Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Dentifrice
Încărcat de
PharmacistBD0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
735 vizualizări26 paginiDentifrices such as toothpastes, toothpowders, and mouthwashes are used to clean teeth and maintain oral hygiene. They contain ingredients like abrasives, detergents, humectants, and flavors. Toothpastes are semi-solid and include binders, while toothpowders are dry mixtures. Mouthwashes are aqueous-alcoholic solutions used to reduce bad breath and promote oral health. Together, these dentifrices help remove plaque and food debris, reduce the risk of cavities and gingivitis, and keep teeth and gums healthy.
Descriere originală:
Dentifrice (Cosmetology) presentation
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDentifrices such as toothpastes, toothpowders, and mouthwashes are used to clean teeth and maintain oral hygiene. They contain ingredients like abrasives, detergents, humectants, and flavors. Toothpastes are semi-solid and include binders, while toothpowders are dry mixtures. Mouthwashes are aqueous-alcoholic solutions used to reduce bad breath and promote oral health. Together, these dentifrices help remove plaque and food debris, reduce the risk of cavities and gingivitis, and keep teeth and gums healthy.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
735 vizualizări26 paginiDentifrice
Încărcat de
PharmacistBDDentifrices such as toothpastes, toothpowders, and mouthwashes are used to clean teeth and maintain oral hygiene. They contain ingredients like abrasives, detergents, humectants, and flavors. Toothpastes are semi-solid and include binders, while toothpowders are dry mixtures. Mouthwashes are aqueous-alcoholic solutions used to reduce bad breath and promote oral health. Together, these dentifrices help remove plaque and food debris, reduce the risk of cavities and gingivitis, and keep teeth and gums healthy.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 26
Dentifrice
Tasniya Nahiyan Zulfiquar, Department of Pharmacy,
Lecturer, Primeasia University.
Dentifrices
Definition: Dentifrices are the preparations intended for
use with a toothbrush for the purpose of cleaning the
accessible surfaces of the teeth.
They have been prepared in paste, powders, liquids or
solid blocks used commercially for cleaning the teeth and
to keep the hygiene for effective development of oral
disease at ganglia surface of the teeth.
Examples: Toothpaste, powder, solid or liquid blocks.
Purpose
To enhance personal appearance by maintaining cleaner teeth.
To clean the accessible surface of the teeth.
To remove dental plaque for maintaining a healthy oral environment
To remove all food debris, accumulations of microorganisms from
the teeth.
To give luster to the teeth.
To reduce calculi formation on the tooth surfaces.
To reduce the risk of formation of dental caries.
To reduce the incident of periodental diseases like Gingivitis and
periodontitis.
To reduce objectionable mouth odors or bad smell.
To assist the mechanical effect of the toothbrush.
To maintain the strength of teeth and healthy enamel.
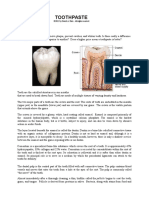
Structure of teeth/ Physiology of teeth
The teeth are hard calcified structures of the body firmly fixed
in boney sockets in the upper and lower jaws and the gums
form the covering membrane.
A tooth consists of four major functional parts:
1. The enamel: The tooth enamel is the most highly mineralized
and hardest tissue in the body. The enamel forms the crown
of the tooth and covers that portion of the dentine, which
projects through the gums into the mouth.
2. The cementum: It is a bone like substance that covers the
root.
3. The dentine: It is an ivory like substance that forms the body
of the tooth.
4. The dental pulp: Dental pulp is composed of connective
tissue containing the nerves arteries, veins and lymphatics that
enter the tooth through an opening at or near open the root.
COMMON DISEASES OF THE TEETH
Good dental health increases the possibility of good general
health. In addition to personal appearance by maintaining
cleaner teeth, brushing with a dentifrice reduces the
incidence of tooth decay, helps maintain healthy gingivae,
and reduces the intensity of mouth odors. Common dental
disorders are briefly described below:
Dental plaque
Dental plaque is a biofilm or mass of bacteria that grows on surfaces
within the mouth . The aggregation of microorganisms, food debris,
epithelial cells and mucin on the tooth surface forms the dental
plaque.
