Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Dystocia: Second Part: Abnormalities of Birth Canal
Încărcat de
fatihahannisahumaira0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
13 vizualizări21 paginipdf
Titlu original
3062 Dystocia
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentpdf
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
13 vizualizări21 paginiDystocia: Second Part: Abnormalities of Birth Canal
Încărcat de
fatihahannisahumairapdf
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 21
Dystocia
Second part: abnormalities of birth
canal
Pelvic contraction
• Birth canal
– bony canal
– soft canal
• abnormal bony canal: pelvic contraction
– any contraction of the pelvic diameters that dimini
shes the capacity of the pelvis can creat dystocia d
uring labor
Classification
I. Contraction of the pelvic inlet
II. contraction of the midpelvis and pelvic outle
t
III. general contraction of the pelvis
IV. pelvic deformities
I. Contracted pelvic inlet
• Anteroposterior d<10cm
• diagonal conjugate d<11.5cm
• external conjugate d<18cm
– simple flat pelvis
– rickets flat pelvis
II. contraction of the midpelvis and p
elvic outlet
contraction of the midpelvis
– Midpelvis: from inferior margin of the symphysis p
ubis through the ischial spines,touches the sacrum
near the junction of the 4th and 5th vertebrae
– contraction: interischial spinous diameter is smalle
r than 8cm(spines are prominent, the pelvic side
walls converge or the sacrosciatic notch is narrow)
Contracted pelvic outlet
Contracted pelvic outlet
– Defination: diminition of the interischial tuberous
diameter to 8cm or less.
– 2 triangles:
• baseof both: interischial tuberous diameter
• anterior triangle
• posterior triangle
III. General contraction of the pelvi
s
•2cm or more shorter than normal
IV. Pelvic deformities
•osteomalacic pelvis
•obliquely contracted pelvis
Effects on mather and fetus
• MOTHER:Inlet
– Malpresentation and malposition
– prolonged labor
– insufficient uterine contraction
• midpelvis and outlet
– persistant occipitotransverse or occipitoposterior p
osition
– fistula formation
– intrapartum infection
– threatening rupture or rupture
fetus
• PROM
• Prolapse
• Distress (HI,IVH)
• Death
• Injury
• Infecion
Soft birth canal
• Lower segment of uterus
• cervix
• vaginal
Fetal malposition
• Occipitoanterior position 90%
• malposition 10%
• abnormal cephalic posion 6-7%
• breech presentation 3-4%
• others
Persistant occipitoposterior (transvers
e) position
• Causes
– abnormal pelvis:transverse narrowing of the midp
elvis
– flexion not well
– hypotonic uterine dysfunction
Breech presentation
• Incidence
– breech presentation is common remote from term.
– 3-4% of singleton deliveries
• Position
– LSA, LST LSP. RSA, RST, RAP
Causes
• Uterine relaxation
• limited uterine cavity
• fetal head obstructed
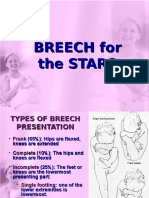
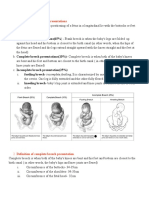
classification
• Frank breech p
– the lower extremities are flexed at the hips and extende
d at the knees, and thus the feet lie in close proximity to
the head.
– It appears most commonly
• complete breech p
– differs in that one or both knees are flexed.
• Incomplete breech p
– one or both hips are not flexed and one or both feet or k
nees lie below the breech, that is, a foot or knee is lower
most in the birth canal.
