Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
7A Covalent Bond and Molecule of Compound
Încărcat de
Vina Octavia AzzahraTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
7A Covalent Bond and Molecule of Compound
Încărcat de
Vina Octavia AzzahraDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Covalent Bond
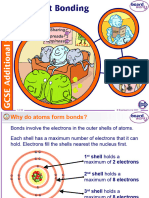
Why do covalent bonds form?
When non-metals react with one another,
their atoms share valence electrons.
The bond formed between atoms that
share electrons is called a covalent bond.
After bonding, each atom attains the electronic
configuration of a noble gas.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
What are molecules?
When atoms combine by sharing electrons, a
molecule is formed.
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms
held together by covalent bonds.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Molecules of Elements
Many non-metallic elements exist as molecules
made up of two or more identical atoms.
Let us look at how electrons are shared and
arranged within molecules of some elements:
hydrogen, chlorine and oxygen
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
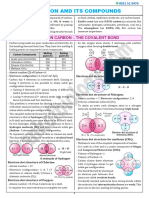
Hydrogen
Two hydrogen atoms share a
A hydrogen atom has pair of electrons so that each
1 valence electron. atom has 2 electrons in its
valence shell.
As a result, both have a stable duplet configuration.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Hydrogen
The sharing of 2 electrons forms a single covalent
bond.
A single covalent bond or a single bond is represented
by a single line ‘–’ in the structural formula.
‘Dot and cross’ Structural Molecular
Model
diagram formula formula
H H H2
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Chlorine
A chlorine atom has 7 valence electrons.
To attain an octet structure, 2 chlorine atoms
combine to share a pair of electrons.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Chlorine
Like hydrogen, chlorine has a single covalent bond.
‘Dot and cross’ Structural Molecular
Model
diagram formula formula
Cl Cl Cl2
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Oxygen
It needs 2 more electrons to
An oxygen atom has 6 form a stable octet structure.
valence electrons.
Each oxygen atom shares two of its electrons with
another oxygen atom.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Oxygen
4 electrons are shared between 2 oxygen atoms.
Such a bond is called a double covalent bond.
‘Dot and cross’ Structural Molecular
Model
diagram formula formula
O O O2
A double bond is represented by ‘ ’ in a structural formula.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Which is strongest covalent bonding?
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Molecules of Compounds
When 2 or more different types of atoms form
covalent bonds, a molecular compound or
covalent compound is formed.
Water, methane and carbon dioxide are examples of
covalent compounds.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Water
Water is formed by the reaction of hydrogen with
oxygen such that all three atoms attain noble gas
configurations.
‘Dot and cross’ Structural Molecular
Model
diagram formula formula
H 2O
Each water molecule contains two single covalent bonds.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Methane
Methane (CH4) contains carbon and hydrogen.
‘Dot and cross’ Structural Molecular
Model
diagram formula formula
CH4
In a methane molecule, the carbon atom has an octet
configuration while each hydrogen atom has a duplet
configuration.
Methane has four single covalent bonds.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Each carbon atom shares 2 electrons each with two
oxygen atoms.
Each oxygen atom shares 2 electrons
with a carbon atom.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
‘Dot and cross’ Structural Molecular
Model
diagram formula formula
CO2
Consequently, a carbon dioxide molecule
contains two double covalent bonds.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Naming Covalent Compound
• 1# The second element end must be –ide.
Example : CO2 (Carbon dioxide)
• 2 # Previxes must be added before the
element names.
• Except : Mono in the first element.
Example : NO2 (Nitrogen dioxide)
N2O3 (Dinitrogen trioxide)
Cl2O (Dichlorine monoxide)
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Writing the formulae of covalent
compounds
What is the chemical formula of carbon tetrachloride?
Thought Process:
We assume the first element named (in this
case, carbon) contains only one atom unless
otherwise stated.
The word ‘tetrachloride’ means ‘four chlorine atoms’.
Answer: CCl4
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
What is the chemical formula of
dinitrogen monoxide?
Answer:
N2O
‘dinitrogen’ means
‘2 nitrogen atoms’.
‘Monoxide’ means ‘1 oxide’.
Notice the subscript ‘1’ is not
indicated on the formula.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
What is the chemical formula of
dinitrogen tetroxide?
Answer:
‘dinitrogen’ = 2 nitrogen atoms ‘tetroxide’ = 4 oxygen atoms
N2O4
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
You should learn the chemical formulae of
some common covalent substances, such as
ammonia (NH3),
hydrogen peroxide (H2O2),
methane (CH4),
ozone (O3) and
water (H2O).
