Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
The Conceptual Fixed Asset System
Încărcat de
Mika Abucay Reyes0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
71 vizualizări10 paginiTitlu original
338867680-The-Conceptual-Fixed-Asset-System.pptx
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
71 vizualizări10 paginiThe Conceptual Fixed Asset System
Încărcat de
Mika Abucay ReyesDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 10
THE CONCEPTUAL
FIXED ASSET SYSTEM
What is Fixed Assets?
◦Fixed assets are the property, plant, and
equipment used in the operation of a
business.
◦Examples of fixed assets include land,
buildings, furniture, machinery, and motor
vehicles.
Fixed Asset System
◦Fixed asset system processes transactions
pertaining to the acquisition, maintenance,
and disposal of its fixed assets.
The specific objectives are to:
1. Process the acquisition of fixed assets as needed and in
accordance with formal management approval and procedures.
2. Maintain adequate accounting records of asset acquisition,
cost, description, and physical location in the organization.
3. Maintain accurate depreciation records for depreciable assets
in accordance with acceptable methods.
4. Provide management with information to help plan for future
fixed asset investments.
5. Properly record the retirement and disposal of fixed assets.
Difference between Expenditure
Cycle and Fixed Asset System
Expenditure Cycle Fixed Asset System
• It processes routine • It processes non-routine
acquisitions of raw material transactions for a wider
and finished goods group of users in the
inventories. organization.
• It treat inventory • It capitalize fixed assets
acquisitions as an expense that yield benefits for
of the current period. multiple periods.
THE LOGIC OF A
FIXED ASSET SYSTEM
Introduction
◦The process involves three categories
of tasks:
◦Asset Acquisition,
◦Asset Maintenance, and
◦Asset Disposal
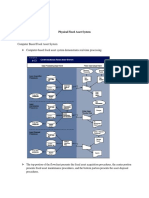
Asset Acquisition
◦ It usually begins with the departmental manager (user)
recognizing the need to obtain a new asset or replace
an existing one.
◦ The receiving department delivers the asset into the
custody of the user/manager rather than a central store
or warehouse.
◦ The fixed asset department, not inventory control,
performs the record-keeping function.
Asset Maintenance
◦ It involves adjusting the fixed asset subsidiary account
balances as the assets (excluding land) depreciate
over time or with usage.
◦ It also involves adjusting asset accounts to reflect the
cost of physical improvements that increase the asset’s
value or extend its useful life.
◦ It must promote accountability by keeping track of the
physical location of each asset.
Asset Disposal
◦ It begins when the responsible manager issues a request
to dispose of the asset.
◦ The disposal options open to the firm are to sell, scrap,
donate, or retire the asset in place.
◦ A disposal report describing the final disposition of the
asset is sent to the fixed asset accounting department
to authorize its removal from the ledger.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Technical Engineering PEEDocument3 paginiTechnical Engineering PEEMariano Acosta Landicho Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Fixed Asset PolicyDocument20 paginiFixed Asset PolicyMandar Jayesh Patel100% (4)
- Learner Assessmenpt Ack: Sitxfin005 Manage Physical AssetsDocument36 paginiLearner Assessmenpt Ack: Sitxfin005 Manage Physical AssetsNitin100% (1)
- Chapter 6 AIS Expenditure Cycle II SummaryDocument6 paginiChapter 6 AIS Expenditure Cycle II Summary0nionringsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auditing-Review Questions Chapter 13Document5 paginiAuditing-Review Questions Chapter 13meiwin manihingÎncă nu există evaluări
- For The Written Activity The Learner Will Complete The Following Assessment. Total Assessment Length Should Be Between 800 - 1500 WordsDocument13 paginiFor The Written Activity The Learner Will Complete The Following Assessment. Total Assessment Length Should Be Between 800 - 1500 WordsAnmol PoudelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Obj For Non-Current AssetsDocument6 paginiControl Obj For Non-Current AssetsTrần TùngÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Conceptual Fixed Asset SystemDocument10 paginiThe Conceptual Fixed Asset SystemSeeker100% (1)
- The Conceptual Fixed Asset SystemDocument7 paginiThe Conceptual Fixed Asset SystemKaith BorjaskyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 Financing and Investing CycleDocument14 pagini03 Financing and Investing CycleDillon MurphyÎncă nu există evaluări
- James Hall Chap 6Document2 paginiJames Hall Chap 6ryan angelica allanicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fas Wps OfficeDocument16 paginiFas Wps OfficeCarl Adrian ValdezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 08 The Expenditure Cycle Fixed Asset SystemDocument8 paginiModule 08 The Expenditure Cycle Fixed Asset SystemDmzjmb SaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIS Chapter 6Document23 paginiAIS Chapter 6Hasan AbirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Integrity AME StandardDocument3 paginiCivil Integrity AME Standarddhanu_lagwankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 Audit of FADocument6 paginiChapter 5 Audit of FAminichelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter FiveDocument13 paginiChapter Fivekitababekele26Încă nu există evaluări
