Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
3 Phase Induction Motor Construction
Încărcat de
sunilkumarece0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
495 vizualizări25 pagini3 phase induction motor
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest document3 phase induction motor
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
495 vizualizări25 pagini3 Phase Induction Motor Construction
Încărcat de
sunilkumarece3 phase induction motor
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 25
An electrical motor is such an electromechanical
device which converts electrical energy into a
mechanical energy. In case of three phase AC
operation, most widely used motor is Three phase
induction motor as this type of motor does not
require any starting device or we can say they are self
starting induction motor.
Rotating Magnetic Field
The production of Rotating magnetic field in 3 phase
supply is very interesting. When a 3-phase winding is
energized from a 3-phase supply, a rotating magnetic
field is produced.
This field is such that its poles do no remain in a fixed
position on the stator but go on shifting their positions
around the stator.
For this reason, it is called a rotating field. It can be
shown that magnitude of this rotating field is constant
and is equal to 1.5 fm where fm is the maximum flux
due to any phase.
A three phase induction motor consists of three phase
winding as its stationary part called stator. The three
phase stator winding is connected in star or delta. The
three phase windings are displaced from each other by
120°. The windings are supplied by a balanced three
phase ac supply.
The three phase currents flow simultaneously through the
windings and are displaced from each other by 120°
electrical.
Each alternating .phase current produces its own flux
which is sinusoidal. So all three fluxes are sinusoidal and
are separated from each other by 120°.
If the phase sequence of the windings is R-Y-B, then
mathematical equations for the instantaneous values of the
three fluxes ΦR , ΦY ,ΦB can be written as,
ΦR = Φmsin(ωt)
ΦY = Φmsin(ωt - 120)
ΦB = Φmsin(ωt - 240)
As windings are identical and supply is balanced, the
magnitude of each flux is Φm .
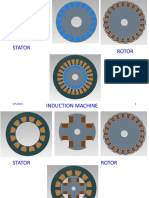
Construction
For better understanding the principle of three
phase induction motor, the basic constructional
feature of this motor must be known to us. This Motor
consists of two major parts:
1) Stator
2)Rotor
Stator:
It consists of a steel frame which encloses a hollow,
cylindrical core made up of thin laminations of silicon
steel to reduce hysteresis and eddy current losses.
A number of evenly spaced slots are provided on the
inner periphery of the laminations .
The insulated connected to form a balanced 3-phase
star or delta connected circuit.
The 3-phase stator winding is wound for a definite
number of poles as per requirement of speed.
Greater the number of poles, lesser is the speed of the
motor and vice-versa. When 3-phase supply is given to
the stator winding, a rotating magnetic field of constant
magnitude is produced.
This rotating field induces currents in the rotor by
electromagnetic induction.
Rotor:
The rotor, mounted on a shaft, is a hollow laminated
core having slots on its outer periphery. The winding
placed in these slots (called rotor winding) may be one
of the following two types:
(i) Squirrel cage type
(ii) Wound type
(i) Squirrel cage rotor.
It consists of a laminated cylindrical core having
parallel slots on its outer periphery. One copper or
aluminum bar is placed in each slot. All these bars are
joined at each end by metal rings called end rings.
The entire construction (bars and end rings)
resembles a squirrel cage and hence the name.
The rotor is not connected electrically to the supply
but has current induced in it by transformer action
from the stator. Those induction motors which employ
squirrel cage rotor are called squirrel cage induction
motors.
Most of 3-phase induction motors use squirrel cage rotor as it
has a remarkably simple and robust construction enabling it
to operate in the most adverse circumstances.
However, it suffers from the disadvantage of a low starting
torque.
It is because the rotor bars are permanently short-circuited
and it is not possible to add any external resistance to the
rotor circuit to have a large starting torque.
(ii) Wound rotor.
It consists of a laminated cylindrical core and carries a
3-phase winding, similar to the one on the stator.
The rotor winding is uniformly distributed in the slots
and is usually star-connected.
The open ends of the rotor winding are brought out
and joined to three insulated slip rings mounted on
the rotor shaft with one brush resting on each slip ring.
