Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Liver Function Test
Încărcat de
Sheldon Miller0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
25 vizualizări22 paginiLFTs interpretation....
errors: elevated >10 fold not <, elevated > 3 fold not <.
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentLFTs interpretation....
errors: elevated >10 fold not <, elevated > 3 fold not <.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
25 vizualizări22 paginiLiver Function Test
Încărcat de
Sheldon MillerLFTs interpretation....
errors: elevated >10 fold not <, elevated > 3 fold not <.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 22
LIVER FUNCTION
TEST
By Sheldon Miller &
Dominique Scott
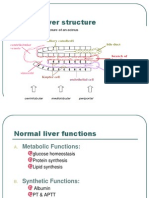
Liver Disease- Overview
● Described as any abnormal state of hepatic
function characterized mainly by:
○ Hx- Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dark
urine, changes in stool, weight changes, peripheral
edema, etc.
○ O/E- Abdominal mass/distension, jaundice, peripheral
edema, portosystemic shunting, ascites, hepatomegaly,
JVP, muscle wasting
○ Laboratory findings- Abnormal AST, ALT, ALP, GGT,
LDH, 5NT, bilirubin, PT, total protein, albumin levels
Liver Screen
● A typical liver screen includes:
○ LFTs
○ Coagulation screen
○ Viral -Hepatitis A,B &C, EBV, CMV,
○ Autoimmune- Anti-mitochondrial antibody (AMA), Anti-smooth
muscle antibody (ASMA), Anti-liver/kidney microsomal antibodies
(Anti-LKM), Antinuclear antibody (ANA), p-ANCA
○ Immunoglobulins – IgM/IgG
○ Alpha-1 Antitrypsin – Alpha-1 Antitrypsin deficiency
○ Serum Copper – Wilson’s disease
○ Ceruloplasmin – Wilson’s disease
○ Ferritin – Haemochromatosis
Liver Function Test
● Defined as a group of tests used to evaluate the
current physiological state of the liver. They include:
○ Ductal/Excretory- Bilirubin (total, direct, indirect), Alkaline
phosphatase (ALP), Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT)
○ Cellular integrity/necroinflammatory indices -Aspartate
aminotransferase (AST), ALT, Alkaline phosphatase (ALP),
GGT, 5’-nucleotidase(5NT)
○ Synthetic
■ Total protein(including clotting factors, acute phase
reactants(i.e. CRP), AFP, albumin, prothrombin time
(PT), lipid profile
ALT
● Mainly found in the liver
● Normal range:
○ Male: 29- 33 U/L
○ Female: 19-25 U/L
● ALT Ddx
○ Acute or chronic viral hepatitis, steatohepatitis, acute
Budd-Chiari syndrome, ischemic hepatitis,
hemochromatosis, medications/toxins, autoimmune,
alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency, wilson disease, celiac
disease
AST
● Non-specific- found in the liver, heart, muscle, and
other places
● Normal Range:
○ Male: 10- 40 U/L
○ Female: 9-32 U/L
● AST Ddx
○ Ethanol-related, steatohepatitis, cirrhosis, non-hepatic
(hemolysis, myopathy, thyroid disease, exercise)
Albumin
● Normal range
○ 40-60 g/L
○ Suggests an acute process in pathologies
○ Ddx: viral hepatitis, choledocolithiasis
● Low Albumin
○ <40 g/L
○ Suggests a chronic process
○ Ddx: cirrhosis, cancer, and other chronic liver disease
Prothrombin Time
● Normal Range
○ 11.0-13.7 seconds
● Prolonged
○ > 13.7 seconds
○ Ddx: DIC, Lupus anticoagulant, warfarin therapy,
factor I, II, V, VII, or X deficiency, AND
■ Hepatic: Vit K deficiency due to malabsorption,
significant hepatocellular dysfunction
○ Failure of correction with Vit K administration suggests
severe hepatocellular injury
ALP
● Indicates high bone turnover
● Ddx: Intrahepatic, or extrahepatic
● Workup: serum calcium, PTH, 25-hydroxy Vit
