Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Wa0002
Încărcat de
Axseal A0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
6 vizualizări16 paginiTitlu original
DOC-20181123-WA0002.pptx
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
6 vizualizări16 paginiWa0002
Încărcat de
Axseal ADrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 16
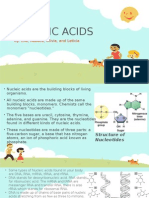
NUCLEIC ACID
• NUCLEIC ACIDS Are the
largest and the most
complex organic
molecules. Friedrich
Miescher who discovered
nucleicacids
in 1871
• NUCLIEC ACIDS are
macromolecules, found in all cells,
which precipitate in the storage,
transmission and translation of
genetic information.
• There are two types of nucleic
acids, the ribose nucleic acid (RNA)
and the deoxyribose nucleic acid
(DNA), which on hydrolysis yield
the sugar ribose and deoxyribose
respectively.
• Nucleic acids were first isolated from the
cellular nucleus, hence the name. Nucleic
acids are macromolecules, huge polymers
with molecular masses of over 100 million.
FUNCTION OF NUCLEIC ACIDS:
Functions of DNA (deoxyribonucleic
acid:
-DNA is a permanent storage place
for genetic information. -DNA
controls the synthesis of RNA
(ribonucleic acid). -The sequence of
nitrogenous bases in DNA
determines the protein
development in new cells.
• The function of the double helix
formation of DNA is to ensure that no
disorders occur. This is because the
second identical strand of DNA that
runs anti-parallel to the first is a back
up in case of lost or destroyed genetic
information. Ex. Down’s Syndrome or
Sickle Cell Anemia.
• Functions of RNA
(ribonucleic acid):
-RNA is synthesized by DNA for
the transportation of genetic
information to the protein
building apparatus in the cell.
-RNA also directs the synthesis of
new proteins using the genetic
information it has transported. -
mRNA (messenger ribonucleic
acid) is used to transfer genetic
information through plasma
membranes
• Nucleic acids (specifically
DNA) carry out a vital role in
the human body. In particular,
nucleic acids play an essential
role in: Mitosis, Meiosis •
Providing Energy / Cellular
Respiration
Composition of Nucleic Acids:
• Nucleic acids are substances
with high molecular weight
ranging from 1,286 to 3,000,000.
They are made up of carbon,
hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and
phosphorus. • Nitrogen is from 15
to 16% while phosphorus is from 9
to 10%. On hydrolysis with either
an enzyme or by heating with
dilute acids or alkalies, nucleic
acids yields a group of compound
known as nucleotides.
Kinds of Nucleic Acids
• DNA( deoxyribonucleic acid)
–found only inside the nucleus of the
cell. Contains the organism’s genetic
information, including instructions for
how to make proteins.
• RNA( ribonucleic acid)
– found both inside and outside of
the nucleus. Directs the building of
proteins. -primarily concerned with
the synthesis of protein.
• POLYPEPTIDES
are the building blocks of nucleic acids.
DNA
• Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic
acid that contains the genetic
instructions used in the development
and functioning of all known living
organisms. The main role of DNA
molecules is the long-term storage of
information and DNA is often
compared to a set of blueprints.
• The DNA segments
that carry this genetic
information are called
genes, but other DNA
sequences have
structural purposes, or
are involved in
regulating the use of
this genetic information
• Deoxyribose is present in the nucleic
acid found in the yeast cell nuclei,
while ribose is contained in the
nucleic acid obtained from pancreas. –
There are cases also were both of
nucleic acids are found together. So
that it is now definitely accepted that
both the ribose and deoxyribose
nucleic acids are found in plants and
animals; and that while the
deoxyribose type is found in the nucleic
of the cells (white) the ribose type
predominate in the cytoplasm
- Some amount of DNA are also
housed in the cell’s
mitochondria, whose main
function is to generate the
energy needed for the cell
functioning, it couldn’t be in
the cell wall, because human
cells are bound by membrane
and lack the cell walls that
plants have
- There are DNA viruses,
like herpes but some of
the most prevalent, like
the common cold or
influenza, as well as
other well-known viruses
like hepatitis C and are
RNA viruses.