The three brushes are connected to a 3-phase star-
connected rheostat.
At starting, the external resistances are included in the
rotor circuit to give a large starting torque. These
resistances are gradually reduced to zero as the motor
runs up to speed.
The external resistances are used during starting period
only. When the motor attains normal speed, the three
brushes are short-circuited so that the wound rotor runs
like a squirrel cage rotor.
Working of Three Phase Induction Motor
Production of Rotating Magnetic Field(RMF)
The stator of the motor consists of overlapping
winding offset by an electrical angle of 120°. When the
primary winding or the stator is connected to a 3 phase
AC source, it establishes a rotating magnetic field
which rotates at the synchronous speed.
According to Faraday’s law an emf induced in any circuit
is due to the rate of change of magnetic flux linkage
through the circuit. As the rotor winding in an induction
motor are either closed through an external resistance or
directly shorted by end ring, and cut the stator rotating
magnetic field, an emf is induced in the rotor copper bar
and due to this emf a current flows through the rotor
conductor.
working principle of three phase induction motor
Thus from the working principle of three
phase induction motor it may observed that
the rotor speed should not reach the
synchronous speed produced by the stator.
If the speeds equals, there would be no such
relative speed, so no emf induced in the rotor,
and no current would be flowing, and therefore
no torque would be generated. Consequently
the rotor can not reach the synchronous speed.
The difference between the stator (synchronous
speed) and rotor speeds is called the slip. The
rotation of the magnetic field in an induction
Three phase induction motor is:
Self-starting.
Less armature reaction and brush sparking because of
the absence of commutators and brushes that may
cause sparks.
Robust in construction.
Economical.
Easier to maintain.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Week 71Document25 paginiWeek 71Raphael SebucÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction of Three Phase Induction MotorDocument18 paginiConstruction of Three Phase Induction MotorRajeev ValunjkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synchronous Machines and SCDocument6 paginiSynchronous Machines and SCivancho04mÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument4 paginiThree Phase Induction MotorAimi Al-YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Induction Motor ConstructionDocument42 paginiChapter 6 Induction Motor Constructionupendra35Încă nu există evaluări
- Design of Three Phase Induction Motor Using Mat Lab ProgrammingDocument6 paginiDesign of Three Phase Induction Motor Using Mat Lab ProgrammingEditor IJRITCCÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Presentation On Shaded Pole Induction Motor: Prepared By: Salunkhe KalpeshDocument20 paginiA Presentation On Shaded Pole Induction Motor: Prepared By: Salunkhe KalpeshKalpesh SalunkheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brushless DC MotorDocument19 paginiBrushless DC MotorSanjeet KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction CookersDocument5 paginiInduction CookersVăn LinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Phase Synchronous MachinesDocument14 paginiThree Phase Synchronous MachinesMohdFirdausÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single-Phase Induction Motors: ConstructionDocument18 paginiSingle-Phase Induction Motors: ConstructionmaakbdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motor Winding ProcedureDocument25 paginiMotor Winding Procedureutility supplyÎncă nu există evaluări
- BLDCDocument4 paginiBLDCmechtex Pvt LtdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelling and Simuation of BLDC Motor in MATLAB GUIDocument5 paginiModelling and Simuation of BLDC Motor in MATLAB GUIvishiwizardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3Document5 paginiUnit 3Narasimman DonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eeeviews: Unit Iv Synchronous Motor DrivesDocument26 paginiEeeviews: Unit Iv Synchronous Motor Driveskrithikgokul selvamÎncă nu există evaluări
- No Load and Block Rotor Test: Premier Trading CorporationDocument11 paginiNo Load and Block Rotor Test: Premier Trading CorporationKsr Akhil100% (1)
- Induction MotorsDocument25 paginiInduction Motorsapi-3827132100% (2)