Incomplete breech presentation
Effects
• Maternal
– greater frequency of operative delivery
– higher maternal morbidity and slightly higher mor
tality
– PROM
– secondary hypotonic uterine dysfunction
– puerperium infection
– postpartum haemorrhage
– laceration of cervix
Effects
• Fetus
– PROM
– cord prolapse
– fetal distress even death
– newborn asphyxia
– brachial plexus injury
– IVH
Face presentation
Compound presentation
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- CPD and Contracted PelvisDocument55 paginiCPD and Contracted PelvisShaells JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ContractedDocument15 paginiContractedswapnil3250Încă nu există evaluări
- CPD and Contracted PelvisDocument53 paginiCPD and Contracted Pelvismaxim tomuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normal and Abnormal Present IonDocument31 paginiNormal and Abnormal Present IondeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cephalo Pelvic DisproportionDocument43 paginiCephalo Pelvic DisproportionPabhat KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Cephalo-Pelvic Disproportion & Contracted PelvisDocument38 paginiUnderstanding Cephalo-Pelvic Disproportion & Contracted PelvisAltynaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pregnancy and Labor at Fetal Malpresentations and Abnormal PelvisDocument40 paginiPregnancy and Labor at Fetal Malpresentations and Abnormal PelvisCoral Srinivasa Ramalu100% (1)
- BreechDocument50 paginiBreechEldrinAbquinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abnormal Labour: Risks and Treatments for MalpositionsDocument92 paginiAbnormal Labour: Risks and Treatments for Malpositionsmohammed farajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obstructed LaborDocument43 paginiObstructed LaborNyangara Rajabu0% (2)
- OppDocument41 paginiOppKiprotich Titus NgetichÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 6 Breach Presentation Transversal Oblique LieDocument51 paginiLecture 6 Breach Presentation Transversal Oblique Lietanmai nooluÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Bony Pelvis and Fetal Skull Measurements for ChildbirthDocument26 paginiThe Bony Pelvis and Fetal Skull Measurements for ChildbirthVictor-Gabriel RuginaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5th Yr Gynec ExamDocument151 pagini5th Yr Gynec ExamHIMANSHU GUPTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPDDocument45 paginiCPDVijith.V.kumar100% (1)
- O&G CompendiumDocument676 paginiO&G Compendiumwalefamous100% (1)
- Cephalopelvic Disproportion and Obstructed LabourDocument40 paginiCephalopelvic Disproportion and Obstructed Labournighat khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Modified Obsgyn Orals-1Document129 paginiFinal Modified Obsgyn Orals-1Ahmed Adel HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- I group of questions 1Document31 paginiI group of questions 1siwap34656Încă nu există evaluări
- Abnormal Labor. BBBB WWPPTXDocument53 paginiAbnormal Labor. BBBB WWPPTXHamss Ahmed100% (2)
- 1 Bony PelvisDocument50 pagini1 Bony PelvisNicole NgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malpresentaton and Breech PresentationDocument32 paginiMalpresentaton and Breech PresentationMuhammad ArshadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obstructed LaborDocument41 paginiObstructed LaborHenok Y KebedeÎncă nu există evaluări
- O&G - Abnormal PresentationDocument32 paginiO&G - Abnormal PresentationAnironOrionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abnormal Labor Positions ExplainedDocument7 paginiAbnormal Labor Positions ExplainedNishaThakuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breech DeliverlyDocument30 paginiBreech DeliverlyHomeground entertainmentÎncă nu există evaluări
- ObsNGyn - Labor AtfDocument39 paginiObsNGyn - Labor AtfarongeremewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malpresentation and MalpositionDocument33 paginiMalpresentation and MalpositionPeprah Ondiba100% (1)
- Bony Pelvis & Fetal SkullDocument130 paginiBony Pelvis & Fetal SkullSalman KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dystocia: DR - Selvaraj, Chinnasamy M.DDocument54 paginiDystocia: DR - Selvaraj, Chinnasamy M.DSelvaraj ChinnasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abnormal Fetus Presentations: D.R Thomas MutanikwaDocument40 paginiAbnormal Fetus Presentations: D.R Thomas Mutanikwaguidance100% (1)
- Breech PresentationDocument57 paginiBreech PresentationShailendra Yadav100% (2)
- Managing Prolonged LaborDocument35 paginiManaging Prolonged Laborteresia trisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abnormal Larour 3Document135 paginiAbnormal Larour 3Eyob MizanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 - DystociaDocument43 pagini5 - DystociaMara Medina - BorleoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normal Abnormal LabourDocument63 paginiNormal Abnormal LabourFelicianna Ashwinie StanleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2anatomy of The Inguinal RegionDocument47 pagini2anatomy of The Inguinal Regionthowell3Încă nu există evaluări