D, X-ray & bone scintigraphy
● Confirming hepatic origin
○ GGT or 5NT elevated if in hepatic origin
○ + elevated bilirubin may not require
confirmation
ALP Workup
ALP Workup
Bone Scintigraphy
GGT
● Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT)- enzyme found mainly in
the liver and is a useful marker for detecting bile duct pathologies
● Isolated GGT
○ Indicates high bone turnover
○ Ddx: bone, placenta
○ Workup: serum calcium, PTH, 25-hydroxy Vit D, X-ray
& bone scintigraphy
○ Confirming hepatic origin
■ GGT or 5NT elevated if in hepatic origin
■ + elevated bilirubin may not require confirmation
Classification
● Abnormal LFTs may be classified according to pattern:
○ Hepatocellular
○ Cholestatic
○ Mixed
○ Isolated Hyperbilirubinemia
OR
● According to duration:
○ Acute(<6 wks)
○ Subacute (6 wks-6 mths)
○ Chronic(>6 mths)
Hepatocellular
● Pattern:
○ Markedly elevated aminotransferases(> 10 fold)
vs elevated ALP levels (> 3 fold)
○ Bilirubin can be elevated
○ Synthetic function may be abnormal
● Ddx:
○ ALT pre-dominant, or AST-predominant
Cholestatic
● Pattern:
○ Markedly elevated ALP(<10 fold) vs aminotransferases (<3 fold)
○ Bilirubin can be elevated
○ Synthetic function may be abnormal
● Ddx:
○ Hepatobiliary: Bile duct obstruction, primary biliary cirrhosis,
primary sclerosing cholangitis, medication-induced, infiltration
(sarcoidosis, amyloidosis, lymphoma, etc.), cystic fibrosis, liver
mets, cholestasis
○ Non-Hepatobiliary: Bone disease, pregnancy, chronic renal
failure, lymphoma or other malignancies, congestive heart failure,
childhood growth, infection or inflammation
Isolated Hyperbilirubinemia
● Total- 0- 1.0 mg/dL or 0-17 µmol/L
● Fractionated:
○ Conjugated(direct)- 0-0.4 mg/dL or 0-7 µmol/L
■ Suggests decreased bile ductule excretion or
hepatocyte pigment leakage into the serum
○ Unconjugated(indirect)- 0.3- 1.0 mg/dL or 5-17
µmol/L
■ Suggests overproduction, impaired uptake, or
impaired conjugation of bilirubin
Ddx- Unconjugated
● Increased bilirubin production- extravascular hemolysis,
extravasation of blood into tissues, intravascular
hemolysis, dyserythropoiesis, wilson disease
● Impaired hepatic bilirubin uptake
○ CCF, portosystemic shunts, gilbert syndrome, rifampin,
probenecid, flavaspadic acid, bunamiodyl
● Impaired bilirubin conjugation
○ Crigler-Najjar syndrome I & II, gilbert syndrome,
neonates, hyperthyroidism, ethinyl estradiol, liver
diseases(chronic hepatitis, advanced cirrhosis)
Ddx- Conjugated
● Canalicular organic anion transport- Dubin- Johnson syndrome
● Impaired sinusoidal bilirubin uptake
● Extrahepatic cholestasis
○ Choledocholithiasis, Intrinsic and extrinsic tumors(cholangiocarcinoma,
pancreatic cancer), Primary sclerosing cholangitis, AIDS cholangiopathy,
Acute/chronic pancreatitis, strictures, parasitic(i.e. ascaris, liver flukes)
● Intrahepatic cholestasis
○ Viral, alcoholic & chronic hepatitis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis,primary
biliary cholangitis, drugs(alkylated steroids, chlorpromazine, herbal
supplements, arsenic), Sepsis(+other hypoperfusion states), total
parenteral nutrition, postoperative, organ transplant, sickle cell hepatic
crisis, pregnancy, end stage liver disease
Summary
References
● Pratt DS, Kaplan MM. Evaluation of abnormal liver-enzyme
results in asymptomatic patients. N Engl J Med 2000;
342:1266.
● Kwo PY, Cohen SM, Lim JK. ACG Clinical Guideline:
Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries. Am J Gastroenterol
2017; 112:18.
● https://www.uptodate.com/contents/approach-to-the-patient-
with-abnormal-liver-biochemical-and-function-
tests?source=bookmarks_widget
● https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482489/
● https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK302/
Thank
You
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Liver Function testsDocument3 paginiLiver Function testslaithmasannatÎncă nu există evaluări
- ALP and GGTDocument9 paginiALP and GGTRazeen RiyasatÎncă nu există evaluări
- CirrhosisDocument10 paginiCirrhosisJames FlanneryÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLD 2Document5 paginiCLD 2macdominic22Încă nu există evaluări
- Liver Function Tests and EnzymesDocument90 paginiLiver Function Tests and EnzymesNaji Mohamed Alfatih100% (1)
- Chronic Liver Disease PresentationDocument202 paginiChronic Liver Disease PresentationMohammadAbdurRahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pemeriksaan Fungsi Hati .: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH)Document51 paginiPemeriksaan Fungsi Hati .: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH)kiki rawitriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abnormal LFTsDocument2 paginiAbnormal LFTsRenu RosyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approach To TransaminitisDocument20 paginiApproach To Transaminitisparik2321Încă nu există evaluări
- Liver CirrhosisDocument50 paginiLiver CirrhosisMK CameraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Function TestsDocument48 paginiLiver Function TestsAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (12)
- Liver Function Tests (LFTS) : Git Block 1 Lecture Dr. Usman GhaniDocument26 paginiLiver Function Tests (LFTS) : Git Block 1 Lecture Dr. Usman Ghaniraanja2100% (1)
- Liver Function Test (LFT) OverviewDocument26 paginiLiver Function Test (LFT) Overviewanisa rachmitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approach To Jaundice (1) .PPT ALAWAJIDocument28 paginiApproach To Jaundice (1) .PPT ALAWAJIayuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDocument22 paginiAlcoholic Liver DiseaseMiraen MkÎncă nu există evaluări
- He Pat OlogyDocument18 paginiHe Pat Ologykhan100% (1)
- Liver Function Tests ExplainedDocument40 paginiLiver Function Tests ExplainedanojÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypolipidemic AgentsDocument39 paginiHypolipidemic AgentsAC ACÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anaesthesia For Liver DieseaseDocument43 paginiAnaesthesia For Liver DieseaseShehan WijayasiriwardanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Function TestsDocument29 paginiLiver Function TestsJohnree A. EvangelistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Liver Tests and DiseasesDocument65 paginiUnderstanding Liver Tests and DiseasesDokter MuhammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curs-5-Mai 2015 - Ficat Si Pancreas - Final de Prezentat-Recovered)Document1.110 paginiCurs-5-Mai 2015 - Ficat Si Pancreas - Final de Prezentat-Recovered)Badea Andreea CristinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AbnormalL Liver Function Test 2012Document59 paginiAbnormalL Liver Function Test 2012Nayan MaharjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Function TestDocument5 paginiLiver Function TestAnne Sison100% (1)
- Pemeriksaan Fungsi Hati, DR - DiahDocument42 paginiPemeriksaan Fungsi Hati, DR - DiahYuliana LatifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penyakit Ginjal KronikDocument37 paginiPenyakit Ginjal KronikKusaini Saddam AkbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- QuartoDocument76 paginiQuartoÁlesson Marcelo Mudelão SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICC2 (079) Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDocument24 paginiICC2 (079) Alcoholic Liver DiseaseMariam Mokhtar ZedanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pemeriksaan Fungsi HatiDocument46 paginiPemeriksaan Fungsi HatiNadyaWevtÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPH Surgery Didactics Gallblader To PancreasDocument170 paginiSPH Surgery Didactics Gallblader To PancreasAbegail IbañezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hepatocellular CarcinomaDocument45 paginiHepatocellular Carcinomamhean azneitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver_testsDocument20 paginiLiver_testsnudu.candlesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jaundice MasterDocument76 paginiJaundice MasterVinoth KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Function Tests Diagnostic GuideDocument2 paginiLiver Function Tests Diagnostic GuideostarburstoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Kidney Injury: Sarah Abigail C. Ong Siu Second Year ResidentDocument41 paginiAcute Kidney Injury: Sarah Abigail C. Ong Siu Second Year ResidentSarah Ong SiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- JaundiceDocument6 paginiJaundiceNiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver function tests, ultrasound, biopsy guide to interpreting resultsDocument14 paginiLiver function tests, ultrasound, biopsy guide to interpreting resultsshihochan100% (2)
