Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
A Demo La Presentation
Încărcat de
Olusola Ademola Adesina0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
19 vizualizări11 paginiDrepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
19 vizualizări11 paginiA Demo La Presentation
Încărcat de
Olusola Ademola AdesinaDrepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 11
Low-Power Consumption for Mobile Healthcare
Monitoring
By
Abidoye Ademola Philip
(Student No: 3008758)
Supervised by: Prof. Henry O. Nyongesa
Tuesday, December 07, 2021 1
Introduction
• A wireless sensor network (WSN) consists of spatially distributed
autonomous sensors to cooperatively monitor physical or
environmental conditions [1]. It is becoming a significant enabling
technology for a wide variety of applications such as:
health monitoring
emergency response
Security
industrial automation
environment and agriculture applications
automotive and aeronautic applications
building automation
military applications e.t.c
Tuesday, December 07, 2021
Introduction conts.
Health monitoring
Wireless sensor networks can greatly be used in healthcare area to
monitor and track conditions of patients [2].
They can be used in conjunction with other wireless devices to collect
patients’ vital signs such as:
blood pressure
heartbeat rate
body temperature,
blood oxygen saturation
blood sugar level e.t.c
Tuesday, December 07, 2021 3
Why Using Wireless Sensors in Healthcare?
they eliminate medical errors by continuously collect more
accurate and objective information from patients for diagnosis.
they reduce workload and increase the efficiency of hospital
staff.
they improve the comfort of patients.
they allow remote monitoring of patients, freeing hospital
resources and home care staff.
Tuesday, December 07, 2021 4
Constraints of Bio-Sensor Wireless Networks
Despite the usefulness and many applications of wireless
sensor networks in healthcare, they have the following
constraints:
High energy consumption
Security Problem
Limited computational power.
Among the wireless sensor networks constraints energy
consumption is one of the main problem.
Tuesday, December 07, 2021 5
Rationale
Wireless Sensor Networks can be deployed in remote or
difficultly accessible areas. As a result, they often cannot rely on
the power grid for their energy source, and recharging/changing
the batteries at all time may affect the performance of the
sensors [3][4].
In order to reach lifetimes of several months or years, WSNs not
only use energy-efficient micro-controllers and radios (hardware
implementation), but also implement power-efficient schemes at
the Medium-Access layer.
Tuesday, December 07, 2021 6
Objectives
• To analyze the energy dissipation characteristics of wireless
sensor nodes.
• To simulate energy consumption at each node of the wireless
sensor networks.
• To encrypt the data transmitted between the devices using
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
Tuesday, December 07, 2021 7
Methodology
• The following devices will be used to carry out the
research:
Wearable Body Sensor Network (WBSN)
Mobile Phone (GPRS Enable) i.e Sony Ericsson or
Nokia E75
• Medical Server called “An Intelligent Database Health
Management System (IDHMS)”.
• Low-Energy Adaptive Clustering Hierarchy (LEACH) approach
will be used to minimize energy consumption at the sensor
nodes.
Tuesday, December 07, 2021 8
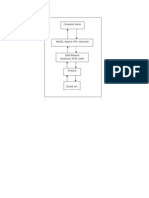
System Architecture
GPRS
Medical Server
ZigBee
Mobile Phone
Sensors
Medical doctor
Tuesday, December 07, 2021 9
Intra-BAN Communications
• ZigBee is used for intra-BAN communication
because of the following reasons:
It
allows higher data rate of about 250Kbits/s at frequency
2.4GHz.
It is available worldwide (unlicensed frequency).
Tuesday, December 07, 2021 10
References
[1] I. F. Akyildiz, SuWeilian, Y. Sankarasubramaniam, and E. Cayirci, “A
survey on sensor networks”, IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 40,
no. 8, pp. 102 – 114, August 2002.
[2] M. Perillo andW. Heinzelman, “ASP: An adaptive energy-efficient
polling algorithm for Bluetooth piconets,” in Proceedings of the
Hawaiian International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS), 2003.
