Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Alloys of Iron and Steel
Încărcat de
Rutvik0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
11 vizualizări12 paginisteel
Titlu original
alloys of iron and steel
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentsteel
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
11 vizualizări12 paginiAlloys of Iron and Steel
Încărcat de
Rutviksteel
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 12
.
Advantages
It has greater hardenability.
Less distortion and cracking.
Less grain growth.
Higher elastic ratio and endurance strength.
Greater high temperature strength.
Better machinability at high hardness.
Greater ductility at high strength.
High cost.
Temper brittleness in certain grades.
Improved corrosion resistance.
Better hardenability.
Grain size control.
Greater strength.
Improved machinability.
Improved high or low temperature stability.
Improved ductility.
Improved toughness.
Better wear resistance.
Improved cutting ability.
Carbon
Nickel
Chromium
Silicon
Titanium
Molybdenum
Vanadium
Tungsten
Manganese
Copper
Boron
Aluminium
Cobalt
When more chromium is added to the iron, a
fine film of chromium forms spontaneously
on the surface exposed to the air. The film
acts as a barrier to retards further oxidation,
rust or corrosion. As this steel can not be
stained easily, it is called stainless steel.
All stainless steel are classified in three group
Austenitic
Ferritic
Martensitic
They posses austenitic structure at room
temperature.
They posses higher corrosion resistance of all the
stainless steel
They retain ductility at temperature at absolute
zero.
They are non magnetic so they can be easily
identified.
They have the composition
C 0.03 to 0.25% , Mn 2 to 10%, Cr 16 to 26%
Si 1 to 2 % , Ni 3.5 to 22%
P and S is normally used.
Aircraft industry.
Chemical process.
Food processing.
House hold items.
Dairy industries.
Transportations industry.
Ferrite stainless steel have a low carbon to
chromium ratio. This elements the effect of
thermal transformation and prevent hardening by
heat treatment.
This steel are magnetic and good ductility.
This steel are more corrosion resistant than
martensitic steel.
Ferrite steel develop maximum softness, ductility
and corrosion resistance in the any condition.
Some chemical composition
C 0.08 to 0.20 %, Si 1%
Mn 1 to 1.5 %, Cr 11 to 27 %
Lining for petroleum industries.
Heating elements for furnaces.
Interior decorative work.
Screw and fitting.
Oil burner parts.
It are identified by their martensitic microstructure in the
hardened condition.
Because of the higher carbon to chromium ratio,
martensitic stainless steel are the only types hardenable by
heat treatment.
These steel are magnetic in all condition and posses the
best thermal conductivity of the stainless steel types.
Hardness, ductility, are the characteristics of martensitic
steels.
It can be cold worked with out difficulty, especially low
carbon content, can be machined satisfactorily, have good
toughness, show the good corrosion resistance to whether
and to some chemicals
It has composition
C 0.15 to 1.2 % , Si 1%
Mn 1 %, Cr 11 to 27 %
Use
Pumps and valve parts
Rulers and tapes
Turbine buckets
Surgical instrument
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- EKM Class II QBankDocument26 paginiEKM Class II QBankRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refrigration & Envor IssueDocument35 paginiRefrigration & Envor IssueRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- EKGDocument30 paginiEKGRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Ship TermsDocument1 pagină11 Ship TermsRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bottom End Bearing Clearance Four Stroke Engine ClassDocument4 paginiBottom End Bearing Clearance Four Stroke Engine ClassRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electro-Pneumatic TransducersDocument1 paginăElectro-Pneumatic TransducersRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refrigration TrublingDocument13 paginiRefrigration TrublingRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 1 ShaftingDocument22 pagini1 1 ShaftingRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refi & AcDocument36 paginiRefi & AcRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Actuators: Motors Are GenerallyDocument5 paginiElectrical Actuators: Motors Are GenerallyRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reference Notes - Chap 7pptxDocument3 paginiReference Notes - Chap 7pptxRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is P-N Junction Semiconductor Diode?Document9 paginiWhat Is P-N Junction Semiconductor Diode?RutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
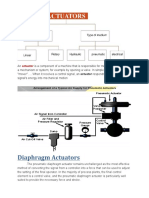
- Diaphragm Actuators: ActuatorDocument4 paginiDiaphragm Actuators: ActuatorRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open and Closed Loop SystemsDocument3 paginiOpen and Closed Loop SystemsRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homogenizer: Management & TreatmentDocument8 paginiHomogenizer: Management & TreatmentRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- 'What Is A Rectifier:-: Types of RectifiersDocument10 pagini'What Is A Rectifier:-: Types of RectifiersRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Various Types of Diodes With Their Characteristics & UsesDocument7 paginiVarious Types of Diodes With Their Characteristics & UsesRutvik100% (1)