- Auditing-Review Questions Chapter 13Document2 paginiAuditing-Review Questions Chapter 13meiwin manihingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 - Audit of Fixed AssetsDocument7 paginiChapter 6 - Audit of Fixed AssetssteveiamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5Document14 paginiUnit 5fekadegebretsadik478729Încă nu există evaluări
- Audit of Property, Plant, and Equipment - Hahu Zone - 1622367787308Document8 paginiAudit of Property, Plant, and Equipment - Hahu Zone - 1622367787308Iam AbdiwaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATERI BAB 15 SISTEM AKUNTANSI PERSEDIAAN - Id.enDocument23 paginiMATERI BAB 15 SISTEM AKUNTANSI PERSEDIAAN - Id.enRima MelatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pertemuan Ke: 16 SC&C Ch-9 LT Assets I: Kode Mata Kuliah: Ea 33401Document35 paginiPertemuan Ke: 16 SC&C Ch-9 LT Assets I: Kode Mata Kuliah: Ea 33401Alvin HartantioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expenditure CycleDocument10 paginiExpenditure CycleKaila Mae Tan DuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auditing-II CH 5Document56 paginiAuditing-II CH 5Tesfaye DesalegnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 Audit of Fixed Assests To StudentsDocument14 paginiChapter 5 Audit of Fixed Assests To StudentsZelalem Hassen100% (1)
- Physical Fixed Asset SystemDocument2 paginiPhysical Fixed Asset SystemGabriel PatronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asfaw, Audit II Chapter 5Document3 paginiAsfaw, Audit II Chapter 5alemayehu100% (1)
- Summer Internship Project Adani Electricity, Dahanu Thermal Power StationDocument34 paginiSummer Internship Project Adani Electricity, Dahanu Thermal Power Stationkruti makvanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cornerstones of Financial Accounting Canadian 2nd Edition Rich Solutions ManualDocument15 paginiCornerstones of Financial Accounting Canadian 2nd Edition Rich Solutions Manualdariusba1op100% (22)
- Property, Plant and EquipmentDocument16 paginiProperty, Plant and EquipmentnurthiwnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter FourDocument18 paginiChapter Fourmubarek oumerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5: Audit of Fixed AssetsDocument4 paginiUnit 5: Audit of Fixed AssetsTilahun S. KuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- M8 Appe LaDocument12 paginiM8 Appe LaGabriel OrolfoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Savings Through Fixed Assets ManagementDocument9 paginiFinancial Savings Through Fixed Assets ManagementRohan ShirdhankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fixed Asset AuditsDocument8 paginiFixed Asset AuditsnabihaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Periodic Inventory SystemDocument16 paginiPeriodic Inventory SystemSohel Bangi100% (1)
- A Business Continuity PlanDocument3 paginiA Business Continuity PlanMaajith Marzook100% (1)
- Facilitators Guide For Accenture-IGNOU Diploma Program: Unit 4Document20 paginiFacilitators Guide For Accenture-IGNOU Diploma Program: Unit 4Vinay SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Public Sector Accounting: Mr. Evans AgalegaDocument35 paginiPublic Sector Accounting: Mr. Evans AgalegaElvis Yarig100% (1)
- Class Notes - Fix Asset AccountingDocument2 paginiClass Notes - Fix Asset AccountinglaolagnesiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LOG 2 6 WAREHOUSE GUIDELINES Inventory Guidelines ProposalDocument3 paginiLOG 2 6 WAREHOUSE GUIDELINES Inventory Guidelines ProposalWilmae Grace ProvidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 - Chapter FiveDocument9 paginiChapter 5 - Chapter FiveBantamkak FikaduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Four-Auditing IIDocument9 paginiChapter Four-Auditing IIBantamkak FikaduÎncă nu există evaluări
- SITXFIN005 Manage Physical Assets-Assessment 2-ProjectDocument20 paginiSITXFIN005 Manage Physical Assets-Assessment 2-ProjectRAMANdeep kaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Audit Program Fixed AssetsDocument6 paginiAudit Program Fixed Assetsnico_pia454Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4Document10 paginiChapter 4Jarra AbdurahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Completing The Test in The Acquisition and Payment CycleDocument19 paginiCompleting The Test in The Acquisition and Payment CycleEsti SetianingsihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auditing AssignmentDocument4 paginiAuditing AssignmentDENEKEW LESEMIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capital Expenditure Review - Work ProgramDocument8 paginiCapital Expenditure Review - Work Programmarikb79Încă nu există evaluări
- Internal Control Affecting AssetsDocument27 paginiInternal Control Affecting AssetsJannefah Saglayan50% (2)
