Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Risk Based Internal Auditing - An Introduction: Slides of Figures and Appendices
Încărcat de
Eko PriadiTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Risk Based Internal Auditing - An Introduction: Slides of Figures and Appendices
Încărcat de
Eko PriadiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Risk based
internal auditing
– an introduction
Slides of figures
and appendices
©David M Griffiths
©David M Griffiths www.internalaudit.biz
Risk based internal auditing – an introduction
slides of figures and appendices
• The following slides are those used in the
book Risk based internal auditing – an
introduction available from
www.internalaudit .biz
• The slides of figures are:
– 1 Internal auditing objectives
– 2 Grid for significance risks
– 3 Stages of an audit
– 4 RBIA documentation
– 5 Processes involved in stage 2
– 6 Grid for frequency of audits
– 7 Factors to reduce inherent risk scores risks
– 8 Processes involved in stage 3
– 9 Grid for significance of residual risks
• Slides of appendices are
– A Internal auditing objectives
– B Hierarchy of objectives, risks and controls
– C Process map
– E Grid for risk workshop
– J Stages of an internal audit
– Other appendices are on the excel spreadsheet RBIA introduction excel v3
©David M Griffiths www.internalaudit.biz
Internal auditing objectives
(Figure 1 and appendix A)
The Internal auditing
management provides an independent and
of an objective opinion to an
organisation organisation’s management as to
have whether its risks are being managed
to acceptable levels.
The main aim of internal
auditing is to assist the
Objectives organisation to achieve its
objectives
An
internal control
is a process which
manages a risk
A
risk
is a set of
circumstances
that hinder the
achievement of
objectives
©David M Griffiths www.internalaudit.biz
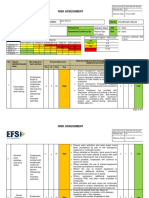
2 Grid for significance of risks
Probable (4) Almost certain (5)
5
Supplementary
10 15 IR 20 25
Issue Issue Unacceptable Unacceptable Unacceptable
4 8 12 16 20
Likelihood of risk
Internal control
Supplementary
Acceptable Issue Issue Unacceptable Unacceptable
Possible (3)
3 6 9 12 15
Supplementary
Acceptable Issue Issue Issue Unacceptable
Unlikely (2)
2 4 6 8 10
Supplementary Supplementary
Acceptable Acceptable Issue Issue Issue
1 2 3 4 5
Rare(1)
Acceptable Acceptable
RR
Acceptable Acceptable Issue
Insignificant (1) Minor (2) Moderate (3) Major (4) Catastrophic (5)
Consequence of risk
Unacceptable: Immediate action required to manage the risk
Issue: Action required to manage the risk
Supplementary issue: Action is advisable if resources are available
Acceptable: No action required
Risk appetite, as defined by the board
IR = Inherent Risk RR = Residual Risk
Fig.2 Grid showing the significance of risks
©David M Griffiths www.internalaudit.biz
3 Stages of an audit
Management's
Risk Register
(if available)
Risk Naive Risk Enabled
Assess risk
Risk Aware maturity Risk Managed Stage 1
Risk Defined
Management's
Facilitate risk Risk Register Use organisation's
identification (amended) risks
Audit universe Assign risks to
audits
Stage 2
Risk and audit
Audit Committee
universe Audit plan
report
(RAU)
Individual audit
Audit report
Stage 3
Feedback results
into RAU
Fig 3 Stages of an audit
©David M Griffiths www.internalaudit.biz
4 RBIA documentation
risk and audit audit databases
universe
objectives objectives
risks risks
scores scores
controls controls
last audits tests
Audit
audit
Committee
reports
report
Fig. 4 RBIA documentation
©David M Griffiths www.internalaudit.biz
5 Processes involved in stage 2
Risk Register
(audited)
Risks within the risk Risks on which
appetite assurance is provided
by others
Filter risks
Risks not requiring an
Risks which will be
audit in this period
tolerated
Risks on which
assurance is
required
Categorise risks
Audit Universe
Link risks to
audits
Risk and Audit Select risks to
Universe be covered
Alllocate
resources to
audits
Audit Committee
Audit plan
report
©David M Griffiths Fig 5 www.internalaudit.biz
Processes involved in Stage 2
6 Grid for frequency of audits
Probable (4) Almost certain (5)
5 10
15 20 25
Every three Every two
Every year Every year Every year
years years
Likelihood of inherent risk
4 8 12
16 20
Every three Every two
Never years years
Every year Every year
Possible (3)
3 6 9 12
15
Every three Every two Every two
Never years years years
Every year
Unlikely (2)
2 4 6 8 10
Every three Every three Every two
Never Never years years years
1 2 3 4 5
Rare(1)
Every three
Never Never Never Never years
Insignificant (1) Minor (2) Moderate (3) Major (4) Catastrophic (5)
Consequence of inherent risk
Fig. 6 Grid for the frequency of audits
©David M Griffiths www.internalaudit.biz
7 Factors to reduce inherent risk scores risks
3 years
0.75 1 1