RNA
• Ribonucleic acid (RNA) functions in
converting genetic information from
genes into the amino acid sequences
of proteins. The three universal types
of RNA include transfer RNA (tRNA) ,
messenger RNA (mRNA), and
ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Messenger
RNA acts to carry genetic sequence
information between DNA and
ribosomes, directing protein synthesis.
Ribosomal RNA is a major component
of the ribosome, and catalyzes peptide
bond formation.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nulcleic AcidDocument32 paginiNulcleic AcidhrankhnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic Acid: Name: Miss Rabaya Akter ID: 1922247649Document8 paginiNucleic Acid: Name: Miss Rabaya Akter ID: 1922247649SymumÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.4 Nucleic AcidDocument35 pagini2.4 Nucleic AcidAzalea BitchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To MGDocument18 paginiIntro To MGfmznn588kcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit VII - Nucleic Acids - MCONDocument30 paginiUnit VII - Nucleic Acids - MCONikram ullah khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic Acid: Nucleic Acids Are The Biopolymers, or Large Biomolecules, EssentialDocument7 paginiNucleic Acid: Nucleic Acids Are The Biopolymers, or Large Biomolecules, EssentialLuis Felipe Mera GrandasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic AcidsDocument4 paginiNucleic Acidsapi-296126866Încă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic Acid: Nucleic Acids Are The Biopolymers, or Large Biomolecules, Essential ToDocument7 paginiNucleic Acid: Nucleic Acids Are The Biopolymers, or Large Biomolecules, Essential ToMujahidul HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochemistry - Nucleic AcidsDocument30 paginiBiochemistry - Nucleic AcidsBalakrishnan Rengesh100% (1)
- Chemistry Project 2019Document15 paginiChemistry Project 2019Aiasha AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic AcidDocument7 paginiNucleic AciddearbhupiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic AcidDocument5 paginiNucleic AcidMAMENDIG, Amerah P.Încă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic AcidsDocument12 paginiNucleic AcidsAntonette SolaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1Document22 paginiLecture 1Ahmad KarimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument24 paginiMolecular Basis of Inheritanceharsh shirsatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochemistry of Nucleic Acids: Dr. Said Al RiyamiDocument19 paginiBiochemistry of Nucleic Acids: Dr. Said Al RiyamiDodo DadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell PhysiologyDocument20 paginiCell PhysiologySerra ÇevikkanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic Acid - WikipediaDocument1 paginăNucleic Acid - WikipediakakunopaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA and RNA Perform Different FunctionsDocument16 paginiDNA and RNA Perform Different FunctionsTamanda SekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbial Genetics: Done By: Samah AlzahraniDocument12 paginiMicrobial Genetics: Done By: Samah AlzahraniSam ZahraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic Acid: Group 2 ReportDocument20 paginiNucleic Acid: Group 2 ReportDiePalAPieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleicacids Dnarna 100618205106 Phpapp01Document40 paginiNucleicacids Dnarna 100618205106 Phpapp01InerTiaOpheliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic AcidDocument5 paginiNucleic AcidAdams DeborahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of Dna: Deoxyribonucleic Acid BY Kapish, Rithish, KrishwanthDocument7 paginiStructure of Dna: Deoxyribonucleic Acid BY Kapish, Rithish, KrishwanthRithish VikramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic Acid ReportDocument15 paginiNucleic Acid Reportmumu memeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic AcidDocument12 paginiNucleic AcidKyle MayanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic Acid: Nucleic Acids Are TheDocument1 paginăNucleic Acid: Nucleic Acids Are TheYuvi RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Blueprint of Protein SynthesisDocument2 paginiThe Blueprint of Protein SynthesislamesaltheamoniqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic Acids - A Basic OverviewDocument13 paginiNucleic Acids - A Basic OverviewSabsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disease and The Genome: Genetic, Developmental, and Neoplastic DiseaseDocument24 paginiDisease and The Genome: Genetic, Developmental, and Neoplastic DiseaseMegan CatilinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic-AcidDocument28 paginiNucleic-AcidIvan Jhon AnamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1 IntroductionADocument62 paginiLecture 1 IntroductionAimensah22Încă nu există evaluări