- Hepatocellula R CarcinomaDocument45 paginiHepatocellula R Carcinomamhean azneitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4-Hepatobiliary DiseaseDocument22 pagini4-Hepatobiliary Diseaseabdalmajeed alshammaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interpretation of Abnormal LftsDocument22 paginiInterpretation of Abnormal LftsIsaac MwangiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neonatal Cholestasis GuideDocument28 paginiNeonatal Cholestasis GuideHafsaJabbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Case PresentationDocument49 paginiClinical Case PresentationRUSSELL CILOTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument18 paginiDrug StudyAntonethe DemdamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Željko Puljiz, MD., PHDDocument67 paginiŽeljko Puljiz, MD., PHDpuljiz7Încă nu există evaluări
- L25 CLD-2Document55 paginiL25 CLD-2S sÎncă nu există evaluări
- CME Acute PancreatitisDocument17 paginiCME Acute PancreatitisDa JunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Long Case JaundiceDocument5 paginiLong Case JaundiceNadia SalwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatty Liver Disease: A Growing EpidemicDocument31 paginiFatty Liver Disease: A Growing EpidemicTia AriantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approach To: Liver Function Tests: Dr. Ashish October 11, 2019Document32 paginiApproach To: Liver Function Tests: Dr. Ashish October 11, 2019Ashish SatyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approach To JaundiceDocument55 paginiApproach To JaundicePankaj IngleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Objective 6Document13 paginiObjective 6suyog raj gautamÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRUGs FOR KIDNEYDocument33 paginiDRUGs FOR KIDNEYaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of Biochemical Tests in Liver Diseases: Prof. Mohamed Sharaf-EldinDocument46 paginiAssessment of Biochemical Tests in Liver Diseases: Prof. Mohamed Sharaf-EldinKomang YogatamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 060 CLIN+PATH+43s Liver+Function+TestDocument43 pagini060 CLIN+PATH+43s Liver+Function+TestMSKCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Function TesDocument58 paginiLiver Function TesnoffrizalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Studi Kasus Penyakit HatiDocument27 paginiStudi Kasus Penyakit HatiEfraim MangalukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardio HPNDocument12 paginiCardio HPNHajime NakaegawaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RSI Embryo NotesDocument1 paginăRSI Embryo NotesSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinds of SynapsesDocument1 paginăKinds of SynapsesSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Common Gospel ChordsDocument25 pagini10 Common Gospel ChordsANDYPAS250% (2)
- General Surgery Differentials, Staging, EtcDocument3 paginiGeneral Surgery Differentials, Staging, EtcSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinds of SynapsesDocument1 paginăKinds of SynapsesSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem Lab 3 Unit 2Document4 paginiChem Lab 3 Unit 2Sheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- RSI Embryo NotesDocument1 paginăRSI Embryo NotesSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- What I Don't Know-ArchiveDocument2 paginiWhat I Don't Know-ArchiveSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rough Work Re-EditsDocument5 paginiRough Work Re-EditsSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Notes 1Document3 paginiBiology Notes 1Sheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cuban RevolutionDocument2 paginiCuban RevolutionSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asdfas LKJDocument1 paginăAsdfas LKJSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Notes 1Document3 paginiBiology Notes 1Sheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cape:Biology Internal AssesmentDocument1 paginăCape:Biology Internal AssesmentSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument1 paginăCirculatory SystemSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Notes 1Document3 paginiBiology Notes 1Sheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATP Production Through Tissue RespirationDocument28 paginiATP Production Through Tissue RespirationSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gravimetric methods analysis guideDocument21 paginiGravimetric methods analysis guideSheldon Miller100% (1)
- BiodieselDocument1 paginăBiodieselSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gravimetric methods analysis guideDocument21 paginiGravimetric methods analysis guideSheldon Miller100% (1)
