Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
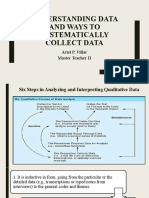
Learning From Others and Reviewing The Literature
Încărcat de
Marianne Gonzales0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
72 vizualizări26 paginiTitlu original
Learning from others and Reviewing the Literature
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
72 vizualizări26 paginiLearning From Others and Reviewing The Literature
Încărcat de
Marianne GonzalesDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 26
Learning from others
and Reviewing the
Literature
(Chapter 2: Review of Related Literature)
Learning Outcomes:
At the end of the unit, the learner shall be able
to:
1. Select relevant literature
2. Cite
related literature using American
Psychological Association Standard
3. Synthesize information from relevant literature
4. Write coherent review of literature
5. Follow ethical standards in writing related
literature
6. Present written review of literature
INTRODUCTION:
Researchers are based on facts and
scholarly works. Researchers based
their studies within the context of
existing knowledge . It is uncommon
for a research study to be conducted
out of one’s own belief or opinion.
Researchers conduct literature review
to familiarize themselves with existing
knowledge about a specific topic. The
roles that literature review play in a
research project will be discussed in
this unit.
CONTENT:
Review of Related
Literature
What is a review of related
Literature?
Review of Related Literature or
literature review is a summary of the
state of existing knowledge on a research
problem or topic. It is an analysis and
synthesis of articles related to the
research topic being studied.
3 processes involve in RRL
1.Searching RELEVANT ARTICLES
2.Reading and analyzing Research
Reports
3.Writing the description of the
existing information on a topic in a
manner that is ethical and based on
standards.
What are the purposes of
literature review?
1. To identify a research problem
2. To improve a research question or hypothesis
3. To determine what is known and unknown
about the topic of inquiry
4. To determine whether a study needs to be
replicated in a different setting or different
group of population.
5. To identify suitable designs or methods for
a specific study
6. To assist researchers in interpreting
findings.
Types of Literature
There are 2 major types of
literature. These are: research
literature, also known as
empirical references and non-
research references.
1. Research Literature – these are
literature based on research
findings. These are data supported
by evidences.
Example: Journal articles, literature
reviews, abstracts of research
studies.
2. Non-research references – these are
literature which are not based on research
findings These literatures can provide insights
and may broaden understanding regarding
topic. However, since they are not based on
research findings, they have limited use and
they do not serve the purpose of review of
related literature.
Example: literary or artistic works,
opinion articles, brochures,
magazines, anecdotes
Sources of Research Literature
Research Literature has two possible sources.
These are:
1. PrimarySource – these refer to description of
studies written by the researchers themselves.
Example: Researches published in a journal,
abstract prepared by the researcher(s),
dissertations, thesis, undergraduate researches,
presentation done by the researcher.
2. Secondary Source – these are
description of studies written by someone
else, other than the researchers who
conducted them. These description or
interpretation of studies by other
researchers should not become substitute
for primary sources because they are less
detailed and may be subjective in nature.
Example: literature review, abstract prepared
by a reviewer, presentation of research done
by someone else other than the researcher.
THE PROCESS OF
LITERATURE
REVIEW
1. SEARCHING RELEVANT ARTICLES
In the past, searching for literature is done
manually. A researcher needs to go to the
libraries and manually look for relevant
documents that he can use in his research
study . With the advent of technology comes
the expanding use of Internet. The
effectiveness and efficiency of searching
literature using online databases are starting
to make manual search for printed resources
obsolete.
However one must understand that there
are certain accessible search engines that
might give you interesting yet questionable
data. A researcher must learn the skill of
investigating which data are research –
based or not.
Searching for Print Resources
Presently, manual searches are being
overshadowed by electronic searches .
However, most top-of-the-line journals are
commercially available only and there are
high subscription fees which can be very
expensive for students. Another reason to do
manual search for printed materials is when a
researcher needs to perform a search to
include early literature on a topic.
Print Indexes
Are books that are used to locate articles in
journals and periodicals, books,
dissertations, publications of professional
organizations, and government documents.
When using a print index, you usually first
need to identify the appropriate subject
heading. Once the proper subject heading
is determined, you can proceed to the
subject section of the index, which lists the
actual references.
If you are doing a completely manual
search, it is a wise practice to begin the
search with the most recent issue of
the index and then to proceed
backward.
