Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Eent Case: Diagnosis: Septic Shock, Pneumonia in Pre Immunocompromised Host, Oropharyngeal CA Stage IV
Încărcat de
Yram Yoj Zerauj0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
17 vizualizări7 paginiToungue cancer NCP
Titlu original
Eent Final NCP (1)
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentToungue cancer NCP
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
17 vizualizări7 paginiEent Case: Diagnosis: Septic Shock, Pneumonia in Pre Immunocompromised Host, Oropharyngeal CA Stage IV
Încărcat de
Yram Yoj ZeraujToungue cancer NCP
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 7
EENT CASE
Diagnosis: Septic Shock, Pneumonia in pre
immunocompromised host, Oropharyngeal CA stage IV
Submitted to: Submitted to:
Mr. Neil Ganchero, RN, MN Mr. Paul John Jalover, RN
MN210 instructor Mrs. Michelle Lynn Lee, RN
Nursing Rationale Nursing Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis Intervention
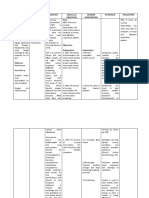
Ineffective airway Normally the lungs are 1. Placed in upright 1. An upright position Goal met.
clearance related to free from secretions. position ( if tolerated, provides for better
increased secretions Pneumonia bacteria are the head of the bed at lung expansion and After immediate
secondary to invading the lung 45 degree). Instruct improved air intervention, patient was
tracheostomy as evidence parenchyma thus, the patient to assist in exchange. Position able to breath normally
by excessive mucus producing inflammatory changing the position changes mobilize as manifested by
production and difficulty process. And these every 2 hours. secretions. decreased respiratory
of breathing. responses leading to rate from 30 breaths per
filling of the alveolar sacs 2. Instill 0.5cc PNSS into minute to 22 breaths per
2. This will help
with exudates leading to tracheostomy tube minute and patient O 2
stimulate coughing
Subjective: consolidation. The airway sat remained > 95%.
up of mucus and
is narrowed thus wheezes
add moisture to the
“ na budlayan c misis mag is being heard. Difficulty
mucucs
ginhawa ky kadamo sang of breathing in some
membranes.
iya plemas,” as verbalized cases.
by folk.
3. Suctioning is
3. Suctioned secretions
indicated when
as needed
patients are unable
Objective:
to remove
secretions from the
-RR: 30bpm
airway by coughing
-CR: 110bpm
because of
-O2 sat: 91%
weakness, thick
-BP: 170/90 mmhg
mucus plug, or
-restlessness
excessive or
-diaphoresis
tenacious mucus
-hypoxemia
production. It can
-hypoxia
also stimulate a
-pallor
cough.
-dyspnea
Nursing Rationale Nursing Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis Intervention
The patient will maintain 4. Instruct the patient to 4. These measures
clear, open airways, as deep breathe improve lung capacity
evidenced by normal adequately, to cough andgas exchange.
breath sounds, normal effectively. Coughing is the most
rate and depth of effective way to remove
respiration, and ability to most secretions.
cough up secretions.
5. Maintain humidified 5. Increasing the
oxygen as prescibed. humidity of inspired air
will reduce the viscosity
of secretions and
facilitate removal.
Nursing Rationale Nursing Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis Intervention
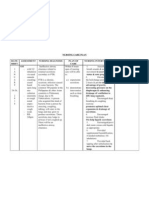
Impaired gas exchange Excess or deficit in 1. Placed in upright 1. An upright position Goal met.
related to collection of oxygenation and carbon position ( if tolerated, provides for better
mucus in airways as dioxide elimination at the the head of the bed at lung expansion and After immediate nursing
evidenced by difficulty in alveolar-capillary 45 degree). Instruct improved air intervention, the goal
breathing. membrane. the patient to assist in exchange. Position was met as evidenced by
changing the position changes moilize O2 sat of 95%, cardiac
every 2 hours. secretions. rate of 90bpm, BP of 130/
Objective: 80 mmhg, absence of
-respiratory rate: 30bpm 2. Monitor vital signs 2. To obtain baseline dysnea.