- Obstetrical Nursing LaborDocument12 paginiObstetrical Nursing LaborJhen BasinilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prolonged & Obstructed Labor Rupture UterusDocument30 paginiProlonged & Obstructed Labor Rupture UterusIndri Heni DamanikÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Problems With The Passenger and Powers of LaborDocument105 pagini3 Problems With The Passenger and Powers of LaborRaquel M. MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cephalopelvic Disproportion, Obstructed Lab Our, UterineDocument49 paginiCephalopelvic Disproportion, Obstructed Lab Our, UterineKerod AbebeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanism of Normal Labor and PartographDocument50 paginiMechanism of Normal Labor and PartographpatsilwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gynecology Tickets All 1Document34 paginiGynecology Tickets All 1moamen.nlÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018my Zamala BreechmalpresentationDocument72 pagini2018my Zamala BreechmalpresentationSaeed HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Dystocia Lect I Final 2019Document159 pagini1 Dystocia Lect I Final 2019marielleaudreeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- BreechDocument44 paginiBreechnohazz0% (1)
- Understanding Key Terms in Normal Pregnancy, Labor and DeliveryDocument270 paginiUnderstanding Key Terms in Normal Pregnancy, Labor and DeliveryCedrick Mesa Sali-otÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abnormal Fetal Positions and Presentations ExplainedDocument14 paginiAbnormal Fetal Positions and Presentations ExplainedAsteway MesfinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic - 5Document96 paginiTopic - 5Sub 7 Grp 3Încă nu există evaluări
- 13 Pelvic Organ Prolapse & Urinary IncontinanceDocument62 pagini13 Pelvic Organ Prolapse & Urinary Incontinancekassahune ayallewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification and investigations of hernia typesDocument56 paginiClassification and investigations of hernia typesFobin VargheseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cephalo Pelvic Disproportion (CPD) & Contracted PelvisDocument45 paginiCephalo Pelvic Disproportion (CPD) & Contracted Pelvisbinipsamuel250% (1)
- Fetal Skull and Maternal Pelvis LandmarksDocument28 paginiFetal Skull and Maternal Pelvis LandmarksAshwanee Jharia0% (1)
- Anorectal Malformatio N: Dr. O. Sankoh M.D. House Officer Pediatric SurgeryDocument123 paginiAnorectal Malformatio N: Dr. O. Sankoh M.D. House Officer Pediatric SurgeryMohamed KamaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breech PresentationDocument53 paginiBreech PresentationVijith.V.kumar100% (6)
- Abnormal Labor Lec 2Document40 paginiAbnormal Labor Lec 2Zahraa HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breech Presentation and Delivery GuideDocument27 paginiBreech Presentation and Delivery GuideTrevor Uratel100% (1)
- Normal and Abnormal Labor DeliveryDocument59 paginiNormal and Abnormal Labor DeliveryRicsy Joie G. FantillanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Everything You Need to Know About HerniasDocument47 paginiEverything You Need to Know About HerniasmalathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hernia, (Different Types) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandHernia, (Different Types) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- PyelonephritisDocument24 paginiPyelonephritisfatihahannisahumairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GGGGDocument18 paginiGGGGfatihahannisahumairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3061 Inkompatibitas DarahDocument6 pagini3061 Inkompatibitas DarahfatihahannisahumairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- High-Risk Pregnancy That Must Be ReferredDocument4 paginiHigh-Risk Pregnancy That Must Be ReferredfatihahannisahumairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neural IntegrationDocument49 paginiNeural IntegrationfatihahannisahumairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LaryngitisDocument24 paginiLaryngitisfatihahannisahumaira100% (1)
- Obstetrical Surgical Procedures ExplainedDocument11 paginiObstetrical Surgical Procedures ExplainedfatihahannisahumairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3059 - Endocrine Disorders in PregnancyDocument58 pagini3059 - Endocrine Disorders in PregnancyfatihahannisahumairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obesitas Minggu 3Document44 paginiObesitas Minggu 3fatihahannisahumairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obesitas Minggu 3Document44 paginiObesitas Minggu 3fatihahannisahumairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3061 Inkompatibitas DarahDocument6 pagini3061 Inkompatibitas DarahfatihahannisahumairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2.3.1 Diathesis HemorragikDocument20 pagini2.2.3.1 Diathesis HemorragikaiysahmirzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EBM CYCLE AND PICO QUESTIONDocument40 paginiEBM CYCLE AND PICO QUESTIONmuthia saniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obstetrical Surgical Procedures ExplainedDocument11 paginiObstetrical Surgical Procedures ExplainedfatihahannisahumairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2.4.4 Leukemia KronikDocument36 pagini2.2.4.4 Leukemia KronikaiysahmirzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2.5.3 Limadenitis Akut Dan KronisDocument21 pagini2.2.5.3 Limadenitis Akut Dan KronisRaisa DilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding the Classification and Mechanisms of AnemiaDocument36 paginiUnderstanding the Classification and Mechanisms of AnemiafatihahannisahumairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3304 37128 Anemia DefisiensiDocument36 pagini3304 37128 Anemia DefisiensifatihahannisahumairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2.6.2 Komponen Darah Yg Ditransfusikan - Indikasi - Dan Tatacara Transfusi DarahDocument21 pagini2.2.6.2 Komponen Darah Yg Ditransfusikan - Indikasi - Dan Tatacara Transfusi DarahRaisa DilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2.3.1 Diathesis HemorragikDocument20 pagini2.2.3.1 Diathesis HemorragikaiysahmirzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PALATOSCHISIS IcahDocument21 paginiPALATOSCHISIS IcahAviZhafiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- PALATOSCHISIS IcahDocument21 paginiPALATOSCHISIS IcahAviZhafiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Article Summary - Revisiting Hawthorne's FeminismDocument3 paginiArticle Summary - Revisiting Hawthorne's FeminismsarahmariefurlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- JURNAL Hypnobreastfeeding-Dan-Hypnopa PDFDocument6 paginiJURNAL Hypnobreastfeeding-Dan-Hypnopa PDFIka Ulfana AmieniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genital ProlapseDocument9 paginiGenital Prolapsesher singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2014reVITALizeObstetricDataDefinitionsV10 PDFDocument5 pagini2014reVITALizeObstetricDataDefinitionsV10 PDFAloah122346Încă nu există evaluări
- A Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 1 (Week 1-2)Document24 paginiA Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 1 (Week 1-2)Daisy Soriano Prestoza100% (3)
- Reproductive and Sexual Health NotesDocument9 paginiReproductive and Sexual Health NotesKayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sketchy GynaecologyDocument28 paginiSketchy GynaecologyHuawei100% (3)
- Development of Female Genital Tract and Its AnomaliesDocument44 paginiDevelopment of Female Genital Tract and Its AnomaliesSuresh KatakamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiology of First Stage LabourDocument19 paginiPhysiology of First Stage LabourKinjal Vasava100% (10)
- OB Case Presentation Inforgraphic Garcia-GumbeDocument2 paginiOB Case Presentation Inforgraphic Garcia-GumbeLara GeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anastasia Flouli AUTH 3 Waves of FeminismDocument11 paginiAnastasia Flouli AUTH 3 Waves of FeminismMehroz BalochÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Summative Test Science 5Document3 paginiFirst Summative Test Science 5Gil Arriola100% (2)
- Reproductive DevelopmentDocument5 paginiReproductive DevelopmentBela MillenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The G-Spot FAQ PDFDocument2 paginiThe G-Spot FAQ PDFDavid HosamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case StudyDocument26 paginiCase StudyGrace Orencia100% (1)
- PBL Report 3 FixDocument24 paginiPBL Report 3 FixtiwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of NSDDocument4 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of NSDkyle otedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 2 - The Wheel Keeps On TurningDocument2 paginiActivity 2 - The Wheel Keeps On TurningKiel Angelo Monterey100% (1)
- Ob Notes EditedDocument28 paginiOb Notes EditedJake IliganÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 1097@aog 0000000000003857Document2 pagini10 1097@aog 0000000000003857Manuel MagañaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIDTERM EXAM REVIEWDocument15 paginiMIDTERM EXAM REVIEWGeneveive GuevaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mizoram Nursing Council: Part I: Objectives Answer All QuestionsDocument3 paginiMizoram Nursing Council: Part I: Objectives Answer All QuestionsAmy LalringhluaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive OrgansDocument8 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive OrgansMarinill Soliman100% (1)
- Worksheet 2Document3 paginiWorksheet 2api-293497823Încă nu există evaluări
- Contraceptive MethodsDocument40 paginiContraceptive MethodsMa. Lourdes CarbonillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument573 paginiUntitledNeil ShebyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Feminism Theory inDocument22 paginiFeminism Theory inRIDICLASIAÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Wife's GiftDocument5 paginiA Wife's GiftKrishna VuddantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology: Functions of The UterusDocument6 paginiAnatomy and Physiology: Functions of The UterusAnthony jesusÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Gender Equality PowerpointDocument18 pagini5 Gender Equality PowerpointIMELDA ESPIRITUÎncă nu există evaluări