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Chemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2De la EverandChemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2Încă nu există evaluări
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDe la EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5)
- Covalent Bond Definition, Types, and ExamplesDocument1 paginăCovalent Bond Definition, Types, and ExamplesFreyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2 - RedactedDocument62 paginiClass 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2 - Redactedraza anandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry - Carbon and Its Compounds - Class Notes - WARRIOR SERIES CLASS-10THDocument136 paginiChemistry - Carbon and Its Compounds - Class Notes - WARRIOR SERIES CLASS-10THashudavid126474Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 (Mcmurry - 9th Edition)Document60 paginiChapter 2 (Mcmurry - 9th Edition)Paolo NaguitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Covalent Bonding 1Document18 paginiCovalent Bonding 1claudia gomesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Should I Care About Carbon: Yes, 10 MillionDocument15 paginiWhy Should I Care About Carbon: Yes, 10 MillionYashÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEM 111: MidtermsDocument9 paginiCHEM 111: MidtermsAira Lene ManaysayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Arihant CBSE Class 10 Term 2 WWW - examSAKHA.in PDFDocument144 paginiScience Arihant CBSE Class 10 Term 2 WWW - examSAKHA.in PDFjasphin ahitha100% (4)
- Covalent Bonding NotesDocument39 paginiCovalent Bonding NotesAmaris HopkinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 63e0ad702290fb001845df74 - ## - CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS - Class Notes - Warrior 2023 PDFDocument110 pagini63e0ad702290fb001845df74 - ## - CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS - Class Notes - Warrior 2023 PDFPRIYANSHU NAMANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2Document62 paginiClass 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2Killer boy SidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Term 2 Class 10 EbookDocument137 paginiScience Term 2 Class 10 EbookHarshit Negi100% (1)
- Group 3 Polarity of MoleculeDocument27 paginiGroup 3 Polarity of MoleculeLEA MAXINE MANAIZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbon Compounds: Grade 9Document21 paginiCarbon Compounds: Grade 9Rosalyn RayosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbon and Its Compounds (One Shot) - Class Notes - (Olympiad Challengers)Document83 paginiCarbon and Its Compounds (One Shot) - Class Notes - (Olympiad Challengers)anantsinghalktp21Încă nu există evaluări
- Science-9 Q2 W5-8Document67 paginiScience-9 Q2 W5-8Berliese FriasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch4 Notes Part 1Document3 paginiCh4 Notes Part 1prabhat7969tiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 (Mcmurry - 9th Edition)Document66 paginiChapter 1 (Mcmurry - 9th Edition)Paolo Naguit100% (3)
- Carbon and Its Compounds Class10Document10 paginiCarbon and Its Compounds Class10panchalprince151Încă nu există evaluări
- SCI 9 3covalent BondDocument7 paginiSCI 9 3covalent BondRaymel HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument8 paginiCarbon and Its CompoundsShalom LogosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Carbon and Its Compounds - 1 PG NotesDocument2 pagini4 Carbon and Its Compounds - 1 PG NotesMarcos D.Încă nu există evaluări
- Class 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2Document62 paginiClass 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2Sudhakar ChollangiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Covalent Bonding in ElementsDocument31 paginiCovalent Bonding in ElementsOsmany Madrigal100% (1)
- TEX - CHEM 103 Organic ChemistryDocument52 paginiTEX - CHEM 103 Organic ChemistrychioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Ncert NotesDocument35 paginiChemistry Ncert Notesvandana dehankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbon & Its CompoundsDocument35 paginiCarbon & Its CompoundsPradipjha JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 8 Notes 61a82274d167fDocument39 paginiModule 8 Notes 61a82274d167fMahi ModiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 BondingDocument4 pagini2 BondingAneeshTandonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Bonding: The Covalent Bond ModelDocument67 paginiChemical Bonding: The Covalent Bond ModelSherwin AlvaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Covalent Bonding LectureDocument33 paginiCovalent Bonding LectureGideon CavidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arihant Science Term 2 Question Bank Class 10thDocument143 paginiArihant Science Term 2 Question Bank Class 10thArnavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Chemistry Text Book 111CHEMDocument74 paginiOrganic Chemistry Text Book 111CHEMyyoosafe23Încă nu există evaluări