-cardiac rate: 120bpm including O2
-BP 170/90 mmhg saturation. 3. Bronchodilator +
mucolytics increases
-O2 sat of 90%
3. Nebulized as ordered patient’s secretion.
-capillary refill of 2-3
(ipratropium salbutamol
seconds
+ ambroxol 1cc) 4. Suctioning is indicated
-paleness of the skin
when patients are unable
-irritability
4. Suctioned secretions as to remove secretions
-dyspnea
needed from the airway by
coughing because of
weakness, thick mucus
plug, or excessive or
Client will maintain
tenacious mucus
optimal gas exchange as
production. It can also
evidenced by
stimulate a cough.
arterial blood gasses
(ABGs) within the client’s
5. Assess for changes in 5. Increased
normal range, oxygen
the level of restlessness, confusion
saturation of 90% or
consciousness. and/or irritability are
greater, alert response
early indicators of
mentation or no further
insufficient oxygenation
reduction in the level of
of the brain and require
consciousness, and
further interventions.
relaxed breathing.
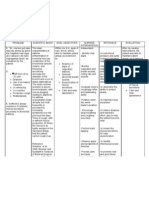
Nursing Rationale Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis
6. Assess for changes in the 6. Tachycardia is associated
client’s HR and temperature. with the increased work of
breathing or hypoxia. Fever
may develop in response to
retained secretions or
atelectasis.
7. Auscultate lung sounds, 7. Changes in lung sounds may
noting any areas of decreased reveal the cause of impaired
ventilation or the presence of gas exchange.
adventitious sounds.
8. Monitor arterial blood 8. Pulse oximetry is a useful
gasses and oxygen saturation. tool to detect early changes in
oxygen saturation. Oxygen
saturation should be kept at
90% or greater. Increasing
PaCo2 and decreasing PaO2are
signs of hypoxemia and
respiratory acidosis.
Nursing Rationale Nursing Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis Intervention
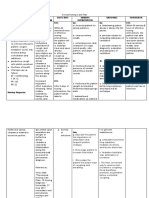
Active infection related to Infection is the invasion 1. Institute airways 1. Accumulation of Goal met.
surgical incision of of an organism’s body suctioning as needed. secretions provides a
tracheostomy as tissues by disease-causing medium for bacterial After 8 hours of nursing
evidenced by redness and agents, their growth. intervention, patient was
presence of purulent multiplication, and the free from signs of
discharges around the reaction of host tissues to 2. Provide tracheostomy 2. Good hygiene and infection as evidenced by
stoma site. the infectious agents and care prevention of temperature of 37.1 from
the toxins they produce. infection 38.1 and absence of
redness around the
3. Assess skin integrity 3. This is a common site stoma site.
Objective: under the tracheal for infection and skin
-Temperature 38.1 ties. breakdown.
-Swelling at stoma site
-Redness at stoma site 4. Observe the stoma for 4. Observe the stoma for
-Skin warm to touch erythema, color, erythema, color,
exudates, and exudates, and
crusting lesions. If crusting lesions. If
present, culture the present, culture the
stoma and notify the stoma and notify the
physician. physician.
Patients remains free of 5. Observe the patient’s 5. Increased amounts of
infection, as evidenced by secretions for color, sputum and colored
normal body consistency, quantity, or odorous secretions
temperature, normal and odor. may indicate
white blood cell count, infection.
