Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
8085 Addressing Modes
Încărcat de
Anil Vaidya0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
33 vizualizări5 paginiThe document discusses different addressing modes of the 8085 CPU. There are 5 addressing modes: immediate, register direct, register indirect, implicit, and direct. Immediate addressing encodes the operand within the instruction itself. Register direct addressing specifies the operand register in the opcode. Register indirect addressing uses a register pair to hold the memory address of the operand. Implicit addressing assumes the accumulator as the operand without specifying its address.
Descriere originală:
Intel 8085 addressing modes
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThe document discusses different addressing modes of the 8085 CPU. There are 5 addressing modes: immediate, register direct, register indirect, implicit, and direct. Immediate addressing encodes the operand within the instruction itself. Register direct addressing specifies the operand register in the opcode. Register indirect addressing uses a register pair to hold the memory address of the operand. Implicit addressing assumes the accumulator as the operand without specifying its address.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
33 vizualizări5 pagini8085 Addressing Modes
Încărcat de
Anil VaidyaThe document discusses different addressing modes of the 8085 CPU. There are 5 addressing modes: immediate, register direct, register indirect, implicit, and direct. Immediate addressing encodes the operand within the instruction itself. Register direct addressing specifies the operand register in the opcode. Register indirect addressing uses a register pair to hold the memory address of the operand. Implicit addressing assumes the accumulator as the operand without specifying its address.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 5
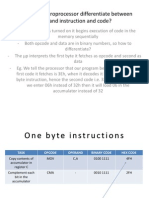
8085 Addressing Modes
The CPU executes any program by processing (or Operating On)
ONE BYTE (8 bits) at a time.
For processing the BYTE (OPERAND) the CPU must access the
BYTE.
The addressing mode specifies the way in which this Operand can
be accessed by CPU.
Immediate Addressing Mode
Register Addressing Mode
Direct Addressing Mode
Indirect Addressing Mode
Implicit Addressing Mode
Immediate Addressing
In this mode the Operand is given along with the Instruction itself
i.e. The Operation Code (OPCODE) is immediately followed by the
Operand.
For 8085 CPU, the Opcode is always ONY BYTE (8 Bits) for all
instructions.
The Operand can be ONE BYTE or TWO BYTES.
E.g. MVI A, #9E h This is a mnemonic representation (assembly
language) of the instruction.
CPU does not understand this. It understand hex code only.
Hence the above instruction is coded as 3E, 9E.
The first BYTE 3E is OPCODE and the second BYTE 9E is
OPERAND.
Hence this instruction is a TWO BYTE instruction.
Another example is LXI H, #45CD h
Opcode format is 21, CD, 45 (THREE BYTE INSTRUCTION)
Register Direct Addressing
In this mode the Operand is available within any of the registers
of CPU. (e.g. A, B, C, D, E, H, L)
These are mostly ONE BYTE instructions.
The address of the concerned register/s is specified in the
OPCODE itself.
In addition to the address of register/s the OPCODE also specifies
the OPERATION to be performed.
E.g. MOV C, H ………. Move (copy) the data byte from H reg. to C
reg.
Opcode is 4C & it is decoded as 0100 1100
01 stands for MOV operation, 001 stands for destination reg. C &
100 stands for source reg. H
Another example is ADD, B
Opcode is 80 & it is decoded as 1000 0000
10000 stands for ADD operation & 000 stands for source reg. B
Register Indirect Addressing
In this mode the address for OPERAND is specified indirectly, by a
register pair.
E.g. LDAX, B ……… Load (copy) the ‘byte’ (8 bit data) into
accumulator from the memory location whose address (16 bit) is
given by BC pair of registers.
Opcode is 0A & it is decoded as 0000 1010
Another example is MOV B, M …… Move (Copy) byte from memory
location to B reg.
The address of the memory location is given by HL pair of
registers.
In both cases the address of the OPERAND (byte to be copied) is
not given directly in the instruction itself but is obtained by the
CPU from a specified register pair.
Implicit Addressing
In this mode the address of the OPERAND is IMPLICIT (granted).
These instructions operate on the contents of the accumulator &
address of the operand need not be specified explicitly.