Site: Between two adjacent teeth.
Formation: Plaque formation is said to occur in two stages: first, an
amorphous, nonbacterial layer is laid down, which is followed by
bacterial invasion and subsequent bacterial proliferation.
Effects:
Formation of tooth cavity which gradually affect the pulp and
surgical intervention is required.
Remedy:
• Daily or twice-daily tooth brushing
• Use of dental floss and interdental brushes.
Dental caries
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries or cavities, is a
breakdown of teeth due to acids made by bacteria. The cavities
may be a number of different colors from yellow to black.
Site: Generally, caries starts on the outer surface of the enamel
in a localized area and penetrates into the dentine.
Microorganisms involved:
Streptococcus
Lactobacilli
Prevention:
Regular cleaning of the teeth
A diet low in sugar
small amounts of fluoride
Disorders of the gums
Gingivitis: This condition is an inflammation of the
gingiva. It is commonly caused by the deposition of
calculus or tartar in or around the gingival crevice.
Pyorrhea: If the simple gingivitis is neglected, the
epithelium around the tooth degenerates, which causes
pyorrhea. As the condition advances, a deep infected
pocket is formed between the gum and the tooth, pus
exudes, the periodontal membrane is destroyed, and the
alveolar bone is resorbed. The tooth then becomes loose
in its socket and at this stage has to be extracted.
Toothpaste
Toothpaste is the most common and popular form of
dentifrices. They are semisolid in nature.
Formulation: The ingredients used in the preparation of
toothpaste can be classified as follows-
Ingredients Amount (%)
Cleansing and polishing agents 40% - 60%
Detergent and foaming agents 1.5% - 3.0%
Humectants 0.5% - 4.5%
Binding agents 0.5% - 2.5%
Sweetening and flavoring agents 0.5% - 3%
Preservative and miscellaneous 0.15 % - 0.2%
Water Qs to 100 %
INGREDIENTS USED IN THE
FORMULATION OF TOOTHPASTE
A balanced formula can only be achieved by considering all the
ingredients together since many of them may have a dual
function or may interact with one another. Cost and availability
may cause formulations to vary from country to country.
Polishing and Cleansing Agent: The main purpose of these
agents is as a means of removing stains on the teeth and
usually contributes about half the total weight of the products.
A dentifrice should be no more abrasive than is necessary to
keep the teeth clean.The most commonly used abrasives are-
• Precipitated calcium carbonate
• Dicalcium phosphate dihydrate
• Tricalcium phosphate
• Calcium pyrophosphate
• Insoluble sodium metaphosphate
Detergent and foaming agents: These agents assist in
the removal of food debris and other mouth soil. They
also cause emulsification and subsequent removal of
mucus. Examples of such agents include:
• Sodium lauryl sulphate (SLS): Most widely used
• Sodium N-lauroyl sarcosinate
• Sodium Ricinoleate
• Sodium lauryl ether sulphate
Binding/ Gelling agents: They are essential
components, which confer stability and largely determine
the texture and consistency of the products. Examples:
• Gum tragacanth
• Carragheen
• Cellulosic derivatives; e.g. methylcellulose, sodium
carboxymethyl cellulose (SCMC)
• Carbopol (carboxy vinyl polymer)
Bleaches: To enhance the whitening effect of
toothpastes and toothpowders, and to assist in stain
removal. Examples: Sodium perborate, Magnesium
peroxide, Hydrogen peroxide.
Humectants: These are particularly required for
toothpastes mainly to prevent drying out of the paste
when it is left exposed to the air. Glycerin and sorbitol
either alone or in combination, are most commonly used.