negative cultures, normal 6. Monitor sputum
vital signs. cultures and 6. Identification of the
sensitivities. infecting
microorganism is
important to
determine antibiotic
coverage.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- THE WATER AND THE BREATH: A guide to using water and breathing towards a stress free and successful lifeDe la EverandTHE WATER AND THE BREATH: A guide to using water and breathing towards a stress free and successful lifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For PneumoniaDocument3 paginiNCP For PneumoniaLeogalvez BedanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SXV RXV ChassisDocument239 paginiSXV RXV Chassischili_s16Încă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 paginiIneffective Breathing PatternEna Katherine CanonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument13 paginiNCP-Ineffective Airway ClearancePaulo Manlangit86% (22)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 paginiNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceNicholas TagleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma NCPDocument3 paginiAsthma NCPjaijai magbanuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economizer DesignDocument2 paginiEconomizer Designandremalta09100% (4)
- LYNX 40 Drilling Mud DecanterDocument2 paginiLYNX 40 Drilling Mud DecanterPierluigi Ciampiconi0% (1)
- NCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyDocument3 paginiNCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyAngie MandeoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Surgical Therapy 13th EditionDocument61 paginiCurrent Surgical Therapy 13th Editiongreg.vasquez490100% (41)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis GOALS and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GoalDocument4 paginiCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis GOALS and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GoalMonica Angelique SalayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Cap MRDocument2 paginiNCP Cap MREngely Mercader100% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument4 paginiImpaired Gas Exchange NCPkimglaidyl bontuyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument8 paginiNursing Care Planalexander abasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 paginiNursing Care Planjnx_anonymousÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis On Retail Management of The Brand 'Sleepwell'Document62 paginiThesis On Retail Management of The Brand 'Sleepwell'Sajid Lodha100% (1)
- NCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyDocument4 paginiNCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathySapna thakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Marilou.... SanitariumDocument9 paginiNCP Marilou.... SanitariumJerry AbleÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP of PnuemoniaDocument13 paginiNCP of PnuemoniaFrando kenneth100% (1)
- Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument8 paginiCamarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationEdelweiss Marie CayetanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 paginiAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationMel Izhra N. MargateÎncă nu există evaluări
- CopdDocument6 paginiCopdapi-3717941100% (2)
- NCPDocument7 paginiNCPRuth MontebonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPLP Benoza100% (2)
- Sample NURSING CARE PLANDocument2 paginiSample NURSING CARE PLANRonzie EstrellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument13 paginiNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Independentyanny03Încă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument3 paginiNCPNikki del Rosario100% (2)
- Asthma AssessmentDocument1 paginăAsthma AssessmentnarstinesirkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 paginiAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Explanation of The Problem Objective Nursing Intervention Rational EvaluationDocument4 paginiExplanation of The Problem Objective Nursing Intervention Rational EvaluationmeteabÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Difficulties in BreathingDocument4 paginiNCP Difficulties in BreathingKingJayson Pacman06Încă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 paginăNursing Care PlanJimmy Andrew YoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument7 paginiAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentSHEILA MAE SACLOTÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP FinalDocument16 paginiNCP FinalEuleen Tria PadrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baiae NCPDocument1 paginăBaiae NCPreignyfayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance (Mary Ann Solomon)Document6 paginiNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance (Mary Ann Solomon)Karissa GuerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuberculosis Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance PDFDocument2 paginiTuberculosis Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance PDFPratiksha AmbedkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Intervention Diagnose 1 Purpose and Criteria Results Intervention Rational NIC Labels Respiratory MonitoringDocument10 paginiNursing Intervention Diagnose 1 Purpose and Criteria Results Intervention Rational NIC Labels Respiratory MonitoringFhicholy Davied VanrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Task NCPDocument12 paginiTask NCPferdy ilhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 paginiNCP - Ineffective Breathing PatternPRINCESS KOBAYASHIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 paginiNursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationGuile RilleraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Requirement in NCP 312 (Medical and Surgical Nursing) : Submitted By: Cadalin, Fremelen Rose CDocument4 paginiRequirement in NCP 312 (Medical and Surgical Nursing) : Submitted By: Cadalin, Fremelen Rose CFremelen Rose CadalinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 