- 08 Lecture 2023Document119 pagini08 Lecture 2023fatemaabulnasrÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO1332 Chemistry 3 Organic Chemistry and Carbon Bonding SlidesDocument43 paginiBIO1332 Chemistry 3 Organic Chemistry and Carbon Bonding SlidesPaul MathewsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbon and It's Components Class 10Document15 paginiCarbon and It's Components Class 10Gowtham LÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Covalent Bonding": Pre-AP Chemistry Charles Page High School Stephen L. CottonDocument105 pagini"Covalent Bonding": Pre-AP Chemistry Charles Page High School Stephen L. CottoninayahviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Science 10th Edition Tillery Solutions ManualDocument9 paginiPhysical Science 10th Edition Tillery Solutions Manualthoabangt69100% (28)
- Chemistry Module 2 - Part 2Document13 paginiChemistry Module 2 - Part 2Francis RecocoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbon ChemistryDocument12 paginiCarbon ChemistrysunabbasconureÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block 1 FoundationsDocument40 paginiBlock 1 FoundationsCheng FuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Bonding: Asst. Prof. Jean Theresa O. GoDocument51 paginiChemical Bonding: Asst. Prof. Jean Theresa O. GoOsannah Irish InsongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Covalent and Metallic BondingDocument53 paginiCovalent and Metallic BondingAaditya MKÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Sample Lesson Plan PDFDocument7 pagini1 Sample Lesson Plan PDFChelsea AbarquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atoms, Elements and Compounds RevisionDocument40 paginiAtoms, Elements and Compounds RevisionAbha RathoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Bonding L-1 - Introduction & Lewis Dot Structure (12.6.2021)Document96 paginiChemical Bonding L-1 - Introduction & Lewis Dot Structure (12.6.2021)Dimpal BisenÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Q) YT - Carbon and Its CompoundDocument35 pagini(Q) YT - Carbon and Its CompoundDeepti KashyapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Theory of Valency &bondingDocument12 paginiElectronic Theory of Valency &bondingshivakafle039Încă nu există evaluări
- Hydrogen: Get The Power of Visual Impact On Your Side Log On ToDocument9 paginiHydrogen: Get The Power of Visual Impact On Your Side Log On ToShantam SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bonding Models For Methane, CH - Models Are NOT Reality. Each Has Its Own Strengths and LimitationsDocument12 paginiBonding Models For Methane, CH - Models Are NOT Reality. Each Has Its Own Strengths and LimitationsRachel AnneÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 4 Carbon and Its Compound NOTESDocument3 paginiCH 4 Carbon and Its Compound NOTESkashvi goelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document34 paginiChapter 1ellina safianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 Chemistry RemedialDocument69 paginiUnit 2 Chemistry Remedialabdimoh7522100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Chemistry 9th GradeDocument7 paginiLesson Plan Chemistry 9th GradeRea A. BilanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Covalent BondingDocument34 paginiCovalent Bondingo b r i g a d oÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument39 paginiCarbon and Its CompoundsSimran BangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction to Physics (Material Science Metallurgy)De la EverandAn Introduction to Physics (Material Science Metallurgy)Încă nu există evaluări
- Organic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsDe la EverandOrganic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (10)
- Trends in Analytical ChemistryDocument14 paginiTrends in Analytical ChemistryGeorge TanasescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Kristiandi2020 - SiamDocument7 pagini11 Kristiandi2020 - SiamVina Octavia AzzahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 Samadi2016 - Hydrodistillation ClevengerDocument8 pagini05 Samadi2016 - Hydrodistillation ClevengerVina Octavia AzzahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Gaydou1997 - Sesquiterpen From PatchouliDocument8 pagini10 Gaydou1997 - Sesquiterpen From PatchouliVina Octavia AzzahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 Liu 2012 - C.nobilis Kulit TerpenoidDocument12 pagini02 Liu 2012 - C.nobilis Kulit TerpenoidVina Octavia AzzahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Study On Steam Distillation and Hydro-Distillation Methods For Agarwood Oil ExtractionDocument4 paginiComparative Study On Steam Distillation and Hydro-Distillation Methods For Agarwood Oil ExtractionTrisna Bagus FirmansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Fruits and Vegetable Peels: A ReviewDocument5 paginiAntimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Fruits and Vegetable Peels: A ReviewMr. Jaga Mohan Meher AGRICULTURE-STAFFÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Ajun2009-Nanoparticle Chitosan CC UpadhyayDocument9 pagini01 Ajun2009-Nanoparticle Chitosan CC UpadhyayVina Octavia AzzahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Covalent Bonding 1Document2 paginiCovalent Bonding 1Vina Octavia AzzahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 