E.g. RAL ….. Rotate Accumulator Left Through Carry
CMA ….. Compliment the CONTENTS of Accumulator
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Practical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationDe la EverandPractical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 6251119711560401156Document26 pagini5 6251119711560401156Vineesh M MadathodiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conceptual Programming: Conceptual Programming: Learn Programming the old way!De la EverandConceptual Programming: Conceptual Programming: Learn Programming the old way!Încă nu există evaluări
- 8051 Instruction SetDocument98 pagini8051 Instruction SetSmt.N.Vasantha Gowri Assistant ProfessorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ilovepdf Merged-8Document56 paginiIlovepdf Merged-8Kobe MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assembly LanguageDocument15 paginiAssembly LanguageLukeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8051 Instruction SetDocument79 pagini8051 Instruction Setgsathishbsa100% (1)
- Microprocessor 8085 InstructionDocument9 paginiMicroprocessor 8085 InstructionRiazahmed9Încă nu există evaluări
- 8051 Instruction Set Rv01Document81 pagini8051 Instruction Set Rv01lizhi0007Încă nu există evaluări
- Module 2Document14 paginiModule 2yashmit maviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microprocessors - III: Yashar HajiyevDocument83 paginiMicroprocessors - III: Yashar HajiyevMurad QəhramanovÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8085 Addressing ModesDocument14 pagini8085 Addressing ModesPooja Anand JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 3Document31 paginiWeek 3Ali AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Co 3Document29 paginiCo 3Gautam ChhabraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec# 8 The Addressing Modes of 8085 MicroprocessorDocument20 paginiLec# 8 The Addressing Modes of 8085 MicroprocessorSalva KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instruction Set 8051 - v1Document10 paginiInstruction Set 8051 - v1avinashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Addressing ModeDocument10 paginiAddressing Modegabesh3192Încă nu există evaluări
- CH 4 - MPinstDocument34 paginiCH 4 - MPinstrahul agarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPU Organisation: Instructions and Instruction SequencingDocument30 paginiCPU Organisation: Instructions and Instruction SequencingSamit NagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intel 8086 Instruction Format: Electrical and Electronic EngineeringDocument4 paginiIntel 8086 Instruction Format: Electrical and Electronic EngineeringWanjira KigokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8051 Instruction SetDocument79 pagini8051 Instruction SetpremsonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8051 Addressing ModesDocument8 pagini8051 Addressing Modeswasif28100% (3)
- CS II Chapter 2Document58 paginiCS II Chapter 2Mehlam SongerwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 8086 Addressing ModeDocument4 pagini7 8086 Addressing ModeJohn Brix Balisteros0% (1)
- Addressing Modes & Instruction SetDocument39 paginiAddressing Modes & Instruction SetlekaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microcontroller - 10ES42Document13 paginiMicrocontroller - 10ES42Laxman nadigÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSE 243: Introduction To Computer Architecture and Hardware/Software InterfaceDocument26 paginiCSE 243: Introduction To Computer Architecture and Hardware/Software Interfaceachaparala4499Încă nu există evaluări
- Instruction SetDocument15 paginiInstruction SetRadhakrishnan PuthalathÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAO Unit 1 Part 2-1Document5 paginiCAO Unit 1 Part 2-1prut.joshÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Does Microprocessor Differentiate Between Data and InstructionDocument60 paginiHow Does Microprocessor Differentiate Between Data and InstructionUbaid Saudagar100% (1)
- Instruction TypesDocument8 paginiInstruction Typestp2006sterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 3Document12 paginiActivity 3api-548516280Încă nu există evaluări
- 8085 MCQDocument20 pagini8085 MCQdeptÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 Q&aDocument14 paginiUnit 2 Q&aLavanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab No. 02 Registers, Memory Segmentaion and Buffers in 80X86 Emulator Assembly LanguageDocument12 paginiLab No. 02 Registers, Memory Segmentaion and Buffers in 80X86 Emulator Assembly LanguageXrein MarkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3Document14 paginiUnit 3Riza Pahama MananaongÎncă nu există evaluări
- XCS 234Document20 paginiXCS 234Balaji VenkatesanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.1 Addressing Modes: ECP2036 Microprocessors System and Interfacing Chapter 3: The 8051 Instruction SetDocument6 pagini3.1 Addressing Modes: ECP2036 Microprocessors System and Interfacing Chapter 3: The 8051 Instruction SetSwetha ChinnikannuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee6502 MM Eee VST Au Units IIDocument19 paginiEe6502 MM Eee VST Au Units IIRaad AljuboryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of InstructionsDocument13 paginiTypes of InstructionsJoseph JoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8051 Instruction SetDocument81 pagini8051 Instruction SetSaket GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Addressing Modes: Department of EIE / Pondicherry Engineering CollegeDocument5 paginiAddressing Modes: Department of EIE / Pondicherry Engineering Collegeprof_ktÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microprocessor PDFDocument30 paginiMicroprocessor PDFAmy OliverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculus With Analytical Geometry B SC SM YousafDocument35 paginiCalculus With Analytical Geometry B SC SM YousafFahad MemonÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hardware: - Three Types of Software ExistDocument50 paginiThe Hardware: - Three Types of Software ExistWilliam manzhi KajjubiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 3 8086 Instruction SetDocument30 paginiLec 3 8086 Instruction SetMikiyas TewodroesÎncă nu există evaluări