Flavouring Agents: These are also important for the
acceptance of any product. The flavour is required to
leave a pleasant, clean and refreshing feeling in the mouth
after use. The most popular flavouring agents are based
on peppermint oils or blends of peppermint and
spearmint oils. Other flavouring agents used in small
quantities are: cloves (eugenol), eucalyptol, cinnamonm
and wintergreen (methyl salicylate).
Sweetening Agents: Saccharin is generally used as the
sweetening material. Chloroform is also used as
sweetener, which gives a sharp fresh sweetness that
differs from the metallic type of sweetness associated
with saccharin.
Corrosion inhibitors: These are intended to prevent
corrosion of the packaging, specially, aluminium tubes.
Sodium silicate is considered to be the most effective
corrosion inhibitor.
Miscellaneous Ingredients: Apart from the aforesaid
materials, preservatives and colors are also used.
Toothpowders
Toothpowders are the original, simplest and the cheapest
compounded forms of dentifrices.
Advantages:
• More stable due to dry nature of ingredients.
• No or less chemical reaction occurs.
• Formulation problems are not as severe since
interaction between components is unlikely in the
absence of water.
• Fluorides and oxidizing agents retain their effective
concentration larger than they would do in a paste
formulation.
Disadvantages:
• Uniform particle size may alter the physical
characteristics such as-
o Separation of the preparation on shaking
o Cake formation on storage
• Permanent settlement of powders can occur at the
bottom of the container.
• If the amount of powder used is too high, the abrasive
action also becomes high. As a result, infection of gum
may occur which ultimately lead to other serious dental
diseases.
Mouthwashes
Mouthwashes consist of aqueous-alcoholic solutions of
essential oils designed to have a delicate odor and impart a
refreshing and pleased flavor during and immediately after use.
They may or may not contain either soap or sodium lauryl
sulphate as a foaming agent. Antiseptics can also be included in
the composition. Methyl salicylate is popularly used as flavoring
agent.
Use:
• For removing bad odors to give a clean refreshing feeling in
the mouth.
• Products containing antiseptic and astringent materials have
more therapeutic effects and are used for gingivitis and
treatment of sore and tender gums.
Differences between toothpastes, tooth
powders and mouthwashes
TOOTHPASTES TOOTH POWDERS MOUTHWASHES
They contain humectants, They do not contain They do not contain
binders and preservatives. humectants, binders and humectants, binders and
preservatives. preservatives.
They must contain They also contain They do not contain
abrasive imparting abrasive imparting abrasive imparting agents.
agents. agents.
They are semisolids in They are solids in nature. They are liquid
nature. dentifrices.
They have mild abrasive They have slightly They do not have any
index. higher abrasive index. abrasive index.
They are generally They are packed in metal They are normally packed
packed in collapsible or plastic cans. in glass tubes.
metal or plastic tubes.