- HeredityDocument24 paginiHeredityvivas.kznne.9Încă nu există evaluări
- ChromosomesDocument4 paginiChromosomesyunisnaquilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Central DogmaDocument16 paginiCentral DogmaRose HaliliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Description of Cell Structure and FunctionDocument7 paginiDescription of Cell Structure and FunctionAin SoberanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic AcidDocument23 paginiNucleic AcidAbdur DapitillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA and Protein Synthesis - Chapter Notes: "Life Is A Three Letter Word!"Document13 paginiDNA and Protein Synthesis - Chapter Notes: "Life Is A Three Letter Word!"Chan Karlok100% (1)
- Nucleic Acids EssayDocument3 paginiNucleic Acids Essaynktechhelp101100% (2)
- Biomolecules - Nucleic AcidsDocument12 paginiBiomolecules - Nucleic AcidsRyan S. CutamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson: Physical Science - Grade 11 Quarter 3 - Module 10: Macromolecules: Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDocument6 paginiLesson: Physical Science - Grade 11 Quarter 3 - Module 10: Macromolecules: Proteins and Nucleic AcidsJAY BALLESTEROSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument69 paginiBasics of Molecular BiologypathinfoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment # 8 Genes & Nucleic AcidsDocument4 paginiAssignment # 8 Genes & Nucleic Acidskyle james duclanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Struktur Dan Fungsi Nukleotida (Purin Dan Pirimidin)Document92 paginiStruktur Dan Fungsi Nukleotida (Purin Dan Pirimidin)hafidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molecular Biology - Introduction-1Document37 paginiMolecular Biology - Introduction-1Abdi JifarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Nucleic AcidsDocument73 pagini5 Nucleic AcidsmjmonforteÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - Genetic Control and FunctionsDocument15 pagini3 - Genetic Control and FunctionssadaffardoosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomolecules Chemistry AssignmentDocument27 paginiBiomolecules Chemistry AssignmentUvan VijayÎncă nu există evaluări
- OnlyIAS - Udaan - Science and TechnologyDocument75 paginiOnlyIAS - Udaan - Science and TechnologyravichandrabanalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Molecular Biology: Tapeshwar Yadav (Lecturer)Document69 paginiBasics of Molecular Biology: Tapeshwar Yadav (Lecturer)Nando NanginÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument154 paginiThe Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeAnnisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic Acids.Document7 paginiNucleic Acids.Mujthaba AdmaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic AcidDocument25 paginiNucleic Acidhasishah710Încă nu există evaluări
- 1 DnaDocument27 pagini1 DnaLethabo MokubeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic Acid: Structure & FunctionsDocument51 paginiNucleic Acid: Structure & FunctionsManahil SardarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidDocument60 paginiNucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidWillar Deanson Navarro100% (1)
- Lecture 1Document87 paginiLecture 1Adnan MurtovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument69 paginiBasics of Molecular BiologyYasin Putra Esbeye100% (2)