paginiCues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationNichol John MalabananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 paginiAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKen IgnacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Ineffective AirwayDocument1 paginăNCP Ineffective AirwayRainier IbarretaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 paginiIneffective Airway ClearanceKarl Angelo MontanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 paginăIneffective Airway ClearancejomerdalonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP FormatDocument8 paginiNCP FormatMack Javier VenturaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP FormatDocument8 paginiNCP FormatCyril JavierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cues Diagnosi S Desired Outcome Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 paginiCues Diagnosi S Desired Outcome Interventions Rationale EvaluationYamete KudasaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP.2F 2B 1Document5 paginiNCP.2F 2B 1JustineÎncă nu există evaluări
- D. Nursing Care Plan: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Supply As Evidenced by Difficulty in BreathingDocument2 paginiD. Nursing Care Plan: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Supply As Evidenced by Difficulty in BreathingReinette LastrillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CoughDocument4 paginiCoughdelavegajealou00Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP AsthmaDocument8 paginiNCP Asthmaqweyo yhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Careplan 1Document11 paginiCareplan 1ligaba1559Încă nu există evaluări
- CareplanDocument14 paginiCareplanligaba1559Încă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBDocument2 paginiIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Requirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaDocument7 paginiRequirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaChloie Marie RosalejosÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For BronchitisDocument2 paginiNCP For BronchitisJefherrson Nericua Jemilo50% (2)
- NCP (Ineffective Airway)Document2 paginiNCP (Ineffective Airway)Angeline CasabuenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student NurseDocument2 paginiStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.Încă nu există evaluări
- GoldDocument1 paginăGoldCallie ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Snoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandSnoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yarn HairinessDocument9 paginiYarn HairinessGhandi AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- DevOps Reference CardDocument2 paginiDevOps Reference CardIntizarchauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- C++ Program To Create A Student Database - My Computer ScienceDocument10 paginiC++ Program To Create A Student Database - My Computer ScienceSareeya ShreÎncă nu există evaluări
- MiddleWare Technology - Lab Manual JWFILESDocument171 paginiMiddleWare Technology - Lab Manual JWFILESSangeetha BajanthriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lifting PermanentmagnetDocument6 paginiLifting PermanentmagnetShekh Muhsen Uddin Ahmed100% (1)
- Process Description of Function For Every Unit OperationDocument3 paginiProcess Description of Function For Every Unit OperationMauliduni M. AuniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attachment 1 Fiber Data SheetDocument2 paginiAttachment 1 Fiber Data SheetflavioovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Designing An Active Directory InfrastructureDocument18 paginiIntroduction To Designing An Active Directory InfrastructurepablodoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anviz T5 RFID ManualDocument52 paginiAnviz T5 RFID ManualLuis Felipe Olaya SandovalÎncă nu există evaluări
- USDA List of Active Licensees and RegistrantsDocument972 paginiUSDA List of Active Licensees and Registrantswamu885Încă nu există evaluări
- Roland Fantom s88Document51 paginiRoland Fantom s88harryoliff2672100% (1)
- Rab Sikda Optima 2016Document20 paginiRab Sikda Optima 2016Julius Chatry UniwalyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physico-Chemical Properties of Nutmeg (Myristica Fragrans Houtt) of North Sulawesi NutmegDocument9 paginiPhysico-Chemical Properties of Nutmeg (Myristica Fragrans Houtt) of North Sulawesi NutmegZyuha AiniiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2Document7 paginiModule 2karthik karti100% (1)
- Caso Estudio: Reliability Analysis of Power Distribution System. A Case StudyDocument6 paginiCaso Estudio: Reliability Analysis of Power Distribution System. A Case StudyCarlos HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles To Action (Short)Document6 paginiPrinciples To Action (Short)nsadie34276Încă nu există evaluări
- Channel & Lomolino 2000 Ranges and ExtinctionDocument3 paginiChannel & Lomolino 2000 Ranges and ExtinctionKellyta RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- HPCL CSR Social Audit ReportDocument56 paginiHPCL CSR Social Audit Reportllr_ka_happaÎncă nu există evaluări
- XU-CSG Cabinet Minutes of Meeting - April 4Document5 paginiXU-CSG Cabinet Minutes of Meeting - April 4Harold John LaborteÎncă nu există evaluări
- RESEARCH 10 Module 1 Lesson 1 (WEEK 1-2)Document5 paginiRESEARCH 10 Module 1 Lesson 1 (WEEK 1-2)DennisÎncă nu există evaluări
- San Mateo Daily Journal 01-28-19 EditionDocument28 paginiSan Mateo Daily Journal 01-28-19 EditionSan Mateo Daily JournalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assembly InstructionsDocument4 paginiAssembly InstructionsAghzuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- IbmautomtiveDocument38 paginiIbmautomtiveMeltz NjorogeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integrator Windup and How To Avoid ItDocument6 paginiIntegrator Windup and How To Avoid ItHermogensÎncă nu există evaluări
- Remedy MidTier Guide 7-5Document170 paginiRemedy MidTier Guide 7-5martin_wiedmeyerÎncă nu există evaluări