THANK
YOU
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- What Is Working ?Document19 paginiWhat Is Working ?shrustipatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shortcut Pharmacy: DentrificesDocument10 paginiShortcut Pharmacy: DentrificesNidhi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MouthwashDocument13 paginiMouthwashheaven.protikÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of ToothpasteDocument3 paginiHistory of ToothpasteE. SubinÎncă nu există evaluări
- ToothpasteDocument15 paginiToothpastesuraj hanvateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thao Tran, Sean Gillespie, Von KaukeanoDocument14 paginiThao Tran, Sean Gillespie, Von KaukeanoTri NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- HTFL Mouth Rinse v2Document2 paginiHTFL Mouth Rinse v2ReemALMousawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Cosmetic ScienceDocument21 paginiIntroduction To Cosmetic ScienceHarshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kapitel 6Document125 paginiKapitel 6Jai Murugesh100% (1)
- TabletsDocument117 paginiTabletscontactamit_shah100% (1)
- Shampoo FormulationDocument4 paginiShampoo Formulationnia_27043471Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3, Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance, B Pharmacy 6th Sem, Carewell PharmaDocument14 paginiUnit 3, Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance, B Pharmacy 6th Sem, Carewell PharmaAshadul IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Millets A Superfood - RevisedDocument5 paginiMillets A Superfood - Revisedshawana rajpootÎncă nu există evaluări
- Suppositories As A Dosage FormDocument11 paginiSuppositories As A Dosage FormMirumbi Kefa MomanyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmaceutical PreparationsDocument40 paginiPharmaceutical PreparationsAreej Hamid50% (2)
- ExcipientsDocument40 paginiExcipientsLidya Ameliana100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Emulsions by Haroon RahimDocument49 paginiPharmaceutical Emulsions by Haroon RahimHaroon Rahim67% (3)
- Unit 5 CosmeticsDocument14 paginiUnit 5 CosmeticsRevathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Citicoline Mode of ActionDocument5 paginiCiticoline Mode of ActionBeverlyÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMIHOPE LL Natural Hair Care FormulasDocument29 paginiAMIHOPE LL Natural Hair Care Formulassandroesandro0% (1)
- WHO and ICH Guidelines For The Assessment of Herbal DrugDocument11 paginiWHO and ICH Guidelines For The Assessment of Herbal DrugEditor IJTSRDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creams Ms - Wajiha Iffat: ObjectivesDocument15 paginiCreams Ms - Wajiha Iffat: ObjectivesRudra PangeniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formulation of EmulsionDocument8 paginiFormulation of EmulsionSyafiqah ZainoddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oral FormulationsDocument10 paginiOral FormulationsSiddhartha MuppallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emulsion S: By: Hannako Faith NgohayonDocument44 paginiEmulsion S: By: Hannako Faith NgohayonHannako NgohayonÎncă nu există evaluări
- SUSPENSIONDocument11 paginiSUSPENSIONAnoosha FarooquiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PerfumesDocument22 paginiPerfumesAngelica Euara Jardeleza Manrique100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical ExcipientsDocument19 paginiPharmaceutical ExcipientsTikaUlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cream Formulation: Kausar Ahmad Kulliyyah of PharmacyDocument35 paginiCream Formulation: Kausar Ahmad Kulliyyah of PharmacyJean Carla Rosario100% (2)
- Pharmaceutical Suspensions PDFDocument8 paginiPharmaceutical Suspensions PDFMaya100% (1)
- Labajo and LaguiabDocument37 paginiLabajo and LaguiabKen LaguiabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ointment Cream and GelsDocument79 paginiOintment Cream and GelsGwyneth Cartalla100% (2)
- Herbal CosmeticDocument17 paginiHerbal CosmeticHely PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmaceutical Statistics NEW: Pharmaceutics / Industrial Pharmacy / Pharmaceutical TechnologyDocument8 paginiPharmaceutical Statistics NEW: Pharmaceutics / Industrial Pharmacy / Pharmaceutical TechnologyIlhan KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMULSIONSDocument39 paginiEMULSIONSDanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- IIR) - Books-Cosmetics and Beauty Products (Ayurvedic - Herbal PDFDocument12 paginiIIR) - Books-Cosmetics and Beauty Products (Ayurvedic - Herbal PDFAnu Kutty67% (3)