- FMPM Module 2Document64 paginiFMPM Module 2riddheshsawntÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assembler Language - 8051: Mairtin O ConghaileDocument56 paginiAssembler Language - 8051: Mairtin O ConghaileBharani RajkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Topics: 17.1 Hardware Control Using I/O PortsDocument34 paginiAdvanced Topics: 17.1 Hardware Control Using I/O Portsbarbarossa17Încă nu există evaluări
- It Is The Mark of An Educated Mind To Be Able To Entertain A Thought Without Accepting It. AristotleDocument29 paginiIt Is The Mark of An Educated Mind To Be Able To Entertain A Thought Without Accepting It. AristotleRhemjohn Dave PitongÎncă nu există evaluări
- MicroprocessorsDocument24 paginiMicroprocessorsarokiarajÎncă nu există evaluări
- MC Mod2@Azdocuments - inDocument18 paginiMC Mod2@Azdocuments - inAman DesaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- COA UNIT 2 NotesDocument13 paginiCOA UNIT 2 Notesvirajnjr10Încă nu există evaluări
- 8051 Instruction Set Rv01Document80 pagini8051 Instruction Set Rv01Anil BpsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assembler Language - 8051powerpoint PresentationDocument56 paginiAssembler Language - 8051powerpoint PresentationtauseeeeeeeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Some Important Previous Year Question Solutions (CA) - 1Document10 paginiSome Important Previous Year Question Solutions (CA) - 1shivammishra492002Încă nu există evaluări
- 1 Unit 2 Assembly Language and Addressing ModesDocument5 pagini1 Unit 2 Assembly Language and Addressing ModesSabareesh SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global Technical Campus: B. Tech II Year, IVSEM, Branch CSE I Mid Term Examination Microprocessors (4-Cs-1A)Document47 paginiGlobal Technical Campus: B. Tech II Year, IVSEM, Branch CSE I Mid Term Examination Microprocessors (4-Cs-1A)Anonymous xN4Z5QJU100% (1)
- CPU Chapter 5Document17 paginiCPU Chapter 5Mahesh BasnetÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2-Microcontroller 8051, Organization and Architecture-08!01!2024Document35 pagini2-Microcontroller 8051, Organization and Architecture-08!01!2024rupinsgmÎncă nu există evaluări
- BPQ REV. 0 Interactive FormDocument2 paginiBPQ REV. 0 Interactive FormcosmicbunnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- About Some Important Items of Composite Insulators Design: February 1999Document6 paginiAbout Some Important Items of Composite Insulators Design: February 1999ipraoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arun Et al-2019-ChemistrySelectDocument8 paginiArun Et al-2019-ChemistrySelectRavi Kumar ARunÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCI Control Valves For Fossil ApplicationsDocument2 paginiCCI Control Valves For Fossil ApplicationsGabrieldiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- INTEC 2019 User Manual PDFDocument30 paginiINTEC 2019 User Manual PDFshriramsusindarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sampling Procedure and Tables For InspectionDocument43 paginiSampling Procedure and Tables For InspectionAnonymous AoTZuNvxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turning Circles and Stopping DistancesDocument7 paginiTurning Circles and Stopping DistancesBisrat100% (1)
- AULA 13 - RespondidoDocument4 paginiAULA 13 - RespondidoRanyelle WanessaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PQ070XF02SZH: Features Outline DimensionsDocument4 paginiPQ070XF02SZH: Features Outline DimensionsJulio Cesar CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1743 LKWActrosXXXXXX 954frDocument4 pagini1743 LKWActrosXXXXXX 954frgeothermal3102100% (1)
- DE GUZMAN - Module 2 Activity No. 2Document4 paginiDE GUZMAN - Module 2 Activity No. 2Alvin De GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic ProbabilityDocument53 paginiBasic ProbabilityGhada SheashaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 08L76 HR3 A21Document6 pagini08L76 HR3 A21liebofreakÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCR Equipment ListDocument1 paginăCCR Equipment Listbehzad parsiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patrick C Hall@yahoo - com-TruthfinderReportDocument13 paginiPatrick C Hall@yahoo - com-TruthfinderReportsmithsmithsmithsmithsmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adirondack Life Media KitDocument8 paginiAdirondack Life Media KitJohnny LibitzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Report JamiaDocument76 paginiProject Report JamiaShoaibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revised Runway Length Discussion (20171206) - 201712211212022318Document3 paginiRevised Runway Length Discussion (20171206) - 201712211212022318Ilham RaffiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Omd Graviner Mk6 ManualDocument90 paginiOmd Graviner Mk6 ManualChristis SavvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ID 2051814.1 Oracle Support Sample SetupDocument9 paginiID 2051814.1 Oracle Support Sample SetupFerasHamdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BC Ii 800Document38 paginiBC Ii 800Pop Ciprian100% (2)
- Quality Related QuestionsDocument22 paginiQuality Related QuestionsHotPriyu OnlyforgalsÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRCCDocument13 paginiCRCCGalih SantanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sand Reclamation - Standard Devices: Shake Out MachinesDocument2 paginiSand Reclamation - Standard Devices: Shake Out MachinesKaarthicNatarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ice Plant TrainerDocument1 paginăIce Plant TrainerVirender RanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DBMS-LM Kavi With MinipjtDocument56 paginiDBMS-LM Kavi With Minipjtkavi_mithuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Juniper Practice QuestionsDocument32 paginiJuniper Practice QuestionsDasaradhiNidamarthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.hydraulic Pressure SpesificationDocument3 pagini6.hydraulic Pressure SpesificationTLK ChannelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual No 13Document3 paginiLab Manual No 13Hammad JawadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diseño de Tuberías C-10 Y C-40Document1 paginăDiseño de Tuberías C-10 Y C-40samuelcordova36Încă nu există evaluări