- Note On Replacement AnalysisDocument3 paginiNote On Replacement AnalysisAkunwa GideonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auditing AssingmentsDocument6 paginiAuditing AssingmentsTumaini EdwardÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5-Auditing 2 - Chapter FiveDocument10 pagini5-Auditing 2 - Chapter Fivesamuel debebeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 16 - Corporate GovernanceDocument34 paginiChapter 16 - Corporate Governancekarryl barnuevoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Property Plant and EquipmentDocument13 paginiProperty Plant and EquipmentWilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Audit of Fixed Assets 1Document3 paginiAudit of Fixed Assets 1Leon MushiÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIS Chap 6 NotesDocument6 paginiAIS Chap 6 NotesKrisshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 AISDocument28 paginiChapter 6 AISNica VizcondeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 - SAP PM Plant Maintenance Universal Process ModelDocument51 pagini02 - SAP PM Plant Maintenance Universal Process ModelNehaSingh645100% (2)
- Fixed Assets PDFDocument6 paginiFixed Assets PDFMika Abucay ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0 Out of 25 CorrectDocument18 pagini0 Out of 25 CorrectMika Abucay ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- HDHHDJDJRJRJRJJ-WPS OfficeDocument1 paginăHDHHDJDJRJRJRJJ-WPS OfficeMika Abucay ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Expenditure Cycle Part 1: Purchases and Cash Disbursements ProceduresDocument41 paginiThe Expenditure Cycle Part 1: Purchases and Cash Disbursements ProceduresFathan MubinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter04 002Document60 paginiChapter04 002Dven JsÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 01 Managerial Accounting Q MXDocument16 paginiCH 01 Managerial Accounting Q MXHadassahFayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sika Saudi Arabia: Safety Data SheetDocument4 paginiSika Saudi Arabia: Safety Data Sheetusman khalid100% (1)
- Drug Study TemplateDocument2 paginiDrug Study TemplateKistlerzane CABALLEROÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics 2 First Quarter - Module 5 "Recognizing Money and Counting The Value of Money"Document6 paginiMathematics 2 First Quarter - Module 5 "Recognizing Money and Counting The Value of Money"Kenneth NuñezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Eh307 Crimpro Case Digests Part 1Document214 pagini01 Eh307 Crimpro Case Digests Part 1Kimberly PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fact Pack Financial Services KenyaDocument12 paginiFact Pack Financial Services KenyaCatherineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalog enDocument292 paginiCatalog enSella KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCHEDULE OF FEES - FinalDocument1 paginăSCHEDULE OF FEES - FinalAbhishek SunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Divider Block Accessory LTR HowdenDocument4 paginiDivider Block Accessory LTR HowdenjasonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Is 10719 (Iso 1302) - 1Document1 paginăIs 10719 (Iso 1302) - 1Svapnesh ParikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Media SchedulingDocument4 paginiMedia SchedulingShreyansh PriyamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erickson Transformer DesignDocument23 paginiErickson Transformer DesigndonscogginÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Base AmplifierDocument6 paginiCommon Base AmplifierMuhammad SohailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oasis 360 Overview 0710Document21 paginiOasis 360 Overview 0710mychar600% (1)
- Strategic Management ModelsDocument4 paginiStrategic Management ModelsBarno NicholusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fcode 54 en El SytucDocument2 paginiFcode 54 en El SytucAga MenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- TNCT Q2 Module3cDocument15 paginiTNCT Q2 Module3cashurishuri411100% (1)
- Rideable Segway Clone - Low Cost and Easy Build: Digital MPU6050 Accelerometer/gyro IMU BoardDocument45 paginiRideable Segway Clone - Low Cost and Easy Build: Digital MPU6050 Accelerometer/gyro IMU BoardpaolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- จัดตารางสอบกลางภาคภาคต้น53Document332 paginiจัดตารางสอบกลางภาคภาคต้น53Yuwarath SuktrakoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manulife Health Flex Cancer Plus Benefit IllustrationDocument2 paginiManulife Health Flex Cancer Plus Benefit Illustrationroschi dayritÎncă nu există evaluări
- Change Language DynamicallyDocument3 paginiChange Language DynamicallySinan YıldızÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tecplot 360 2013 Scripting ManualDocument306 paginiTecplot 360 2013 Scripting ManualThomas KinseyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Best Practices in Developing High PotentialsDocument9 paginiBest Practices in Developing High PotentialsSuresh ShetyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Electrical Protection Relays or Protective RelaysDocument7 paginiTypes of Electrical Protection Relays or Protective RelaysTushar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Unbrick Tp-Link Wifi Router Wr841Nd Using TFTP and WiresharkDocument13 paginiHow To Unbrick Tp-Link Wifi Router Wr841Nd Using TFTP and WiresharkdanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Incoterms 2010 PresentationDocument47 paginiIncoterms 2010 PresentationBiswajit DuttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMI-EMC - SHORT Q and ADocument5 paginiEMI-EMC - SHORT Q and AVENKAT PATILÎncă nu există evaluări
- VRIODocument3 paginiVRIOJane Apple BulanadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Org ChartDocument1 paginăOrg Chart2021-101781Încă nu există evaluări
- Ril Competitive AdvantageDocument7 paginiRil Competitive AdvantageMohitÎncă nu există evaluări