- Bio NoteDocument5 paginiBio NoteErikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid State13thDocument19 paginiSolid State13thRaju SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stones: DefinitionsDocument4 paginiStones: DefinitionsAr Mohd NadeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environment EngineerDocument35 paginiEnvironment EngineerPoirei ZildjianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1 A Silly PolymerDocument3 paginiExperiment 1 A Silly PolymerRuby GoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corrosion by Concentrated Sulfuric Acid Steel Pipes and Tanks I21319914Document8 paginiCorrosion by Concentrated Sulfuric Acid Steel Pipes and Tanks I21319914carlos sotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- US8034246 PatentDocument9 paginiUS8034246 PatentCatalina SarriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form Four Revision On ChemistryDocument17 paginiForm Four Revision On Chemistrypatkhsheng@hotmail.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework ProblemsDocument96 paginiHomework ProblemsGautamist's Gautamism50% (2)
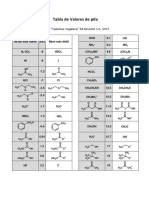
- Tabla de Valores de Pka: S. Ege "Química Orgánica" Ed Reverté S.A. 1997Document7 paginiTabla de Valores de Pka: S. Ege "Química Orgánica" Ed Reverté S.A. 1997loaca95Încă nu există evaluări
- 4 Quartz Pods 2004 2pDocument2 pagini4 Quartz Pods 2004 2pAlberto Lobo-Guerrero SanzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport Across Cell Membrane.: DR Nilesh Kate MBBS, MD Associate ProfDocument67 paginiTransport Across Cell Membrane.: DR Nilesh Kate MBBS, MD Associate ProfAspireÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Learning Materials in Biosciences) Aydin Berenjian - Essentials in Fermentation Technology-Springer International Publishing (2019) PDFDocument319 pagini(Learning Materials in Biosciences) Aydin Berenjian - Essentials in Fermentation Technology-Springer International Publishing (2019) PDFAlan Raphael MoraesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pancreatin 1 Nf-UspDocument1 paginăPancreatin 1 Nf-UspMonica Angeline SudarsonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - Part 1 RefiningDocument46 paginiChapter 3 - Part 1 RefiningAzhan FikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 10 PDFDocument17 paginiChem 10 PDFDishank AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acematt® Ok 500: Description Typical ApplicationsDocument1 paginăAcematt® Ok 500: Description Typical ApplicationsD'luchitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- External Carbon Surces For Nitrogen Removal Fact Sheet P100il8fDocument5 paginiExternal Carbon Surces For Nitrogen Removal Fact Sheet P100il8fIng Maria Del Pilar GonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Acids and AlkalisDocument5 pagini10 Acids and Alkalisrashmi_harry100% (1)
- Experiment 5: Analysis of Carbohydrates (Post-Lab Report)Document9 paginiExperiment 5: Analysis of Carbohydrates (Post-Lab Report)Jemina SacayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optibor: Product Data SheetDocument5 paginiOptibor: Product Data Sheetanon_993394650Încă nu există evaluări
- Contoh Daftar PustakaDocument2 paginiContoh Daftar PustakaGandiNainggolanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoich SHS 2018Document37 paginiStoich SHS 2018Cheska Mendoza0% (1)
- An Analytical Experiment For General Chemistry: Ascorbic Acid As A Standard For Iodometric TitrationsDocument7 paginiAn Analytical Experiment For General Chemistry: Ascorbic Acid As A Standard For Iodometric TitrationsniltonÎncă nu există evaluări
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,759,419 B2: Stoffer Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010Document24 paginiUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,759,419 B2: Stoffer Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010Alexander Franco CastrillonÎncă nu există evaluări
- KimiaDocument28 paginiKimiazannubaqotrunnadhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiber Craft ReportDocument37 paginiFiber Craft ReportJoyce Daganato100% (1)
- 1I InfoDocument2 pagini1I InfobarmarwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of ElectrochemistryDocument7 paginiBasics of Electrochemistryaman pandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discovery of S Adenosyl L Homocysteine Hydrolase 2014 Bioorganic MedicinaDocument5 paginiDiscovery of S Adenosyl L Homocysteine Hydrolase 2014 Bioorganic MedicinaDeden IndraDinataÎncă nu există evaluări