[3] W. Heinzelman, A. Chandrakasan, H. Balakrishnan, „Energy-efficient
communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks“,
Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on System Sciences
(HICSS '00), January 2000.
[4] J. Y. Khan and M. R. Yuce, “ Performance Evaluation of a Wireless
Body Area Sensor Network for Remote Patient Monitoring,” in the
conference of the IEEE Engineering in
Medicine and Biology Society (IEEE EMBC08), (August 2008).
11
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Way of The Samurai, Shadowrun BookDocument19 paginiThe Way of The Samurai, Shadowrun BookBraedon Montgomery100% (8)
- Opening The Third EyeDocument13 paginiOpening The Third EyekakamacgregorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legends & Lairs - Giant LoreDocument66 paginiLegends & Lairs - Giant LoreGary DowellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 - Shear and Diagonal Tension On Beams PDFDocument55 paginiChapter 5 - Shear and Diagonal Tension On Beams PDFJhe Taguines100% (1)
- Wireless Sensor Network NotesDocument158 paginiWireless Sensor Network NotesPradeep Prakash Samal100% (2)
- Takeover Strategies and DefencesDocument20 paginiTakeover Strategies and DefencesJithu JoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sip TrunkDocument288 paginiSip TrunkSayaOtanashiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Survivable and Scalable Wireless Solution For E-Health and E-Emergency ApplicationsDocument5 paginiSurvivable and Scalable Wireless Solution For E-Health and E-Emergency ApplicationskeerthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Plan Proposal: The Iis University, JaipurDocument17 paginiResearch Plan Proposal: The Iis University, JaipurchanduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developing Residential Wireless Sensor Networks For ECG Healthcare MonitoringDocument8 paginiDeveloping Residential Wireless Sensor Networks For ECG Healthcare MonitoringSyedah MaryamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Privacy Protection For Wireless Medical Sensor DataDocument14 paginiPrivacy Protection For Wireless Medical Sensor DataSiddharth RamrakhianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZigBee Based Data Collection in Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument13 paginiZigBee Based Data Collection in Wireless Sensor NetworksIJICT JournalÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Context-Aware Data Fusion Approach For Health-IoTDocument5 paginiA Context-Aware Data Fusion Approach For Health-IoTAlain Gómez CabreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pulse Oximeter WirelessDocument6 paginiPulse Oximeter WirelessJeanCarlos Chavarría HughesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimal Operating Performance of Wireless Protocols For Intelligent Sensors ApplicationsDocument11 paginiOptimal Operating Performance of Wireless Protocols For Intelligent Sensors ApplicationsSaad ChakkorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensors: An Efficient and Secure Revocation-Enabled Attribute-Based Access Control For Ehealth in Smart SocietyDocument23 paginiSensors: An Efficient and Secure Revocation-Enabled Attribute-Based Access Control For Ehealth in Smart SocietyshahzadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelling An Energy-Efficient Zigbee (Ieee 802.15.4) Body Area Network in Iot-Based Smart HomesDocument5 paginiModelling An Energy-Efficient Zigbee (Ieee 802.15.4) Body Area Network in Iot-Based Smart HomesCindy CynthiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2010-Wireless Sensor Network Based E-Health SystemDocument8 pagini2010-Wireless Sensor Network Based E-Health Systemsm2nictÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neonatal Management SystemDocument17 paginiNeonatal Management SystemShashi PÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biometric Behavior Authentication Exploiting Propagation Characteristics of Wireless ChannelDocument8 paginiBiometric Behavior Authentication Exploiting Propagation Characteristics of Wireless ChannelFizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smart Patient Monitoring System Using WSN & AndroidDocument6 paginiSmart Patient Monitoring System Using WSN & AndroidEditor IJRITCC0% (1)
- IJEACS Paper4 - CorrectionsDocument8 paginiIJEACS Paper4 - CorrectionsDaniel OmolewaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Healthcare Iot M-Greencardio Remote Cardiac Monitoring System - Concept, Theory of Operation and ImplementationDocument8 paginiHealthcare Iot M-Greencardio Remote Cardiac Monitoring System - Concept, Theory of Operation and ImplementationUriHaimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trust Key Management Scheme For Wireless Body Area NetworksDocument9 paginiTrust Key Management Scheme For Wireless Body Area NetworksGeneration GenerationÎncă nu există evaluări