2. Reading and Analyzing Research
Reports
TIPS ON READING RESEARCH REPORTS
1. Makeresearch reading a habit. With this,
you will become familiar with its style of
writing.
2. Highlight
significant information and do
not hesitate to write marginal notes on
photocopies of research reports.
3. Initially scan the report then read them
more slowly next time.
4. Ensure that you understand what you read.
This must be a constant effort on the part of
the reader. Asking one’s self whether
comprehension of the material is taking
place.
5. Do not be discouraged by technical terms or even
statistical data. Try to understand the general idea of
the report.
6. Translate research jargons into more familiar terms
.Glossary or Terminologies sections of research
textbooks may guide you in this activity.
7. For beginning student researchers, critical
evaluation of research reports may be challenging. But
do not underestimate the value of your sense while
reading.
3. Writing the description of the existing
information on a topic
There are no fixed systems in preparing a written review. What is important is to
organize
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- RES 101 Activity SheetDocument25 paginiRES 101 Activity SheetJonel SorianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cordillera A+ College research course syllabusDocument6 paginiCordillera A+ College research course syllabusAveryl LadipÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Monthly Test (Practical Research 1)Document1 paginăFirst Monthly Test (Practical Research 1)Lorena N. GayolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Data and Ways To Systematically Collect DataDocument15 paginiUnderstanding Data and Ways To Systematically Collect DataAriel NubeÎncă nu există evaluări
- PR1 FM3 Research MethodologyDocument8 paginiPR1 FM3 Research MethodologyRichell OrotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Long Test MILDocument3 paginiLong Test MILBern PabÎncă nu există evaluări
- PR1 Q2 Modules 1 To 3Document32 paginiPR1 Q2 Modules 1 To 3Rhae Diaz DarisanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theoretical and Conceptual FrameworkDocument8 paginiTheoretical and Conceptual FrameworkSTEPHANIE FAYE FRANCISCOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument2 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningReynalyn HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Self-Learning Module in Practical Research I Lesson:: III 1&2 Day and Time: Learning CompetenciesDocument11 paginiSelf-Learning Module in Practical Research I Lesson:: III 1&2 Day and Time: Learning CompetenciesGhaniella B. JulianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module in Practical Research 1 Week1 2Document6 paginiModule in Practical Research 1 Week1 2Jamaica ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualitative Research in Across Different FieldsDocument1 paginăQualitative Research in Across Different FieldsGerwin Elsisura AldianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English Grade 11Document11 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in English Grade 11Maricel DiapanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Writing Research Titles in 11th GradeDocument2 paginiWriting Research Titles in 11th GradeCyril DofelizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adolescent Risky Behaviors and Mental Health ChallengesDocument18 paginiAdolescent Risky Behaviors and Mental Health ChallengesjulietpamintuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 PR 1Document27 paginiModule 1 PR 1Alexis FontanillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Individual Learning Activity Package (Ilap) No. 4: Department of EducationDocument22 paginiIndividual Learning Activity Package (Ilap) No. 4: Department of EducationJazer Batacan LeuterioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Lesson 2 - Criteria in Selecting, Citing, and Synthesizing The Related LiteratureDocument58 paginiChapter 4 Lesson 2 - Criteria in Selecting, Citing, and Synthesizing The Related LiteratureRomeo LicarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Research 1 Q2W8Document16 paginiPractical Research 1 Q2W8VERDADERO LevisthoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 paginiDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesAshley CarlosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2 - Practical Research 1Document23 paginiModule 2 - Practical Research 1Ziana Ross Hampac100% (1)