- Survival at SeaDocument13 paginiSurvival at SeaRutvik100% (1)
- Reference Notes Chap 6Document7 paginiReference Notes Chap 6RutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment Chap7Document1 paginăAssignment Chap7RutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reference: Water Proof ComponentDocument3 paginiReference: Water Proof ComponentRutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reference Notes (Chap3)Document8 paginiReference Notes (Chap3)Rutvik100% (1)
- Assignment: 1. What Is Colreg? 2. Meaning of Each Flags 3. What Are The Light Pattern For Ships?Document1 paginăAssignment: 1. What Is Colreg? 2. Meaning of Each Flags 3. What Are The Light Pattern For Ships?RutvikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Fabricante de HPFF CableDocument132 paginiFabricante de HPFF Cableccrrzz100% (1)
- Cge 526 Petroleum GeologyDocument3 paginiCge 526 Petroleum GeologyNazim FauziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Akhila ResumeDocument2 paginiAkhila ResumejeelaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is MEMS TechnologyDocument6 paginiWhat Is MEMS TechnologyMAHDILEE100% (2)
- Rancang Bangun Alat Pendeteksi Tingkat Kematangan Buah Durian Dengan Metode Naïve BayesDocument10 paginiRancang Bangun Alat Pendeteksi Tingkat Kematangan Buah Durian Dengan Metode Naïve BayesMega Erika ErnawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation Instructions USB v1.0.21Document3 paginiInstallation Instructions USB v1.0.21Luis Alvaro MolinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Cold Formed Sections by Satish KumarDocument62 paginiDesign of Cold Formed Sections by Satish Kumarspawar1988Încă nu există evaluări
- Danfoss Install Operation and Manitenance IOM APP1.5-3.5Document70 paginiDanfoss Install Operation and Manitenance IOM APP1.5-3.5warshipvnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet Ls 7222Document4 paginiDatasheet Ls 7222Martín NestaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SECTION 307-01: Automatic Transaxle/Transmission - 6R80 2012 F-150 Workshop Manual General ProceduresDocument3 paginiSECTION 307-01: Automatic Transaxle/Transmission - 6R80 2012 F-150 Workshop Manual General ProceduresPriscilla Kelly Freitas dos SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fasson 0828 DatasheetDocument2 paginiFasson 0828 DatasheetGregory Alan Francisco IIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESMF 2 Collective CLOA Environmental Social Performance CC-ESP Assessment - Latest Version - Labels - 2022-10!03!02!09!12Document212 paginiESMF 2 Collective CLOA Environmental Social Performance CC-ESP Assessment - Latest Version - Labels - 2022-10!03!02!09!12Liko DollÎncă nu există evaluări
- C1 (1 - Storey Roof Sheets)Document11 paginiC1 (1 - Storey Roof Sheets)John Michael TalanÎncă nu există evaluări
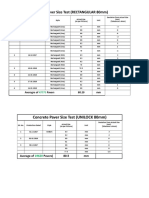
- Concrete Paver Size Test (RECTANGULAR 80mm) : 80.29 MM Averagre of PaversDocument2 paginiConcrete Paver Size Test (RECTANGULAR 80mm) : 80.29 MM Averagre of PaversNaveed Ul Qamar MughalÎncă nu există evaluări
- RT-1000 Terex, RT-100 TonDocument14 paginiRT-1000 Terex, RT-100 TonMaximo CC100% (1)
- ME205 - Fall 2018 - Sheet 6 - Pure Bending Stress in BeamsDocument3 paginiME205 - Fall 2018 - Sheet 6 - Pure Bending Stress in BeamsgjhghjhgjÎncă nu există evaluări
- 307 Bsi PinoutDocument5 pagini307 Bsi Pinoutmohhizbar0% (1)
- MC3361BPDocument5 paginiMC3361BPtonymathew03Încă nu există evaluări
- Board 2Document1 paginăBoard 2kristine_nilsen_2Încă nu există evaluări
- Dimensional Modelling by ExampleDocument132 paginiDimensional Modelling by ExampleFeras Alswairky100% (1)
- API MPMS ListaDocument6 paginiAPI MPMS ListaeduinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Powerflex 40 - User ManualDocument154 paginiPowerflex 40 - User ManualtrunerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tai Sin Singapore Cable Brochure Small FilesizeDocument2 paginiTai Sin Singapore Cable Brochure Small Filesizesuresh6265100% (1)
- ACCF - CSR Reconciliation-Darrang-18-08-20Document7 paginiACCF - CSR Reconciliation-Darrang-18-08-20Hunny VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intelligent Platform Management Interface Specification v1.0Document205 paginiIntelligent Platform Management Interface Specification v1.0alexchuah100% (1)
- Annexure-I: 1. Safety Precaution Used in Laboratory LevelDocument36 paginiAnnexure-I: 1. Safety Precaution Used in Laboratory Levelraghu sweetdreamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simatic St80 Add Ons Complete English 2015 OkDocument28 paginiSimatic St80 Add Ons Complete English 2015 OkTimothy FieldsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angle Grinder Gws 7 100 06013880f0Document128 paginiAngle Grinder Gws 7 100 06013880f0Kartik ParmeshwaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handout Contoh SoalDocument12 paginiHandout Contoh SoalIntan NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BOSL Controllers Standard-1Document82 paginiBOSL Controllers Standard-1Anonymous bnhNfqZXaÎncă nu există evaluări