- RM Assignment1 - DDocument4 paginiRM Assignment1 - DImtiaz HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Said, 2021Document25 paginiSaid, 2021Faisal AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report 1123Document46 paginiReport 1123RakshithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Survey On Medical Remote Monitoring of Multiple Physiological Parameters Based On Wireless Embedded InternetDocument7 paginiA Survey On Medical Remote Monitoring of Multiple Physiological Parameters Based On Wireless Embedded InternetIJRASETPublicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 1145@2818869 2818889 PDFDocument6 pagini10 1145@2818869 2818889 PDFDjamel JamelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Katzis IMCTH 5G Totally Connected Healthcare TVWS FinalDocument5 paginiKatzis IMCTH 5G Totally Connected Healthcare TVWS FinalAdetunji TimileyinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSC 472E Cat Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument12 paginiCSC 472E Cat Wireless Sensor NetworksEzra KenyanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN) : A Survey On Architecture, Technologies, Energy Consumption, and Security ChallengesDocument34 paginiWireless Body Area Network (WBAN) : A Survey On Architecture, Technologies, Energy Consumption, and Security ChallengesNischal KataraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar ReportDocument34 paginiSeminar ReportAswanth GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Challa Et - AlDocument21 paginiChalla Et - AlAkash PoudelÎncă nu există evaluări
- WSN Based Smart Sensors and Actuator For Power Management in Intelligent BuildingsDocument8 paginiWSN Based Smart Sensors and Actuator For Power Management in Intelligent BuildingsnhatvpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Continuous Health-Monitoring For Early Detection of Patient by Web Telemedicine SystemDocument8 paginiContinuous Health-Monitoring For Early Detection of Patient by Web Telemedicine SystemAmali JayawardhanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- .A Survey On WSN For Environment Monitoring by Using LC and LP SensorsDocument5 pagini.A Survey On WSN For Environment Monitoring by Using LC and LP SensorsNigussie JaletaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wireless Sensor Networks - Future of Wireless ApplicationsDocument11 paginiWireless Sensor Networks - Future of Wireless ApplicationssingaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multi-Stage Real Time Health Monitoring Via Zigbee in Smart HomesDocument7 paginiMulti-Stage Real Time Health Monitoring Via Zigbee in Smart HomesPhoyagerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bluetooth Based Wireless Sensor Networks - Implementation Issues and SolutionsDocument7 paginiBluetooth Based Wireless Sensor Networks - Implementation Issues and SolutionsSai Divya GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ijettcs 2013 06 22 115Document5 paginiIjettcs 2013 06 22 115International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3114 PHTDocument13 pagini3114 PHTA.Mohammad idhrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Simple Internship Pptsor - NetworksDocument10 paginiEngineering Simple Internship Pptsor - Networksshahriarhabib12Încă nu există evaluări
- Body Area NetworksDocument10 paginiBody Area NetworksUjwala GangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MWC WordDocument5 paginiMWC WordRajni ShelkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Balid 2016Document6 paginiBalid 2016Rock Feller Singh RussellsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elsevier-ABE - Health CareDocument11 paginiElsevier-ABE - Health CareDr. V. Padmavathi Associate ProfessorÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECG Monitoring System Using Wireless Sensor Networ PDFDocument9 paginiECG Monitoring System Using Wireless Sensor Networ PDFAhmed MsfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Challenges and Approches For WSNDocument23 paginiChallenges and Approches For WSNNisumba SoodhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- PAPER - 2 (Compat Multiband Wireless Energy Harvesting)Document8 paginiPAPER - 2 (Compat Multiband Wireless Energy Harvesting)Adarsh SrivatsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Optimization Algorithms in Wireless Body ArDocument19 paginiReview Optimization Algorithms in Wireless Body Arumamahesh nitrklÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zigbee Home AutomationDocument5 paginiZigbee Home AutomationsumitsalviÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Proposed Healthcare Architecture Using Cloud Computing in WSN Environment With A Case StudyDocument9 paginiA Proposed Healthcare Architecture Using Cloud Computing in WSN Environment With A Case StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Area NetworkDocument10 paginiBody Area NetworkPrincess KokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- BharathDocument24 paginiBharathGeethaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WSN Unit 1Document22 paginiWSN Unit 1Gaurav bansodeÎncă nu există evaluări
- R - Implantable Antennas For Bio-Medical ApplicationsDocument13 paginiR - Implantable Antennas For Bio-Medical ApplicationsJAYESH HARLALKAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Android Based Home Automation and Energy ConservationDocument19 paginiAndroid Based Home Automation and Energy ConservationPrototype GenX 1478Încă nu există evaluări
- E-Health Applications Over 5G Networks: Challenges and State of The ArtDocument8 paginiE-Health Applications Over 5G Networks: Challenges and State of The ArtAnant SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- With Cover Page v2Document11 paginiWith Cover Page v2Cường Dương QuốcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wireless Sensor Networks: Security, Attacks and ChallengesDocument13 paginiWireless Sensor Networks: Security, Attacks and ChallengesPradip KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wireless Sensor Network Using Zigbee: Nidhi Patel, Hiren Kathiriya, Arjav BavarvaDocument5 paginiWireless Sensor Network Using Zigbee: Nidhi Patel, Hiren Kathiriya, Arjav BavarvaDavidleonardo GalindoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis and Comparative Study of Data Communication Protocols in Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument4 paginiAnalysis and Comparative Study of Data Communication Protocols in Wireless Sensor NetworksMuh MuhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementation of Wireless Sensor Network For Medical ApplicationsDocument11 paginiImplementation of Wireless Sensor Network For Medical ApplicationsFanta StyleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Co-operative and Energy Efficient Body Area and Wireless Sensor Networks for Healthcare ApplicationsDe la EverandCo-operative and Energy Efficient Body Area and Wireless Sensor Networks for Healthcare ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Fuzzy String-Matching Model For Information Retrieval Based On Incongruous User QueriesDocument6 paginiDynamic Fuzzy String-Matching Model For Information Retrieval Based On Incongruous User QueriesOlusola Ademola AdesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Text Staganography A Novel ApproachDocument8 paginiText Staganography A Novel ApproachOlusola Ademola AdesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steganography Is It Becoming A Double-Edged Sword in Computer SecurityDocument17 paginiSteganography Is It Becoming A Double-Edged Sword in Computer SecurityOlusola Ademola AdesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Survey Report - State of The Art in Digital Steganography Focusing Ascii Texts DocumentDocument10 paginiSurvey Report - State of The Art in Digital Steganography Focusing Ascii Texts DocumentOlusola Ademola AdesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Using Clouds CapeDocument8 paginiUsing Clouds CapeOlusola Ademola AdesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Security and Privacy Issues With Health Care Information TechnologyDocument6 paginiSecurity and Privacy Issues With Health Care Information TechnologyOlusola Ademola AdesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2004 01 21 Presentation SteganographyDocument34 pagini2004 01 21 Presentation Steganographyym84545ymÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pronunciation Modeling in Spelling CorrectionDocument6 paginiPronunciation Modeling in Spelling CorrectionOlusola Ademola AdesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- J2ME StepbystepDocument36 paginiJ2ME Stepbystepsrinivasvadde100% (11)