- Practical Research 2 Quarter 4 Module 9Document3 paginiPractical Research 2 Quarter 4 Module 9alexis balmoresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Significance of The StudyDocument9 paginiSignificance of The StudyClarynce CaparosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iplan - DLP - Format - PR1 - Understanding Data - ResearchdesignsDocument6 paginiIplan - DLP - Format - PR1 - Understanding Data - Researchdesignsjenenn ann cacayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Choosing A Research Topic Revised 2010Document15 paginiChoosing A Research Topic Revised 2010mashitivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proposal Defense Rubrics FinalDocument3 paginiProposal Defense Rubrics FinalHerbert Quinto SolisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Writing A Research TitleDocument13 paginiWriting A Research TitleRojane L. AlcantaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review of The Related ReviewDocument7 paginiReview of The Related ReviewKaiA.SermenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Research ReportDocument20 paginiPractical Research ReportRose SemblanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan Pr1Document3 paginiLesson Plan Pr1EvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applied Practical Research1 Q1 M17 Synthesizing Information From Relevant LiteratureDocument12 paginiApplied Practical Research1 Q1 M17 Synthesizing Information From Relevant LiteratureJOEL MALSI JRÎncă nu există evaluări
- PR1 - LESSON PLAN - Week 2.0 - Feb 20, 2023Document5 paginiPR1 - LESSON PLAN - Week 2.0 - Feb 20, 2023Jhon Ivy Jhon IvyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Methods for Academic SuccessDocument4 paginiResearch Methods for Academic SuccessLorianne ArcuenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PR1 - LESSON PLAN - Week 3.0 - Feb 22, 2023Document5 paginiPR1 - LESSON PLAN - Week 3.0 - Feb 22, 2023Jhon Ivy Jhon IvyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualitative Research and Its Importance in Daily LifeDocument43 paginiQualitative Research and Its Importance in Daily LifeJelly Joy Campomayor100% (1)
- MODULE7 State The Research QuestionsDocument12 paginiMODULE7 State The Research QuestionsJenny Mae LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- LP - Practical Research 2Document8 paginiLP - Practical Research 2Fredinel Malsi Arellano100% (1)
- Research Problem vs. Research QuestionDocument4 paginiResearch Problem vs. Research Questionmariel viteÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sentence Patterns of LanguageDocument10 paginiThe Sentence Patterns of LanguageMaxpein AbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning From Others and Reviewing The LiteratureDocument25 paginiLearning From Others and Reviewing The Literaturekailah1cassandra1vilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 5 - Chapter 1Document67 paginiWeek 5 - Chapter 1Maria Laarnie D. MoriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Choosing Research Topics and Crafting Effective QuestionsDocument33 paginiChoosing Research Topics and Crafting Effective QuestionsJulieSanchezErsandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- III - Topic 3 Reading On Related Studies (Lesson 1-3)Document63 paginiIII - Topic 3 Reading On Related Studies (Lesson 1-3)Jemimah CorporalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualitative and Quantitative Data Individual Worksheet PDFDocument2 paginiQualitative and Quantitative Data Individual Worksheet PDF'AcqhoziihFamousxzSzupfisxzticqkeiytEdÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAS English in Academic Purpose Quarter Module 3Document4 paginiLAS English in Academic Purpose Quarter Module 3Abigail MasotisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research 101 Building On The BasicsDocument7 paginiResearch 101 Building On The Basicscris annÎncă nu există evaluări
- RS101 - MODULE 3 - Week 6 To 7 (PDF File)Document12 paginiRS101 - MODULE 3 - Week 6 To 7 (PDF File)Jay DhelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q2 - (LAS) PRACTICAL RESEARCH 1 WK 4 PDFDocument5 paginiQ2 - (LAS) PRACTICAL RESEARCH 1 WK 4 PDFJazer LeuterioÎncă nu există evaluări
- PracticalResearch - G11 Q1 Mod2 v3 RemovedDocument26 paginiPracticalResearch - G11 Q1 Mod2 v3 Removedjasper panglaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Long Quiz ReviewerDocument8 paginiLong Quiz Reviewerloisse camaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan in Practical Research 2: (Quantitative Research For SHS) - Manila: Lorimar Publishing, IncDocument1 paginăLesson Plan in Practical Research 2: (Quantitative Research For SHS) - Manila: Lorimar Publishing, IncJan QuinicioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Johnny Ang National High School Katangawan, General Santos City Lesson Plan in Practical Research Ii - Grade 12 I. ObjectivesDocument2 paginiJohnny Ang National High School Katangawan, General Santos City Lesson Plan in Practical Research Ii - Grade 12 I. ObjectivesAljon Domingo TabuadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnswerSheet RWS - 4th QuarterDocument8 paginiAnswerSheet RWS - 4th QuarterVine AlfecheÎncă nu există evaluări