Time since last audit
2 years
0.5 0.75 1
1 year
0.25 0.5 0.75
Green Amber Red
Audit result
Fig. 7 Factors to reduce inherent risk scores
©David M Griffiths www.internalaudit.biz
8 Processes involved in stage 3
Audit plan
Define draft audit
scope
Examine the risk
management process
for the area audited
Conclude on risk
maturity for the
area audited
Decide on audit
approach
Meetings to determine
Agreed scope
objectives, risks and
agree scope
Obtain relevant
documentation on
processes
Set up an audit database
Risk and audit universe to record the audit
details, or update the Audit
Risk and Audit Universe database
©David M Griffiths www.internalaudit.biz
9 Grid for significance of residual risks
Probable (4) Almost certain (5)
5 10 15 20 25
Supplementary
Issue Issue Unacceptable Unacceptable Unacceptable
Likelihood of residual risk
4 8 12 16 20
Supplementary
Acceptable Issue Issue Unacceptable Unacceptable
Possible (3)
3 6 9 12 15
Supplementary
Acceptable Issue Issue Issue Unacceptable
Unlikely (2)
2 4 6 8 10
Supplementary Supplementary
Acceptable Acceptable Issue Issue Issue
1 2 3 4 5
Rare(1)
Supplementary
Acceptable Acceptable Acceptable Acceptable Issue
Insignificant (1) Minor (2) Moderate (3) Major (4) Catastrophic (5)
Consequence of residual risk
Unacceptable: Immediate action required to control the risk
Issue: Action required to control the risk
Supplementary issue: Action is advisable if it is cost-effective
Acceptable: No action required
Risk appetite, as defined by the board
Fig. 9 Grid for the significance of residual risks
©David M Griffiths www.internalaudit.biz
Hierarchy of objectives, risks and controls
(Appendix B)
Objective level 1 Relieve famine in
central Africa
risks
No clear Unable to Do not have
Unable to
strategy as predict where the staff and
Unable to deliver the
to how to and when systems to
obtain food food to the
achieve our famines will support the
starving
objective occur operation
Objective level 2
Devise a Establish
Set up a Set up Establish
strategy for delivery
system which agreements functions to
the next five systems to
enables us to with donors deliver food
support the
years to
predict to obtain when and where field
deliver our
famine areas food it is required operations
objectives
Establish a supply chain to
ensure prompt delivery of
food to the highest priority
area
risks
Unable to Insufficient Do not know
Lorries
obtain lorries to Insufficient Roads are where food is
break impassable required
space on transport drivers
down most urgently
ships grain
Objective level 3
Establish Decide how
contacts future needs Identify
Set up Set up
with are to be Lorries to how to
possible strategy for
shipping met, by be properly recruit at
companies local carrier alternativ prioritizing
maintained short
to anticipate or own e routes camps
notice
problems lorries
©David M Griffiths www.internalaudit.biz
Objectives map
(appendix C)
objective Relieve famine in
central Africa
Level 2 objectives
2 3
Set up a Set up 4
1
system which agreements Establish 5
Devise a
enables us to with donors delivery Establish
strategy for
predict to obtain systems to functions to
the next five
famine areas food deliver food support the
years to
when and field
deliver our
where it is operations
objectives
required
1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4
Agree a Communicate Deliver Update
strategy strategy strategy strategy
Level 3 objectives
4.1 4.2
4.5
Establish Decide how 4.4
4.3 Set up 4.6
contacts with future needs Identify how
Lorries to be possible Set up strategy
shipping are to be to recruit
properly alternative for prioritizing
companies to met, by local drivers at
maintained routes for camps
anticipate carrier or own short notice
delivery
problems lorries
5.2 5.3 5.5
5.4 5.6
5.1 Provide Provide Provide
Provide legal Provide human
Raise money financial transaction information
services resources
advice processing technology
©David M Griffiths www.internalaudit.biz
Grid for risk workshop
(appendix E) Probable (4) Almost certain (5)
5 10 2 15 20
1 25
5
Supplementary
Issue Issue Unacceptable Unacceptable Unacceptable
4 8 12 16 20
Likelihood of risk
Supplementary
Acceptable Issue Issue Unacceptable Unacceptable
Possible (3)
3 6 9 12 15
6
Supplementary
Acceptable Issue Issue Issue Unacceptable
Unlikely (2)
2 4 6 8 10
Supplementary Supplementary
Acceptable Acceptable Issue Issue Issue
1 2 3 3 4 5 4
Rare(1)
Acceptable Acceptable Acceptable Acceptable Issue
Insignificant (1) Minor (2) Moderate (3) Major (4) Catastrophic (5)
Consequence of risk
©David M Griffiths www.internalaudit.biz
Stages of an internal audit (appendix J)
The Internal auditing
management Internal auditing: provides an
of an independent and objective opinion to
organisation an organisation’s management as to
have whether its risks are being managed
to acceptable levels.