- Types of Motor Used in Traction SystemDocument8 paginiTypes of Motor Used in Traction SystemShrestha Sanju100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - DC Motors and GeneratorsDocument80 paginiChapter 8 - DC Motors and GeneratorsZargham RanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Special Purpose MotorsDocument16 paginiSpecial Purpose MotorsHari ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3phase Induction Motor (Sukhpreet)Document17 pagini3phase Induction Motor (Sukhpreet)Ankesh KunwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp 9 Boost ConverterDocument8 paginiExp 9 Boost ConverterusmpowerlabÎncă nu există evaluări
- PX7203-Special Electrical Machines PDFDocument11 paginiPX7203-Special Electrical Machines PDFvaishnavisriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Development of Three Phase Permanent Magnet BrushlessDocument11 paginiDesign and Development of Three Phase Permanent Magnet BrushlessteomondoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synchronous MotorsDocument25 paginiSynchronous MotorsParvesh NainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sinkron Motor - AtmiDocument87 paginiSinkron Motor - AtmiHaryo Probo100% (1)
- Brushless DC MotorDocument19 paginiBrushless DC MotorKhalid MahmudÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCEG 403 Lab No. 1 Title: Simulation of Single Phase Half Wave Converter DC DriveDocument5 paginiPCEG 403 Lab No. 1 Title: Simulation of Single Phase Half Wave Converter DC DriveJanup PokharelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction GeneratorDocument12 paginiInduction GeneratorSumaira SaifÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE 442 642 IntroductionDocument14 paginiEE 442 642 IntroductionUSERNAME12340987Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab 3 Squirrel Cage Induction Machine-1Document8 paginiLab 3 Squirrel Cage Induction Machine-1max100% (1)
- Stepper MotorsDocument26 paginiStepper MotorsRam Kumar GogadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase Induction MotorDocument5 paginiSingle Phase Induction MotorSridhar SridharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction Motor: Navigation SearchDocument8 paginiInduction Motor: Navigation SearchSoni Mishra TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC-Choppers Class A B C D EDocument18 paginiDC-Choppers Class A B C D EAnonymous iTJLpNVÎncă nu există evaluări
- BLDC Brushless DC MotorDocument22 paginiBLDC Brushless DC MotorNyn SoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC MotorDocument53 paginiDC MotorK04Anoushka TripathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Injection of EMF in The Rotor CircuitDocument3 paginiInjection of EMF in The Rotor CircuitAbhishekGuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- D C Machines-IntroductionDocument25 paginiD C Machines-Introductionprashanth6876050% (2)
- Electric Machinery FundamentalsDocument6 paginiElectric Machinery FundamentalsKashyap Dubey0% (1)
- PMBLDC Motor DriveDocument55 paginiPMBLDC Motor DriveSushant SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.chapter Five - Ignition and Fuel Injection SystemsDocument21 pagini5.chapter Five - Ignition and Fuel Injection SystemsAhmed M MerzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stepper MotorDocument26 paginiStepper MotorSupriya Rakshit100% (1)
- Induction Motor Construction and OperationDocument36 paginiInduction Motor Construction and Operationkyaw winÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMECDocument73 paginiEMECdivyansh singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction of Machine PDFDocument110 paginiConstruction of Machine PDFAvinash SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simocode Alarme PDFDocument7 paginiSimocode Alarme PDFMa VioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brushless D.C. Motors: Prepared By: Manuj Garg (2k13/EE/070) Mohit Goswami (2k13/EE/073)Document17 paginiBrushless D.C. Motors: Prepared By: Manuj Garg (2k13/EE/070) Mohit Goswami (2k13/EE/073)Manuj GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synchronous GeneratorsDocument17 paginiSynchronous GeneratorsAman AnsariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brushless DC Motor Working Principle and ApplicationsDocument6 paginiBrushless DC Motor Working Principle and ApplicationsMd Samee MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ac Series MotorDocument15 paginiAc Series MotorMani Balaji TÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE333 Electrical Machines Lab IIDocument2 paginiEE333 Electrical Machines Lab IIvpzfarisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Phase Induction Motor Construction (Autosaved)Document17 pagini3 Phase Induction Motor Construction (Autosaved)ZUBAIRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction MotorDocument21 paginiInduction Motoragbajelola idrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument2 paginiThree Phase Induction MotorsamyramuÎncă nu există evaluări