- PHM4153 Cream Formulation - PPSXDocument38 paginiPHM4153 Cream Formulation - PPSXEdgardo Ed RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mouth WashesDocument33 paginiMouth WashesMaxÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01.nasal Dosage FormsDocument6 pagini01.nasal Dosage FormskhalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mouth/Nose/Eyes/Ears: 2. 1.1 Lip and Skin ButterDocument2 paginiMouth/Nose/Eyes/Ears: 2. 1.1 Lip and Skin ButterRoshan Baskota100% (1)
- Formula 1304 SkinWhite C Serum PDFDocument1 paginăFormula 1304 SkinWhite C Serum PDFHM IthvzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Powders and Granules For Syrups: Nasal PreparationsDocument2 paginiPowders and Granules For Syrups: Nasal PreparationsAat Prayoga MuhtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ElementisPersonalCareFormulary PDFDocument20 paginiElementisPersonalCareFormulary PDFAlberto Huaman100% (1)
- Solid Dosage Form Part 1Document48 paginiSolid Dosage Form Part 1Claire Marie AlvaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Novel Techniques For Oil/water Separation: U. Daiminger, W. Nitsch, P. Plucinski, S. HoffmannDocument7 paginiNovel Techniques For Oil/water Separation: U. Daiminger, W. Nitsch, P. Plucinski, S. HoffmannSahil KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 131 Matte Liquid LipstickDocument2 pagini131 Matte Liquid LipstickFelix Martin GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Non-Gmo Product List: The World's Best Organic Superfoods Since 1993Document8 paginiOrganic Non-Gmo Product List: The World's Best Organic Superfoods Since 1993Melissa LaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Techniques of SolubilizationDocument33 paginiTechniques of SolubilizationSreekanth NamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pesticide Formulation (AGCH 357)Document72 paginiPesticide Formulation (AGCH 357)Kaium Sau100% (1)
- Factors Affecting Renal ExcretionDocument19 paginiFactors Affecting Renal ExcretionV. SravaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- EmulsionDocument27 paginiEmulsionSharanya SrinivasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cosmetice GenralitatiDocument73 paginiCosmetice GenralitatiIoana NicolaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semi SolidsDocument27 paginiSemi SolidsDrVenu Madhav KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Cosmetics and CosmeceuticalsDocument38 paginiIntroduction To Cosmetics and CosmeceuticalsNuhaRasheed100% (2)
- Pharma Laboratory ExperimentsDocument34 paginiPharma Laboratory Experimentsapi-3748748100% (4)
- Ivivc: in Vitro-In Vivo CorrelationDocument46 paginiIvivc: in Vitro-In Vivo CorrelationMubammad Mursaleen100% (1)
- Counseling For Gargle, Magic Mouth Wash & Mucositis in Cancer PTDocument3 paginiCounseling For Gargle, Magic Mouth Wash & Mucositis in Cancer PTAthirah BidinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toothpaste For Bleeding Gums J Sensitive Teeth. Teeth Whitening J MouthwashDocument20 paginiToothpaste For Bleeding Gums J Sensitive Teeth. Teeth Whitening J Mouthwashsharyurangari111Încă nu există evaluări
- Amity Institute of Pharmacy: B. Pharm., Semester One Pharmacy Dr. Pawan Kumar PorwalDocument25 paginiAmity Institute of Pharmacy: B. Pharm., Semester One Pharmacy Dr. Pawan Kumar Porwalpawankumar guptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piyush ProjectDocument20 paginiPiyush ProjectVishwjeet Kumar ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Information Technology-PharmacyDocument57 paginiInformation Technology-PharmacyPharmacistBDÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 EvaporationDocument36 pagini04 EvaporationPharmacistBDÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHM141H1 PharmaceuticsDocument15 paginiPHM141H1 PharmaceuticsPharmacistBDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmaceutical Formulation: Principles and Dosage FormsDocument3 paginiPharmaceutical Formulation: Principles and Dosage FormsPharmacistBDÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Essential Drugs BangladeshDocument1 paginăList of Essential Drugs BangladeshPharmacistBDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fixed Orthodontic Retainers: A ReviewDocument5 paginiFixed Orthodontic Retainers: A ReviewhelmysiswantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- JCRR-22-RA-242 Reviewer FileDocument14 paginiJCRR-22-RA-242 Reviewer FileFlaviu Ionuț FaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grenier (1996), Effect of Chlorhexidine On The Adherence Properties of Porphyromonas GingivaliDocument4 paginiGrenier (1996), Effect of Chlorhexidine On The Adherence Properties of Porphyromonas GingivaliPhuong ThaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2024 Msyi Final ProgramDocument12 pagini2024 Msyi Final Programapi-654587216Încă nu există evaluări