Objectives
1
The
4 audit
An
internal control
is a process which 3
manages a risk
A
risk 2
is a set of
circumstances
that hinder the Significant risks generate
achievement of
objectives the audit plan
©David M Griffiths www.internalaudit.biz
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Risk Assessment P3 Permanent Power Provision at IthraDocument2 paginiRisk Assessment P3 Permanent Power Provision at Ithraghazi4uÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step 2 Risk Assess L5 Control AssessmentDocument8 paginiStep 2 Risk Assess L5 Control AssessmentВалентин БеркутÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Assessment Matrix: Consequence (C) Low Risk Moderate Risk High Risk Extreme RiskDocument3 paginiRisk Assessment Matrix: Consequence (C) Low Risk Moderate Risk High Risk Extreme RiskBIIS QAQC Babu SivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Management Worksheets Risk Assessment WorksheetDocument4 paginiRisk Management Worksheets Risk Assessment Worksheetkapil ajmaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Management - Appendix 7.4 - Risk Matrix and Tolerance Levels - v2.0Document1 paginăRisk Management - Appendix 7.4 - Risk Matrix and Tolerance Levels - v2.0Mohammad HegazyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Management Plan JWM029Document16 paginiRisk Management Plan JWM029Eng hassan hussienÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cyber Trust Self Assessment V202208Document74 paginiCyber Trust Self Assessment V202208lava.sky10Încă nu există evaluări
- Risk Assessment Fitout SalonDocument19 paginiRisk Assessment Fitout SalonVision ConceptÎncă nu există evaluări
- RAStandardDocument14 paginiRAStandardMelwin DsouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SEPL RR 001 Risk RegisterDocument5 paginiSEPL RR 001 Risk RegisterRajkumar PrajapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- (GFB) Risk Assessment Tool - Make ADocument100 pagini(GFB) Risk Assessment Tool - Make Aeya dridiÎncă nu există evaluări
- RAID Register - SapphireDocument11 paginiRAID Register - SapphireMuhammadMuzammalJamilÎncă nu există evaluări
- H&S RR Health and Safety Risk Review Form Issue 1 Rev 4Document5 paginiH&S RR Health and Safety Risk Review Form Issue 1 Rev 4mash2.am80Încă nu există evaluări
- Registro de RiesgosDocument4 paginiRegistro de Riesgosdairene torresÎncă nu există evaluări
- RMH HiraDocument12 paginiRMH HiraShirley SetshediÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Construction - Roof Membrane ReplacementDocument6 paginiGeneral Construction - Roof Membrane ReplacementShannon MooreÎncă nu există evaluări
- HR Risk AssessmentDocument14 paginiHR Risk AssessmentMohab AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retail Client - Risks and Risk Ratings TemplateDocument31 paginiRetail Client - Risks and Risk Ratings TemplatessglcnÎncă nu există evaluări
- 49.risk Assessment For Control of Corona VirusDocument3 pagini49.risk Assessment For Control of Corona VirusManzur AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blank Risk Assessment TemplateDocument4 paginiBlank Risk Assessment TemplateMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Heat Map: A Risk Assessment Tool To Assist in Risk Assessment ProductivityDocument6 paginiRisk Heat Map: A Risk Assessment Tool To Assist in Risk Assessment ProductivityRiz DeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Management PlanDocument46 paginiRisk Management PlanJohn Oo100% (4)
- Triple Bottom Line Risk Management: Enhancing Profit, Environmental Performance, and Community BenefitsDe la EverandTriple Bottom Line Risk Management: Enhancing Profit, Environmental Performance, and Community BenefitsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Register TemplateDocument14 paginiRisk Register TemplateAli EsmaeilbeygiÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPM 22 - 2013 - Au - T8 - W10 My TRANDocument10 paginiIPM 22 - 2013 - Au - T8 - W10 My TRANTrần Trà MyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 009.1c Risk Scoring Matrix 250713Document2 pagini009.1c Risk Scoring Matrix 250713idrisngrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ra Concrete Chipping 7514Document5 paginiRa Concrete Chipping 7514Charles DoriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydro Static Test: Risk AssessmentDocument10 paginiHydro Static Test: Risk Assessmentmohammed a hseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Assessment For Split AC UnitsDocument2 paginiRisk Assessment For Split AC UnitsAhmed mahlawyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management Dashboard - Issues & Risks: Issue Summary Risk Summary Issue StatusDocument6 paginiManagement Dashboard - Issues & Risks: Issue Summary Risk Summary Issue Statustrader123Încă nu există evaluări