- BenzeneDocument1 paginăBenzeneSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBBScocurricularformDocument2 paginiMBBScocurricularformAmaara WhiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assembling of The NucleusDocument3 paginiAssembling of The NucleusSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ohm's Law and Electric Current ExplainedDocument2 paginiOhm's Law and Electric Current ExplainedSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhotosynthesisDocument2 paginiPhotosynthesisSheldon MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Focus Shooting Method CourseDocument48 paginiThe Focus Shooting Method CourseKobiXDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian War of Independence 1857 - Part 2Document150 paginiIndian War of Independence 1857 - Part 2BISWAJIT MOHANTYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Development of Manually Operated ReaperDocument8 paginiDesign and Development of Manually Operated ReaperIOSRjournalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vectors FoundationDocument8 paginiVectors FoundationNaning RarasÎncă nu există evaluări
- STPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes Short Notes PDFDocument2 paginiSTPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes Short Notes PDFbendanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smart Asthma ConsoleDocument35 paginiSmart Asthma ConsoleMohamad Mosallam AyoubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Information for 2x660 MW Lube Oil PumpsDocument93 paginiProject Information for 2x660 MW Lube Oil PumpsghostamirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel 17-4PH MmpdsDocument18 paginiSteel 17-4PH MmpdsManoj ManoharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 43-101 Technical Report Quimsacocha, February 2009Document187 pagini43-101 Technical Report Quimsacocha, February 2009Marco Vinicio SotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- M2030 PA300 Siren Data Sheet 5-2021Document2 paginiM2030 PA300 Siren Data Sheet 5-2021parak014Încă nu există evaluări
- Exercise Questions (Materials) .: BFT 112 Introduction To EngineeringDocument1 paginăExercise Questions (Materials) .: BFT 112 Introduction To EngineeringSK DarsyanaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Chemistry Lecture Exercise 2 Mole-Mole Mass-Mass: Sorsogon State CollegeDocument2 paginiAnalytical Chemistry Lecture Exercise 2 Mole-Mole Mass-Mass: Sorsogon State CollegeJhon dave SurbanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tyco TY8281 TFP680 - 03 - 2023Document17 paginiTyco TY8281 TFP680 - 03 - 2023First LAstÎncă nu există evaluări
- M O Publications Index Worldwide CoverageDocument5 paginiM O Publications Index Worldwide CoverageloloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Durango GS 6-7 Helitack OutreachDocument4 paginiDurango GS 6-7 Helitack OutreachdcgmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Masterbrand Guidelines - September 2012: Confidential - For Internal Use OnlyDocument35 paginiMasterbrand Guidelines - September 2012: Confidential - For Internal Use OnlyDemerson CamposÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spcr-TagbayaganDocument76 paginiSpcr-TagbayaganReycia Vic QuintanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mahavir Glass Proforma InvoiceDocument2 paginiMahavir Glass Proforma Invoicemahendra patelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orpheus' Tragic Love and Quest to Save EurydiceDocument3 paginiOrpheus' Tragic Love and Quest to Save EurydiceShiedrose Allaina ArangorinÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPECIFIC GRAVITY - DENSITY OF HYDRAULIC CEMENT (IS - 4031-Part 11-1988)Document6 paginiSPECIFIC GRAVITY - DENSITY OF HYDRAULIC CEMENT (IS - 4031-Part 11-1988)Pritha DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Filtros MaquinasDocument34 paginiFiltros MaquinasAndres AlfonzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Science EnvironmentDocument28 paginiGeneral Science EnvironmentHamza MujahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rooftop Solar PV Opportunity in Tempe, Arizona: A Consultancy PlanDocument4 paginiRooftop Solar PV Opportunity in Tempe, Arizona: A Consultancy PlanAli KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Your Song RitaDocument1 paginăYour Song Ritacalysta felix wÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hart Transmitter Calibration: Application NoteDocument8 paginiHart Transmitter Calibration: Application NoteThulasi Raman KowsiganÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2017 Scoring Materials Math g6Document119 pagini2017 Scoring Materials Math g6KRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Misamis Occidental Plans to Protect Aquamarine ResourceDocument8 paginiMisamis Occidental Plans to Protect Aquamarine ResourcejelosalisaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traxonecue Catalogue 2011 Revise 2 Low Res Eng (4!5!2011)Document62 paginiTraxonecue Catalogue 2011 Revise 2 Low Res Eng (4!5!2011)Wilson ChimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework Helpers - Chemistry PDFDocument311 paginiHomework Helpers - Chemistry PDFTamby100% (1)
- Iot Finals Clap Switch Group 5Document15 paginiIot Finals Clap Switch Group 5RICHYBOY SALACÎncă nu există evaluări