- IM (1) NotesDocument4 paginiIM (1) NotesHarshitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit - 3 Electrical Machines: 1. Generation of Rotating Magnetic FieldDocument10 paginiUnit - 3 Electrical Machines: 1. Generation of Rotating Magnetic FieldAtharv BhedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnetic Field Faraday's Law Magnetic Flux Induction Motor Resistance Magnetic Field CurrentDocument2 paginiMagnetic Field Faraday's Law Magnetic Flux Induction Motor Resistance Magnetic Field CurrentyokeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction MachineDocument40 paginiInduction MachineJunior heroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 135-Wind Farm To Weak-Grid Connection 2003Document80 pagini135-Wind Farm To Weak-Grid Connection 2003Pardha Saradhi JÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 8Document14 paginiUnit 8sunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- 135 Wind Farm To Weak-Grid ConnectionDocument6 pagini135 Wind Farm To Weak-Grid ConnectionVenkat Raghavendra Reddy100% (1)
- A Solar Power Generation System With A Seven-Level Inverter: Jinn-Chang Wu, Member, IEEE, Chia-Wei ChouDocument9 paginiA Solar Power Generation System With A Seven-Level Inverter: Jinn-Chang Wu, Member, IEEE, Chia-Wei Chouckrishna625Încă nu există evaluări
- Final RoundDocument17 paginiFinal RoundsunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final RoundDocument17 paginiFinal RoundsunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Give The Names of Each ElementDocument15 paginiGive The Names of Each ElementsunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 8Document14 paginiUnit 8sunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-2: Network Matrices-2Document13 paginiUNIT-2: Network Matrices-2sunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMCAT Sample Questions For BtechDocument18 paginiAMCAT Sample Questions For BtechRachit Gupta100% (3)
- Energies 12 00157 PDFDocument17 paginiEnergies 12 00157 PDFsunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Phase Induction Motor ConstructionDocument25 pagini3 Phase Induction Motor ConstructionsunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solar PV Array Modelling PDFDocument13 paginiSolar PV Array Modelling PDFsunilkumarece100% (1)
- EE394V DG Week2 Part 2Document14 paginiEE394V DG Week2 Part 2Armando MaloneÎncă nu există evaluări
- R16B TECHEEEIIIYearSyllabusDocument37 paginiR16B TECHEEEIIIYearSyllabusPrasad ApvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multilevel PDFDocument15 paginiMultilevel PDFkosmitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture1423813026 PDFDocument92 paginiLecture1423813026 PDFKarthikeyanKarunÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Efficient Constant Current Controller For PV Solar Power Generator Integrated With The GridDocument6 paginiAn Efficient Constant Current Controller For PV Solar Power Generator Integrated With The GridsunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Efficient Constant Current Controller For PV Solar Power Generator Integrated With The GridDocument6 paginiAn Efficient Constant Current Controller For PV Solar Power Generator Integrated With The GridsunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- MMC DetailsDocument14 paginiMMC DetailssunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solar Multilevel PDFDocument7 paginiSolar Multilevel PDFsunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Power and Energy Systems: Banaja Mohanty, Sidhartha Panda, P.K. HotaDocument9 paginiElectrical Power and Energy Systems: Banaja Mohanty, Sidhartha Panda, P.K. HotasunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementation of Graphical User Interface For Single Area Load Frequency ControlDocument4 paginiImplementation of Graphical User Interface For Single Area Load Frequency ControlsunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- LFC AnfisDocument6 paginiLFC AnfissunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arduino Code Dual AxisDocument2 paginiArduino Code Dual AxissunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- B TechopenelectivesforiiiyearDocument118 paginiB TechopenelectivesforiiiyearsunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short AnswersDocument9 paginiShort AnswerssunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Realtime Pacer LicenseDocument1 paginăRealtime Pacer LicensesunilkumareceÎncă nu există evaluări