- FOR PRINT PR1 Module 4Document30 paginiFOR PRINT PR1 Module 4jay jay mancinganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument5 paginiDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesJanna GunioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benefits and Beneficiaries of ResearchDocument25 paginiBenefits and Beneficiaries of ResearchELA REYESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q4-S1 Practical Research 1Document1 paginăQ4-S1 Practical Research 1julieanne_portalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selecting Citing and Synthesizing Related LiteratureDocument19 paginiSelecting Citing and Synthesizing Related LiteratureCloud Stephen JindaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Project Summative TestDocument1 paginăResearch Project Summative TestReiven TolentinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- WHLP HOPE 1 Week 8Document2 paginiWHLP HOPE 1 Week 8Marianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summative Test in HOPE 1 Week 1 To 3Document3 paginiSummative Test in HOPE 1 Week 1 To 3Marianne Gonzales0% (1)
- Summative Test in HOPE 1 Week 1 To 3Document3 paginiSummative Test in HOPE 1 Week 1 To 3Marianne Gonzales0% (1)
- Stem - Bio11 /12-La-C-5: Wake Up, Eat Breakfast and Get Ready For The Scheduled LessonsDocument2 paginiStem - Bio11 /12-La-C-5: Wake Up, Eat Breakfast and Get Ready For The Scheduled LessonsMarianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parents/guardian Will Get The SLM That Is Good For 6 Weeks in The Assigned Area by Purok On Monday October 5, 2020 at 7:30-8:30am andDocument3 paginiParents/guardian Will Get The SLM That Is Good For 6 Weeks in The Assigned Area by Purok On Monday October 5, 2020 at 7:30-8:30am andMarianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weekly school health plan focuses on fitnessDocument1 paginăWeekly school health plan focuses on fitnessMarianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weekly school health plan focuses on fitnessDocument1 paginăWeekly school health plan focuses on fitnessMarianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- WHLP Gen Bio 1 Week 5Document2 paginiWHLP Gen Bio 1 Week 5Marianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade-11-Philo - Q1 Mod 2 Method of Philospphizing v3Document26 paginiGrade-11-Philo - Q1 Mod 2 Method of Philospphizing v3Lani Bernardo Cuadra83% (93)
- Parents/guardian Will Hand Over The Answer Sheet For Modules 14 To 15 (Week 7) Then Will Get The Weekly Home Learning Plan For Module 16 (Week 8)Document2 paginiParents/guardian Will Hand Over The Answer Sheet For Modules 14 To 15 (Week 7) Then Will Get The Weekly Home Learning Plan For Module 16 (Week 8)Marianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wake Up, Eat Breakfast and Get Ready For The Scheduled LessonsDocument2 paginiWake Up, Eat Breakfast and Get Ready For The Scheduled LessonsMarianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stem - Bio11 /12-La-C-5: Wake Up, Eat Breakfast and Get Ready For The Scheduled LessonsDocument2 paginiStem - Bio11 /12-La-C-5: Wake Up, Eat Breakfast and Get Ready For The Scheduled LessonsMarianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- FOCUS CHARTING OR F-DAR CHARTINGDocument23 paginiFOCUS CHARTING OR F-DAR CHARTINGMarianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gen Bio Ref1 PDFDocument25 paginiGen Bio Ref1 PDFGexel Cecilio78% (9)
- Module in Crossing Over and RecombinationDocument26 paginiModule in Crossing Over and RecombinationMarianne Gonzales100% (6)
- Chapter 1-3 ThesisDocument20 paginiChapter 1-3 ThesisMarianne Gonzales100% (1)
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module - : Title: Cell CycleDocument25 paginiGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module - : Title: Cell CycleEvangelene Esquillo Sana100% (7)
- Gen. Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Structure and Function of Animal TissueDocument27 paginiGen. Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Structure and Function of Animal TissueMarianne Gonzales60% (5)
- Instructions (Affidavit of Undertaking) : Do Not Print This PageDocument3 paginiInstructions (Affidavit of Undertaking) : Do Not Print This PageMacxieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alberts Introductory PagesDocument33 paginiAlberts Introductory PagesMarianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument3 paginiSubject Verb AgreementMarianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Cell & Molecular Biology Techniques: ImmunofluorescenceDocument38 paginiIntroduction To Cell & Molecular Biology Techniques: ImmunofluorescenceMarianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Worksheet Belongs ToDocument2 paginiThis Worksheet Belongs ToMarianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q2 Week I - Meaning of LifeDocument4 paginiQ2 Week I - Meaning of Lifebebot magno olarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Number Tracing WorksheetDocument5 paginiNumber Tracing WorksheetMarianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1-3 ThesisDocument20 paginiChapter 1-3 ThesisMarianne Gonzales100% (1)