- Baseline Risk Assessment1 PDFDocument25 paginiBaseline Risk Assessment1 PDFRico100% (2)
- Risk Assessment - Issues - SKIDocument6 paginiRisk Assessment - Issues - SKISekar KrishÎncă nu există evaluări
- RA Existing Asphalt Milling WorksDocument8 paginiRA Existing Asphalt Milling WorksSolimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legal and Management: GA03 Risk Assessment (Quantitative)Document2 paginiLegal and Management: GA03 Risk Assessment (Quantitative)LucianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management Dashboard - Issues & Risks: Issue Summary Risk Summary Issue StatusDocument6 paginiManagement Dashboard - Issues & Risks: Issue Summary Risk Summary Issue StatusSteve MedhurstÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Based Internal AuditDocument19 paginiRisk Based Internal AuditL N Murthy KapavarapuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cross Docking Distribution - Project ManagementDocument48 paginiCross Docking Distribution - Project ManagementOshini WimalasenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bosh - Hirac - LlagunoDocument2 paginiBosh - Hirac - LlagunoCGD ReviewÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2017 ORM Assessment - BlankDocument4 pagini2017 ORM Assessment - BlankMario AstroñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Assessment Format For SampleDocument3 paginiRisk Assessment Format For SampleSaqib RasoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- RAID ExampleDocument14 paginiRAID Exampleanhthu.dlbtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hazard Identification Risk Assessment and Risk Control Register HIRARC Review / Revision Control SheetDocument38 paginiHazard Identification Risk Assessment and Risk Control Register HIRARC Review / Revision Control Sheetusman4428Încă nu există evaluări
- Sample ISMS Risk RegisterDocument6 paginiSample ISMS Risk RegisterRemyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample ISMS Risk RegisterDocument6 paginiSample ISMS Risk RegisterAHM Pervej KabirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Assessment For CONCRETE WORKS - SUBSTRUCTURE - 01Document6 paginiRisk Assessment For CONCRETE WORKS - SUBSTRUCTURE - 01Bulent AkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Assessment FormDocument2 paginiRisk Assessment FormahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk AssessmentDocument1 paginăRisk AssessmentCelz GraciadasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verse Security AuditDocument6 paginiVerse Security AuditLeciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Rating Matrix: Low Medium Medium HighDocument3 paginiRisk Rating Matrix: Low Medium Medium HighTharaka Samarasekara100% (1)
- PTD DIV 0007 03 Att 4 Risk Assessment MatrixDocument1 paginăPTD DIV 0007 03 Att 4 Risk Assessment MatrixYan JanuardiÎncă nu există evaluări
- EFS-SLB-SRA-002 Risk Assessment For Carpet Cleaning Vacuum & ShampooDocument4 paginiEFS-SLB-SRA-002 Risk Assessment For Carpet Cleaning Vacuum & Shampoomohammed ayazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hazard Identification & Risk AssessmentDocument9 paginiHazard Identification & Risk AssessmentLathakula RajashekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- EFS-SLB-SRA-004 Risk Assessment For Bodily Fluid Spillage CleansDocument2 paginiEFS-SLB-SRA-004 Risk Assessment For Bodily Fluid Spillage Cleansmohammed ayazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bidaa Tower Risk Assessment From CALISTO UpdatedDocument5 paginiBidaa Tower Risk Assessment From CALISTO Updatedirshad gÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Assessment For Excavation and BackfillingDocument5 paginiRisk Assessment For Excavation and BackfillingBulent AkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk MatrixDocument1 paginăRisk MatrixJoseph GraciousÎncă nu există evaluări
- HIRAC FormDocument9 paginiHIRAC FormGERALD DAYRITÎncă nu există evaluări