- Ipoletse Call Centre Manual 28 2 VersionDocument47 paginiIpoletse Call Centre Manual 28 2 VersionOlusola Ademola AdesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Profile of Prospective Supervisor FormDocument3 paginiProfile of Prospective Supervisor FormOlusola Ademola AdesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interface Interaction Design For Illiterate and Semi-Illiterate MobileDocument26 paginiInterface Interaction Design For Illiterate and Semi-Illiterate MobileOlusola Ademola AdesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intercepting GSM 2008-09-14Document9 paginiIntercepting GSM 2008-09-14Olusola Ademola AdesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Improving Letter-To-Pronunciation Accuracy With AutomaticDocument4 paginiImproving Letter-To-Pronunciation Accuracy With AutomaticOlusola Ademola AdesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Java Steganography ToolDocument6 paginiA Java Steganography ToolOlusola Ademola AdesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Call Analysis With Classification Using Speech and Non-SpeechDocument4 paginiCall Analysis With Classification Using Speech and Non-SpeechOlusola Ademola AdesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ArchitectureDocument1 paginăArchitectureOlusola Ademola AdesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- English 7 q3 Week2 Daily Lesson LogDocument5 paginiEnglish 7 q3 Week2 Daily Lesson LogKILVEN MASIONÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anin, Cris Adrian U. Experiment Water Flirtation ELECTIVE 103Document2 paginiAnin, Cris Adrian U. Experiment Water Flirtation ELECTIVE 103Cris Adrian Umadac AninÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 9Document1 paginăGroup 9Kyla Jane GabicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preprints201808 0216 v1Document15 paginiPreprints201808 0216 v1Baptista Jaime MilioneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Training ReportDocument19 paginiIndustrial Training ReportKapil Prajapati33% (3)
- Cs09 404 Programming Paradigm (Module 1 Notes)Document24 paginiCs09 404 Programming Paradigm (Module 1 Notes)Rohith BhaskaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atmosphere Study Guide 2013Document4 paginiAtmosphere Study Guide 2013api-205313794Încă nu există evaluări
- BERKLYNInformation SheetDocument6 paginiBERKLYNInformation SheetvillatoreubenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Updated PDPDocument540 paginiUpdated PDPnikulaaaasÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP IAG Admin GuideDocument182 paginiSAP IAG Admin GuidegadesigerÎncă nu există evaluări
- APPSC GR I Initial Key Paper IIDocument52 paginiAPPSC GR I Initial Key Paper IIdarimaduguÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zoomlion Gulf FZE Introduction: 1.1 ME Service Support 1.2 Construction CasesDocument13 paginiZoomlion Gulf FZE Introduction: 1.1 ME Service Support 1.2 Construction CasesArk TradingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20131022-Additive Manufacturing & Allied Technologies, PuneDocument56 pagini20131022-Additive Manufacturing & Allied Technologies, Puneprakush_prakushÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAKUTDocument50 paginiCAKUTsantosh subediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotic I and II HWDocument4 paginiAntibiotic I and II HWAsma AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Repro Indo China Conf PDFDocument16 paginiRepro Indo China Conf PDFPavit KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSC 200Document18 paginiMSC 200Amit KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Methods of Data Collection MSC N I YrDocument256 paginiMethods of Data Collection MSC N I Yrdr.anu RkÎncă nu există evaluări
- W1 - V1 MultipleWorksheets SolnDocument3 paginiW1 - V1 MultipleWorksheets SolnAKHIL RAJ SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psi Engines Product Sheet PDFDocument2 paginiPsi Engines Product Sheet PDFDaniel DelgadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grounding & Bonding - The Foundation For Effective Electrical Protection PDFDocument76 paginiGrounding & Bonding - The Foundation For Effective Electrical Protection PDFFabian Nina Aguirre100% (1)
- Biology Concepts and Applications 9th Edition Starr Solutions ManualDocument9 paginiBiology Concepts and Applications 9th Edition Starr Solutions Manualscarletwilliamnfz100% (31)
- SITXWHS001 - Participate in Safe Work Practices Student GuideDocument42 paginiSITXWHS001 - Participate in Safe Work Practices Student GuideMarianne FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asin URL Index URL/keyword DomainDocument30 paginiAsin URL Index URL/keyword DomainStart AmazonÎncă nu există evaluări