- LicenseDocument5 paginiLicensedany_erwcomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To Computing SyllabusDocument7 paginiIntro To Computing SyllabusAireen Rose Rabino ManguiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sales Manager Dashboard Template: Daily TrackerDocument12 paginiSales Manager Dashboard Template: Daily TrackerAwais ZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cybersecurity Essentials 1.0 Release Notes: PurposeDocument5 paginiCybersecurity Essentials 1.0 Release Notes: PurposeRonny Kimer Fiestas VargasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 Index of Military Strength Air Domain EssayDocument15 pagini2018 Index of Military Strength Air Domain EssayThe Heritage FoundationÎncă nu există evaluări
- York Peek Style Refrigerant Level Sensor CalibrationDocument6 paginiYork Peek Style Refrigerant Level Sensor CalibrationCharlie GaskellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harmony XB4 - ZB4 Metal Push Buttons - XB4BD912R10KDocument6 paginiHarmony XB4 - ZB4 Metal Push Buttons - XB4BD912R10KLorentzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norphonic VoIP D10003Document2 paginiNorphonic VoIP D10003Topcom Toki-VokiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A320 CBT Fuel System: Table of ContentDocument8 paginiA320 CBT Fuel System: Table of ContentAman VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Choose Circuit Breakers For Electric MotorsDocument2 paginiHow To Choose Circuit Breakers For Electric Motorsحسن التميميÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poster BC - Bored PileDocument1 paginăPoster BC - Bored PileZaim Adli100% (1)
- ANSI-IEEE, NEMA and UL Requirements For SwitchgearDocument4 paginiANSI-IEEE, NEMA and UL Requirements For Switchgearefmartin21Încă nu există evaluări
- China Chassis Cj14Document1 paginăChina Chassis Cj14David Argote BellidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Install OpenERP On UbuntuDocument9 paginiInstall OpenERP On UbuntuQuynh NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 1 Valve and Instrumentation SymbolsDocument8 paginiTopic 1 Valve and Instrumentation SymbolshatiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urethyn HG 0 - Pi - (Gb-En)Document2 paginiUrethyn HG 0 - Pi - (Gb-En)CriVe OffeÎncă nu există evaluări
- MGT 162Document2 paginiMGT 162Myra Choyy100% (1)
- KW Tedder LeafletDocument32 paginiKW Tedder Leafletinfo4826Încă nu există evaluări
- Goniophotometer For Automotive and Signal Lamps 1950sDocument6 paginiGoniophotometer For Automotive and Signal Lamps 1950sLisun GroupÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMILE System For 2d 3d DSMC ComputationDocument6 paginiSMILE System For 2d 3d DSMC ComputationchanmyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OZ Racing Rims: Name Method Size Weight (LBS.) Weight (KGS.)Document4 paginiOZ Racing Rims: Name Method Size Weight (LBS.) Weight (KGS.)ilpupÎncă nu există evaluări
- USA Cutter Suction Dredger Simulator TrainingDocument2 paginiUSA Cutter Suction Dredger Simulator TrainingAbdullah Badawi BatubaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bomba - Weir - Warman Horizontal Pumps PDFDocument8 paginiBomba - Weir - Warman Horizontal Pumps PDFWanderson Alcantara100% (1)
- Business Plan ScrunshineDocument2 paginiBusiness Plan ScrunshineEnjhelle MarinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eaton Fuller FS-4205A Transmission Parts ManualDocument18 paginiEaton Fuller FS-4205A Transmission Parts ManualJuan Diego Vergel RangelÎncă nu există evaluări
- PTC ThermistorsDocument9 paginiPTC ThermistorsbuspersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dem 1Document12 paginiDem 1Vicks BTBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nift Panchkula Thesis Gaurav Bajaj 2009 Uar 646Document10 paginiNift Panchkula Thesis Gaurav Bajaj 2009 Uar 646vedahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrograph - Analysis - 2 Hydro PDFDocument68 paginiHydrograph - Analysis - 2 Hydro PDFNurul QurratuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ddal Players Guide v5Document12 paginiDdal Players Guide v5Jakob Cherpovsky100% (1)
- Códigos de Fallas de Problemas Específicos de PEUGEOTDocument8 paginiCódigos de Fallas de Problemas Específicos de PEUGEOTJesus GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări