Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Qualitative & Quantative
Încărcat de
A.M.S. CLUBTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Qualitative & Quantative
Încărcat de
A.M.S. CLUBDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Hemchand Yadav vishva vidyalaya,Durg
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE
RESEARCH
PH.D.Course Work(2018-19)
Seminar Presentation
(22/11/2018)
KALYAN P.G. COLLEGE BHILAI NAGAR ( C.G.)
Dr.Anita Shrivastava Mrs. Sarika Sharma
(Guide) (Ph.d.Scholar)
Introduction
• Research is the most widely used tool to increase
and brush-up the stock of knowledge about
something and someone. In the field of
marketing, business, sociology, psychology,
science & technology, economics, etc. there are
two standard ways of conducting research, i.e.
qualitative research or quantitative research.
While the qualitative research relies on verbal
narrative like spoken or written data,
the quantitative research uses logical or statistical
observations to draw conclusions.
DEFINATION
Qualitative research is used to gain an in-depth understanding of human
behaviour, experience, attitudes, intentions, and motivations, on the basis of
observation and interpretation, to find out the way people think and feel. It is a
form of research in which the researcher gives more weight to the views of the
participants. Case study, grounded theory, ethnography, historical and
phenomenology are the types of qualitative research
Quantitative research is a form of research that relies on the methods of
natural sciences, which produces numerical data and hard facts. It aims at
establishing cause and effect relationship between two variables by using
mathematical, computational and statistical methods. The research is also known as
empirical research as it can be accurately and precisely measured.
TYPES OF QUANTITATIVE
1.Experimental Research: This research is guided specifically by a hypothesis. It
uses manipulation of one or more variable to determine effect on dependent variable.
It also uses controlled testing to understand casual process.
2.Survey Research: It is a very commonly used method of collecting information
about a population of interest done mainly through questionnaires or sampling. It
allows researches to judge behaviours and present findings in most accurate way.
3.Correlational Research: It tests the relationship between two variables. here, a
level of manipulation is involved with the specific variables being researched. For
example it establishes effect of A on B and how that effects relationship of A and B.
4.Causal-comparative Research: It examines the relationship between difference
that exists among members of population and possible causes of difference. In short,
it uncovers a cause and effect relationship.
TYPES OF QUALITATIVE
• Field research This technique requires the researchers to literally go to the field (or
the environment the case requires) and to observe the subject in its natural
environment.
• Ethnography This is a little bit different from the field research. While in field
research, the researcher will mix amongst the participants and take notes, while
ethnographer will make observations from the outside.
• Case studies This involves analysis of a specific case. Unlike Field and ethnographic
research, it only focuses on one particular case study, person or activity.
• Grounded theory In this method, the grounded theory researchers try to develop
theories about the phenomena that is the subject of the study, however these theories
must be based on observations.
•Phenomenology This is a philosophical approach, which is undertaken understand
different perspectives and how other’s view may vary from the general perceptions
based on subjective interpretations.
TOOLS
Quantitative Qualitative
•TELEPHONE SURVEY •IN DEPTH INTERVIEW
•ONLINE SURVEY •FOCUS GROUPS
•IN PERSON SURVEY •ASYNCHRONOUS GROUPS
•MOBILE SURVEY •QUALITATIVE TECHNIQUES
•ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES
BASIS FOR COMPARISON QUALITATIVE RESEARCH QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
Meaning Qualitative research is a method of inquiry Quantitative research is a research method
that develops understanding on human and that is used to generate numerical data and
social sciences, to find the way people hard facts, by employing statistical, logical
think and feel. and mathematical technique.
Nature Holistic Particularistic
Approach Subjective Objective
Research type Exploratory Conclusive
Reasoning Inductive Deductive
Sampling Purposive Random
Data Verbal Measurable
Inquiry Process-oriented Result-oriented
Hypothesis Generated Tested
Elements of analysis Words, pictures and objects Numerical data
Objective To explore and discover ideas used in the To examine cause and effect relationship
ongoing processes. between variables.
Methods Non-structured techniques like In-depth Structured techniques such as surveys,
interviews, group discussions etc. questionnaires and observations.
Result Develops initial understanding Recommends final course of action
Quantitative Research Vs Qualitative Research
Comparison
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Comparative Education in Developing CountriesDocument16 paginiComparative Education in Developing CountriesPoppi HSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intervening VariableDocument32 paginiIntervening VariableJhedine Sumbillo - TabaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- AncovaDocument18 paginiAncovaJoanne LewÎncă nu există evaluări
- PR 1.2 Different Types of ResearchDocument17 paginiPR 1.2 Different Types of ResearchAizel Joyce Domingo100% (1)
- Differentiate Qualitative and Quantitative DesignDocument3 paginiDifferentiate Qualitative and Quantitative DesignJanine Pelayo100% (1)
- (Report) Data Gathering Procedure (Group II)Document58 pagini(Report) Data Gathering Procedure (Group II)Norjenn BarquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Outline PDFDocument12 paginiCourse Outline PDFBelen HumiwatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education Assesment CH #1Document29 paginiEducation Assesment CH #1Waqas Lucky100% (1)
- Planning Survey ResearchDocument6 paginiPlanning Survey ResearchOxfamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview of Research ProcessDocument3 paginiOverview of Research ProcessKenneth GuingabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measuring Quality in Qualitative ResearchDocument13 paginiMeasuring Quality in Qualitative ResearchAbhilash PonnamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualities of Good Research DesignDocument4 paginiQualities of Good Research DesignMuhammad Adeel100% (4)
- What Are We Talking About When We Talk About Impact?Document22 paginiWhat Are We Talking About When We Talk About Impact?impactsp2Încă nu există evaluări
- Research Course Outline For Resarch Methodology Fall 2011 (MBA)Document3 paginiResearch Course Outline For Resarch Methodology Fall 2011 (MBA)mudassarramzanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychometry Unit 2Document18 paginiPsychometry Unit 2Deepti SwamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advance Research Method 01Document33 paginiAdvance Research Method 01owaishazaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meaning of ResearchDocument11 paginiMeaning of ResearchRahulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study MethodDocument18 paginiCase Study MethodsubhashreeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Feedback On Teachers and Its Practices: 1. Clarify Context and FocusDocument4 paginiStudent Feedback On Teachers and Its Practices: 1. Clarify Context and FocusVishal KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Survey 2011-SeniorsDocument11 paginiStudent Survey 2011-SeniorsBrendan Lewis DelgadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sociometrc TechniqueDocument6 paginiSociometrc Techniqueprash_hingeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experimental and Quasi Experimental Designs For Research PDFDocument2 paginiExperimental and Quasi Experimental Designs For Research PDFAmy100% (1)
- Ethnographic ResearchDocument6 paginiEthnographic ResearchKatherine Lapore Llup - Porticos100% (1)
- Non-Probability Sampling 1. Incidental or Accidental SaplingDocument2 paginiNon-Probability Sampling 1. Incidental or Accidental SaplingheyheyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research ObjectiveDocument16 paginiResearch ObjectiveMuhammad AbdurrahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mixed Methods - PresentationDocument16 paginiMixed Methods - PresentationObote DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Item AnalysisDocument2 paginiItem Analysisapi-26570979Încă nu există evaluări
- Intro To PsychologyDocument29 paginiIntro To PsychologyNardeep GehlawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classroom Assessment TechniquesDocument4 paginiClassroom Assessment TechniquesFabricio FurtadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Collecting Techniques: Ebede. Ary EkuamwerkDocument70 paginiData Collecting Techniques: Ebede. Ary EkuamwerkkemimeÎncă nu există evaluări
- QuestionnaireDocument7 paginiQuestionnaireAnjo Pasiolco CanicosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 :THE RESEARCH DESIGNDocument1 paginăChapter 7 :THE RESEARCH DESIGNalia.delareineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Questions and HypothesesDocument15 paginiResearch Questions and HypothesesSakshyam KhatiwadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument33 paginiNature of Inquiry and ResearchJoshua VicenteÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 Qualitative Research PDFDocument4 pagini15 Qualitative Research PDFAdam Bin Abu BakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2: Ethics and Business ResearchDocument10 paginiUnit 2: Ethics and Business Researchmba departmentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysing Quantitative DataDocument33 paginiAnalysing Quantitative DataSumayyah ArslanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Hypothesis & TypesDocument11 paginiResearch Hypothesis & TypesMahendra Dhoni100% (1)
- OUTLINE Statistics in EducationDocument5 paginiOUTLINE Statistics in EducationAshiq ShahzadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantitative Vs Qualitative ResearchDocument36 paginiQuantitative Vs Qualitative ResearchNor Fadzleen100% (1)
- Consumer BehaviourDocument1 paginăConsumer BehaviourMimi MyshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experimental ResearchDocument1 paginăExperimental ResearchCharmen Diaz RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Write A Research ArticleDocument3 paginiHow To Write A Research Articlejaden rocksÎncă nu există evaluări
- ValidityDocument17 paginiValidityifatimanaqvi1472100% (1)
- Thesis Writing Guide: The Preparation StageDocument35 paginiThesis Writing Guide: The Preparation StageavtandiarovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research PhilosophyDocument4 paginiResearch Philosophynad101100% (1)
- VARIABLESDocument19 paginiVARIABLESBellyJane LarracasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Research ProcessDocument43 paginiChapter 2 Research ProcessMebruka Abdul RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theresa Hughes Data Analysis and Surveying 101Document37 paginiTheresa Hughes Data Analysis and Surveying 101Youngtae KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Pretest and Pilot StudyDocument31 pagini6 Pretest and Pilot StudyChandan ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paradigm Shifts in MathematicsDocument16 paginiParadigm Shifts in MathematicsAaditya Narayan PathakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mixed Method ResearchDocument15 paginiMixed Method ResearchLaw Xian HernÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment Educational PsychologyDocument7 paginiAssignment Educational PsychologyNouman AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questionnaire DesignDocument66 paginiQuestionnaire DesignNavuru JagannadhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enrichment and AccelerationDocument65 paginiEnrichment and AccelerationJomar Carabot100% (1)
- Experimental Research DesignDocument3 paginiExperimental Research Designnabeel100% (1)
- Qualatitive Vs Quantative ResearchDocument5 paginiQualatitive Vs Quantative ResearchKashif MehmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualitative & Quantitative ResearchDocument4 paginiQualitative & Quantitative Researchsajid bhattiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative ResearchDocument5 paginiDifference Between Qualitative and Quantitative ResearchRegine AvelinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sara Arshad 030386 BS English VII Research Methodology What Is ResearchDocument3 paginiSara Arshad 030386 BS English VII Research Methodology What Is ResearchSarah ArshadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative DataDocument4 paginiDifference Between Qualitative and Quantitative Datasisay gebremariamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classroom Action Research FixDocument16 paginiClassroom Action Research FixIman NugrohoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eapp Q2 W5 Ref.Document57 paginiEapp Q2 W5 Ref.not deniseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research MethodologyDocument13 paginiResearch MethodologyVivian A. MendezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Methodology (RM) Solved MCQs (Set-4)Document5 paginiResearch Methodology (RM) Solved MCQs (Set-4)Ritika SaraswatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 11 1ST Quarter Periodical Test Schedule T1 2023 2024Document5 paginiGrade 11 1ST Quarter Periodical Test Schedule T1 2023 2024cabugocrissethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research MethodDocument26 paginiResearch Methodabrham haileyesusÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 HUMSS Lesson 1Document40 pagini11 HUMSS Lesson 1tabojane48Încă nu există evaluări
- Sample Chapter 3Document5 paginiSample Chapter 3Jessie AndreiÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Week1 - Lesson 1) Origin of The UniverseDocument3 pagini(Week1 - Lesson 1) Origin of The UniverseLysa TurredaÎncă nu există evaluări
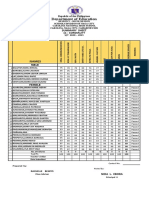
- Summary of Grades 3rd QTRDocument19 paginiSummary of Grades 3rd QTRRonald RosalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1, RESEARCH METHODOLOGY (MBA General 1st Semseter) by Dr. Qamar ZamanDocument31 paginiLecture 1, RESEARCH METHODOLOGY (MBA General 1st Semseter) by Dr. Qamar ZamanAsjad Jamshed91% (22)
- Participant and Non-Participant Observation.Document4 paginiParticipant and Non-Participant Observation.Bushra Ali100% (2)
- RSC2601 Exam Preparation - Questions and Answers: AdelesDocument237 paginiRSC2601 Exam Preparation - Questions and Answers: AdelesBarbbra MalazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example Research Task Sheet #1Document7 paginiExample Research Task Sheet #1Deo AyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Flow CaseDocument3 paginiDiagnostic Flow CaseIntan PermataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualitative Action Research DesignDocument2 paginiQualitative Action Research DesignKotrun NadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Are Moral Properties Natural Properties?Document3 paginiAre Moral Properties Natural Properties?Marceli PotockiÎncă nu există evaluări
- English 8 DLP q4 Week 2Document3 paginiEnglish 8 DLP q4 Week 2Daniel Fabian100% (1)
- Research 8 Quarter 1 Module 3Document22 paginiResearch 8 Quarter 1 Module 3marvielse100% (1)
- MCE Cambridge Primary Science 4 Student's Book (2nd Edition)Document178 paginiMCE Cambridge Primary Science 4 Student's Book (2nd Edition)Astri Mustika dewiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Perfect Biology Lab ReportDocument17 paginiThe Perfect Biology Lab ReportJenniferÎncă nu există evaluări
- Be Ssssss SssssssssDocument12 paginiBe Ssssss SsssssssscaroletopularÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypothesis TestingDocument128 paginiHypothesis TestingJulia Nicole OndoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NSPNational Scholarship SchemeDocument4 paginiNSPNational Scholarship Schemenav33nÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finch Curriculum Table FinalDocument3 paginiFinch Curriculum Table Finalapi-241054379Încă nu există evaluări
- Despre Celsius Și Kelvin - OdpDocument8 paginiDespre Celsius Și Kelvin - OdpAni AlexandruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 2 Science Planning DocumentDocument14 paginiYear 2 Science Planning Documentapi-339908787Încă nu există evaluări
- Pengaruh Terapi Relaksasi Terhadap Tingkat Stres Kerja PerawatDocument7 paginiPengaruh Terapi Relaksasi Terhadap Tingkat Stres Kerja PerawatAnonymous dRAu54Încă nu există evaluări
- BPSC-101E XpsDocument1 paginăBPSC-101E XpsNIKHIL KANAUJIYAÎncă nu există evaluări