- Checklist WeldingDocument5 paginiChecklist WeldingMarko RisticÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Audit Risk Scale and AssessmentDocument4 paginiInternal Audit Risk Scale and AssessmentWasim ArshadÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT Risk Control and AuditDocument112 paginiIT Risk Control and Auditreddaiah karumuruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Family Law 2 Final.Document11 paginiFamily Law 2 Final.Vedant VyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ncert BookDocument14 paginiNcert Bookviswanathan periyasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wellington Investment v. TrajanoDocument1 paginăWellington Investment v. TrajanoNicole Kalingking100% (1)
- Body Dressing (Dress, Body, Culture) PDFDocument263 paginiBody Dressing (Dress, Body, Culture) PDFpoulomi roy100% (2)
- Building Brand Architecture by Prachi VermaDocument3 paginiBuilding Brand Architecture by Prachi VermaSangeeta RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proposal Argument (FINAL)Document10 paginiProposal Argument (FINAL)NgoziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sustainable Development The Challenge of TransitionDocument241 paginiSustainable Development The Challenge of TransitionIsmael De Oliveira GerolamoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LorealDocument2 paginiLorealviaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurisdiction (Three Hours) Lesson OutlineDocument7 paginiJurisdiction (Three Hours) Lesson OutlineChaÎncă nu există evaluări
- YSI Saving 2022Document2 paginiYSI Saving 2022koamanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example of Scholarship EssayDocument4 paginiExample of Scholarship EssayertzyzbafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Divine Word University of Tacloban vs. Secretary of Labor and Employment, G. R. No. 91915, Sept. 11, 1992, 213 SCRA 759Document3 paginiDivine Word University of Tacloban vs. Secretary of Labor and Employment, G. R. No. 91915, Sept. 11, 1992, 213 SCRA 759Maria Celiña PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAMPLE AR Narrative Word FormatDocument12 paginiSAMPLE AR Narrative Word FormatElle Sta TeresaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 175 PMP Sample QuestionsDocument78 pagini175 PMP Sample QuestionsJuan Luis FerretÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 6 Lesson 4 Holy EucharistDocument25 paginiGrade 6 Lesson 4 Holy EucharistJim TuscanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Report On Comparative Analysis of 4-Stroke BikesDocument72 paginiProject Report On Comparative Analysis of 4-Stroke BikesvinnetTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accessing Resources For Growth From External SourcesDocument14 paginiAccessing Resources For Growth From External SourcesHamza AdilÎncă nu există evaluări
- TVL-EMTECH-W-1-TUNAY-NA-TUNAY 70 CopiesDocument7 paginiTVL-EMTECH-W-1-TUNAY-NA-TUNAY 70 CopiesMiyu VianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter One: Perspectives On The History of Education in Nigeria, 2008Document26 paginiChapter One: Perspectives On The History of Education in Nigeria, 2008Laura ClarkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Registration of Patient Transport VehicleDocument2 paginiRegistration of Patient Transport VehicleMenGuitar100% (1)
- Architect Delhi Urban Art CommissionDocument2 paginiArchitect Delhi Urban Art CommissionshahimabduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo Léon Preparatoria 15, Unidad MaderoDocument4 paginiUniversidad Autónoma de Nuevo Léon Preparatoria 15, Unidad MaderoCarlos Lopez cortezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapters Particulars Page NoDocument48 paginiChapters Particulars Page NoKuldeep ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Key Considerations For A Successful Hyperion Planning ImplementationDocument45 paginiKey Considerations For A Successful Hyperion Planning Implementationayansane635Încă nu există evaluări
- SWO AresultDocument19 paginiSWO Aresultdamodar_111Încă nu există evaluări
- Islam PPT Outline (Script)Document2 paginiIslam PPT Outline (Script)Paulene MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- R.A 3135&P.D 604&e.o 590Document11 paginiR.A 3135&P.D 604&e.o 590Jhet Ardian CoritanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kashmir DisputeDocument13 paginiKashmir DisputeAmmar ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iso 27001Document84 paginiIso 27001sboukhal100% (2)
- FI Market Research TemplateDocument3 paginiFI Market Research TemplateAnonymous DCxx70Încă nu există evaluări