: Lecturer Reham M.M. Almosawi Medical Microbiologymustafa7calligrapherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tejido Muscular Usp 2022Document44 paginiTejido Muscular Usp 2022Gisela VilelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscular Tissue: Anatomy and Physiology LectureDocument25 paginiMuscular Tissue: Anatomy and Physiology LecturehanzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of Skeletal MuscleDocument12 paginiStructure of Skeletal MuscledilsharakaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscular SystemDocument20 paginiMuscular SystemAltaf Hussain KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 - Muscle Tissue DR - Vera 2021-2Document45 pagini6 - Muscle Tissue DR - Vera 2021-2Wilmarilys Ramos MartellÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-6 Muscular SystemDocument48 paginiUNIT-6 Muscular SystemChandan ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poly Project Front Page 1122Document1 paginăPoly Project Front Page 1122Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation1 Deepali Raut 11Document6 paginiPresentation1 Deepali Raut 11Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poly Project Front Page 11221122Document1 paginăPoly Project Front Page 11221122Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAHATMA GANDHI - ppt1111Document27 paginiMAHATMA GANDHI - ppt1111Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synopsis All OkDocument16 paginiSynopsis All OkPatricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSM PPT Washim Dist DT 19 11 2016 Swati Dhoble 11111Document19 paginiPSM PPT Washim Dist DT 19 11 2016 Swati Dhoble 11111Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mahale Project Reserve Bank of India 11Document12 paginiMahale Project Reserve Bank of India 11Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Nursing Service and Education FileDocument1 paginăManagement of Nursing Service and Education FilePatricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impactofictineducation 131020100612 Phpapp02Document18 paginiImpactofictineducation 131020100612 Phpapp02Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kims University Kaiet-2015.PDF 11111Document2 paginiKims University Kaiet-2015.PDF 11111Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Swine FluDocument17 paginiThe Swine FluPatricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impactofictineducation 131020100612 Phpapp02Document18 paginiImpactofictineducation 131020100612 Phpapp02Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Seminar Report: Big Data: Issues and Challenges Moving ForwardDocument7 paginiA Seminar Report: Big Data: Issues and Challenges Moving ForwardPatricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Active MaterialsDocument21 paginiAdvanced Active MaterialsRajeswari DhamotharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Underwater Welding: A Seminar Report ONDocument5 paginiUnderwater Welding: A Seminar Report ONPatricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar Report Solar TowerDocument24 paginiSeminar Report Solar TowerPatricia Joseph100% (1)
- PSM PPT Washim Dist DT 19 11 2016 Swati Dhoble 11111Document19 paginiPSM PPT Washim Dist DT 19 11 2016 Swati Dhoble 11111Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Underwater Welding Seminar11Document18 paginiUnderwater Welding Seminar11Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation1 21212121212121Document1 paginăPresentation1 21212121212121Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- R A College LogoDocument1 paginăR A College LogoPatricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Greeting Card Math Christmas Card BoxDocument28 paginiGreeting Card Math Christmas Card BoxPatricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- UGProspectus17-18 English PDFDocument53 paginiUGProspectus17-18 English PDFPatricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effective - Presentation - PPT BED SHAMALDocument6 paginiEffective - Presentation - PPT BED SHAMALPatricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- New New 11 111Document9 paginiNew New 11 111Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Om Fancy Jewellers": Project Report ONDocument53 pagini"Om Fancy Jewellers": Project Report ONPatricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAHATMA GANDHI - ppt1111Document27 paginiMAHATMA GANDHI - ppt1111Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation1 pptx1Document2 paginiPresentation1 pptx1Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- New New 11 111Document9 paginiNew New 11 111Patricia JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal 4 Uji Jalan 6 MenitDocument10 paginiJurnal 4 Uji Jalan 6 MenitSandy Tama Okvan YudhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muhs 2K17 PDFDocument24 paginiMuhs 2K17 PDFJenniferÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECG - NotesDocument33 paginiECG - NotesNaveen ChandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVD in Diabetes - EADSG 2016Document57 paginiCVD in Diabetes - EADSG 2016OmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CV Dr. Dr. Jacub Pandelaki 2016 (Edit Jan 2017)Document6 paginiCV Dr. Dr. Jacub Pandelaki 2016 (Edit Jan 2017)hasanuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Is There A Circulation Without A Heart?Document16 paginiIs There A Circulation Without A Heart?pborutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nurs 2200 Asthma Case StudyDocument6 paginiNurs 2200 Asthma Case StudyBrandee StantonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Attunement With A Benevolent Universe 2Document2 pagini5 Attunement With A Benevolent Universe 2muzickaueÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECGDocument62 paginiECGSanju TanwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heart Failure Pelatihan Dokter KeluargaDocument55 paginiHeart Failure Pelatihan Dokter KeluargaDelia NingrumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1 and 2 Cardiac PhysiologyDocument40 paginiLecture 1 and 2 Cardiac PhysiologyRobert BakerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Biology: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1)Document20 paginiHuman Biology: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1)Nang Seng Tawng HparawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acls Study Guide 2016Document2 paginiAcls Study Guide 2016Caridad RodasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anestesia Consideraciones de Anesthesia en Paciente Geratricos PDFDocument3 paginiAnestesia Consideraciones de Anesthesia en Paciente Geratricos PDFFernanda PérezÎncă nu există evaluări
- DOWLEX™ 2047G: Polyethylene ResinDocument3 paginiDOWLEX™ 2047G: Polyethylene Resinujang sukartaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Framingham Category Risk ScoreDocument1 paginăFramingham Category Risk Scoresyaiful rinantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CMRIDocument20 paginiCMRINauman JavedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anemia Approach S.elyaDocument51 paginiAnemia Approach S.elyaAnonymous JqvBHcsYrEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics: Mdcat Grand Test Test # 1Document12 paginiPhysics: Mdcat Grand Test Test # 1Ahmed SaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0 - Anesthetic Management of A Case With Aortic Regurgitation Posted For Laproscopic Hernia Mesh RepairDocument4 pagini0 - Anesthetic Management of A Case With Aortic Regurgitation Posted For Laproscopic Hernia Mesh RepairAromal SatheeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Risk Newborn: Problems Related To Maturity Preterm NewbornDocument36 paginiHigh Risk Newborn: Problems Related To Maturity Preterm Newbornwerismy daddyÎncă nu există evaluări