SeatworkDocument3 pagini01 SeatworkVina Octavia AzzahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Errors in Academic Writing 20 OKTOBER 2020Document33 paginiCommon Errors in Academic Writing 20 OKTOBER 2020Vina Octavia AzzahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7B Simple Molecular StructuresDocument28 pagini7B Simple Molecular StructuresVina Octavia AzzahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- MYE 2018 CHEM S3A QP FinalDocument17 paginiMYE 2018 CHEM S3A QP FinalVina Octavia AzzahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Is A Hydrogen Atom.: How Are They Different From The First One?Document6 paginiThis Is A Hydrogen Atom.: How Are They Different From The First One?Vina Octavia AzzahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- INORGANIC CHEMISTRY III (100 Items)Document14 paginiINORGANIC CHEMISTRY III (100 Items)Marco SarmientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning Module: Mole ConceptDocument133 paginiLearning Module: Mole ConceptArnel BoholstÎncă nu există evaluări
- LET ReviewerDocument4 paginiLET ReviewerJaycee Silveo SeranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hybridization Review WorksheetDocument6 paginiHybridization Review WorksheetRejed VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11th Chemistry Centum Coaching Team Question Paper English MediumDocument5 pagini11th Chemistry Centum Coaching Team Question Paper English MediumpradeepvcpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group IV Elements 23 ChemistryDocument67 paginiGroup IV Elements 23 Chemistrysurvanity wilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bs ChemistryDocument84 paginiBs ChemistryFahad AsgharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic BondingDocument80 paginiAtomic BondingChan Chan M100% (1)
- Module 5 Polarity and Itermolecular ForcesDocument28 paginiModule 5 Polarity and Itermolecular ForcesJhon AlbadosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Chemistry With A Biological Emphasis Volume I PDFDocument467 paginiOrganic Chemistry With A Biological Emphasis Volume I PDFKARISHMA BHATIA0% (1)
- EVAN BLIZZARD - 20-21 PhET Simulation - Molecular GeometryDocument7 paginiEVAN BLIZZARD - 20-21 PhET Simulation - Molecular GeometryEVAN BLIZZARDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Behavior of The EBehavior of The Electronic Dielectric Constant in Covalent and Ionic Materialslectronic Dielectric Constant in Covalent and Ionic MaterialsDocument14 paginiBehavior of The EBehavior of The Electronic Dielectric Constant in Covalent and Ionic Materialslectronic Dielectric Constant in Covalent and Ionic MaterialsHoang Van DungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry PFT613S1Q. 2177: Instructor Vlad PremyslovDocument5 paginiPharmaceutical Chemistry PFT613S1Q. 2177: Instructor Vlad PremyslovSujatha DamuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report Chem PBL 4Document24 paginiReport Chem PBL 4Dian Ratri CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 4 Chemistry IA IBDocument3 paginiTopic 4 Chemistry IA IBDanisa IriantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Guides 2.1-2.3Document8 paginiStudy Guides 2.1-2.3MA. ASUNCION BeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alkanes: Nomenclature, Isomerism, and ConformationsDocument30 paginiAlkanes: Nomenclature, Isomerism, and ConformationsTr Mazhar PunjabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psma PrelimsDocument42 paginiPsma PrelimsPrincess Rose GamboaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To VSEPR Theory and Molecular GeometryDocument10 paginiIntroduction To VSEPR Theory and Molecular Geometrykjj7760Încă nu există evaluări
- Chemicals of LifeDocument4 paginiChemicals of LifeZoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polar and Nonpolar Molecules WorksheetDocument2 paginiPolar and Nonpolar Molecules WorksheetElixirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 2 QuestionsDocument16 paginiTopic 2 QuestionsthasmiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 09 Covalent Bonding OrbitalsDocument96 paginiChapter 09 Covalent Bonding Orbitals一念倾尘Încă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Bonding Board Level Assignment: 1. Which of The Following Has Maximum Bond Angle? HDocument7 paginiChemical Bonding Board Level Assignment: 1. Which of The Following Has Maximum Bond Angle? HLightÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ionic Bonding: Group ActivityDocument27 paginiIonic Bonding: Group ActivityTherese Eva Marie DequitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- C117 F2019 Syllabus v7 PDFDocument9 paginiC117 F2019 Syllabus v7 PDFKevin ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2004 Local Olympiad Exam PDFDocument8 pagini2004 Local Olympiad Exam PDFJunard AsentistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Fajan's RuleDocument13 pagini3 Fajan's RuleNazmi LatifÎncă nu există evaluări
- DFFHMDocument9 paginiDFFHMyaswanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Intermolecular Forces (S)Document15 pagini4 Intermolecular Forces (S)Mr TanÎncă nu există evaluări