- DepEd's Guidelines on Enrollment Procedures for SY 2020-2021Document37 paginiDepEd's Guidelines on Enrollment Procedures for SY 2020-2021AlexAbogaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DepEd Forms CollectionDocument4 paginiDepEd Forms CollectionMarianne GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Title and Chapter 1Document89 paginiResearch Title and Chapter 1Marianne Gonzales100% (1)
- Possition Paper On Teaching Grammar PDFDocument9 paginiPossition Paper On Teaching Grammar PDFapi-289724333Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1A Human NatureDocument7 paginiLecture 1A Human NatureerickssonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bpa MMW Slm4 Problem Solving and ReasoningDocument4 paginiBpa MMW Slm4 Problem Solving and ReasoningJim V. BongayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fuster 2001Document15 paginiFuster 2001Jane SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Achievement Test - Concept and TypesDocument29 paginiAchievement Test - Concept and TypesDr. Nisanth.P.M67% (6)
- HCI Course Outlines SEDocument3 paginiHCI Course Outlines SEZubair AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essay ArgumentativeDocument1 paginăEssay ArgumentativeyogibaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Train PHD Student To Be Thinkers Not Just SpecialiDocument1 paginăTrain PHD Student To Be Thinkers Not Just Specialiandik_y100% (1)
- The Natural Approach: Alexis Martínez-RamírezDocument33 paginiThe Natural Approach: Alexis Martínez-RamírezAlePsics MrtínzÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDev DLLDocument3 paginiPDev DLLbry100% (3)
- INTP CareersDocument2 paginiINTP CareersharshadspatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample CogatDocument1 paginăSample Cogatapi-368875401Încă nu există evaluări
- LESSON PLAN For AllomorphsDocument2 paginiLESSON PLAN For AllomorphsLc ItamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Origin of The Qatardebate Style: Djudicating Ebating in AtarDocument11 paginiOrigin of The Qatardebate Style: Djudicating Ebating in AtarMohammad Latef Al-AlsheikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 13 Cognitive Development of Infants and ToddlersDocument12 paginiModule 13 Cognitive Development of Infants and ToddlersJovielyn Rosewell100% (3)
- Anna Kouppanou PHD ThesisDocument256 paginiAnna Kouppanou PHD ThesisLaura SeverinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machine Learning Seminar ReportDocument26 paginiMachine Learning Seminar ReportSuparna Mishra20% (5)
- Questions For Your VivaDocument2 paginiQuestions For Your VivaHusnain ArifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy 210-Physics 1 SyllabusDocument2 paginiPhy 210-Physics 1 SyllabusHarold TaylorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection: "How To Avoid Death by Powerpoint" by David JP PhillipsDocument2 paginiReflection: "How To Avoid Death by Powerpoint" by David JP PhillipsFerl Diane SiñoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modern TheosophyDocument98 paginiModern TheosophyBruce Good100% (1)
- Zima, Peter v. - Subjectivity and Identity. Between Modernity and Identity (2015)Document345 paginiZima, Peter v. - Subjectivity and Identity. Between Modernity and Identity (2015)Luis Carlos Ruiz CoronaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Value of Studying the History of Economic ThoughtDocument15 paginiThe Value of Studying the History of Economic ThoughtdavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Science and History of TranslationDocument18 paginiHistory of Science and History of TranslationAAliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Delivering IS4 Instruction ResourceDocument2 paginiDelivering IS4 Instruction Resourcetoddy747Încă nu există evaluări
- Historia de La PsicologíaDocument2 paginiHistoria de La PsicologíaYahir Nava RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hewitt - What Do Our Intuitions About The Experience Machine Really Tell Us About HedonismDocument20 paginiHewitt - What Do Our Intuitions About The Experience Machine Really Tell Us About Hedonismherac12Încă nu există evaluări
- Motivation 1980007641Document12 paginiMotivation 1980007641kshitizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 3 Caribbean HistoryDocument6 paginiLesson 3 Caribbean HistoryOla100% (1)