- Aunger Toothbrushing Routines PDFDocument13 paginiAunger Toothbrushing Routines PDFNabila RizkikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risks in Orthodontic TreatmentDocument60 paginiRisks in Orthodontic TreatmentPaRpArOsSaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quizzes For MicrobiologyDocument13 paginiQuizzes For MicrobiologychicatÎncă nu există evaluări
- BDS Fifth Year & Final Prof. NewDocument4 paginiBDS Fifth Year & Final Prof. NewSumeet SodhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gingival Bleeding in Children: Causes and Treatments: Opinion ISSN: 2637-6636Document3 paginiGingival Bleeding in Children: Causes and Treatments: Opinion ISSN: 2637-6636Cloud NeilalungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elementary JeopardyDocument62 paginiElementary JeopardyRebecca Forstadt OlkowskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prosthodontic Treatment in Parkinson'S Disease Patients:: Literature ReviewDocument60 paginiProsthodontic Treatment in Parkinson'S Disease Patients:: Literature ReviewSalma RafiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calcium and Oral Health: A Review: International Journal of Scientific Research September 2013Document3 paginiCalcium and Oral Health: A Review: International Journal of Scientific Research September 2013Maqbul AlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examiner Alignment and Assessment in Clinical Periodontal Researchhefti - Et - Al-2012-Periodontology - 2000Document20 paginiExaminer Alignment and Assessment in Clinical Periodontal Researchhefti - Et - Al-2012-Periodontology - 2000Dr. DeeptiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gilut Dental CariesDocument49 paginiGilut Dental CariesFawzia Devi FitrianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Toothbrushes: A Critical Review: C PenickDocument5 paginiPower Toothbrushes: A Critical Review: C PenickEltonJCSilveiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blueprint For Men'S Health: A Guide To A Healthy LifestyleDocument76 paginiBlueprint For Men'S Health: A Guide To A Healthy LifestyleJacqMarreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical PH PDFDocument3 paginiCritical PH PDFIradatul HasanahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Al Makhmari, S. A., Kaklamanos, E. G., & Athanasiou, A. E. (2017) - Short-Term and Long-Term Effectiveness of Powered Toothbrushes in Promoting PeriodontalDocument21 paginiAl Makhmari, S. A., Kaklamanos, E. G., & Athanasiou, A. E. (2017) - Short-Term and Long-Term Effectiveness of Powered Toothbrushes in Promoting PeriodontalMarco Antonio García LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GLI GlisterCollection en USDocument7 paginiGLI GlisterCollection en USCt HajarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perio Notes CombinedDocument71 paginiPerio Notes CombinedHayley WelshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dental Asia JulDocument96 paginiDental Asia JulAnonymous A8l9OjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baking Soda For TeethDocument9 paginiBaking Soda For Teethkata OmoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perio Project PresentationDocument20 paginiPerio Project Presentationapi-39062903Încă nu există evaluări
- Sheet 1 (Dental Caries)Document70 paginiSheet 1 (Dental Caries)ardesh abdilleÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Consequences ENDocument11 pagini3 Consequences ENFrancisco AntónioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dental PLAQUE: by Dr. Nitika Jain Post Graduate StudentDocument70 paginiDental PLAQUE: by Dr. Nitika Jain Post Graduate StudentJee ArceoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adolescent Oral Health Care: Latest RevisionDocument10 paginiAdolescent Oral Health Care: Latest Revisionnona aryanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology: PAPER 6 Alternative To PracticalDocument12 paginiBiology: PAPER 6 Alternative To PracticalLuckÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demineralization and Remineralization Processes in EnamelDocument56 paginiDemineralization and Remineralization Processes in EnamelmzusaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cet Chews DogsDocument2 paginiCet Chews DogsdougdougdougÎncă nu există evaluări