Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
"Transformers": AV-222 Electromechanical Systems
Încărcat de
Syed Haider0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
20 vizualizări21 paginidsffsfafasxc
Titlu original
intro
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentdsffsfafasxc
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
20 vizualizări21 pagini"Transformers": AV-222 Electromechanical Systems
Încărcat de
Syed Haiderdsffsfafasxc
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 21
AV-222
ELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEMS
Lecture No 3
“TRANSFORMERS”
Instructor: Sqn Ldr Ahnaf Lodhi
Class: 84 E.C.
Book: Electric Machinery Fundamentals 5th ed
Chapter : 2
Avionics Engineering Department
Transformers of another dimension
Transformers: Current Dimension
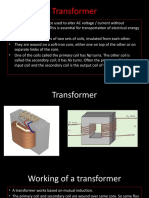
• Device used to convert voltage levels of ac power through
the action of a magnetic field
• Frequency remains constant
• No effect on total power in ideal scenario
• Consists of two or more coils wrapped around a
ferromagnetic core
• Connection between coils
• Common magnetic flux
• Types of windings
• Primary/Input
• Connected to the source of electrical power
• Secondary/Output
• Connected to the load
• Tertiary windings
• Intermediate stage/s
Transformers
• Importance
• Low voltage transmission accompanied by high currents in earlier times
• Large power losses
• Equal to square of current in the transmission line in general
• Limited region of service for power stations
• Ability of transformers
• Convert power into higher voltage levels with smaller currents significantly
reducing the power losses
• Modern power generation systems
• Generated levels around 2 to 25kV
• Stepped up to 110kV to 1000kV for transmission
• Stepped down to 12-34.5kV for local distribution
• Stepped down to local levels i.e. 220V for normal safe use
• Other uses
• Voltage sampling
• Current sampling
• Impedance transformation
Types of Transformers
• Two types of cores for power transformers
• Core form
• Shell form
• Either case core constructed from thin laminations electrically
isolated from each other to minimize eddy currents
Transformers Construction
• Primary and secondary windings wound on top of each
other
• Low voltage windings to be inner most
• Purpose
• Simplifies insulation of high voltage windings
from the core
• Results in less leakage flux than for a core
separated by a distance
• Functional classification
• Unit transformer
• Connected to generator to step voltage up to +110KV
• Substation Transformer
• Step down levels of unit transformer to distribution level (2-35kV)
• Distribution Transformer
• Steps voltage down from distribution levels to normal use
Power Distribution System
Types of Transformers
• Special purpose transformers
• Potential transformers
• Sample a high voltage and produce a low voltage directly
proportional to it
• Designed to handle small amounts of current
• Current Transformer
• Provide a secondary current much smaller but directly
proportional to primary current
Ideal Transformer
• Lossless
device
• NP primary windings turns
• NS secondary windings turns
• Relationship between primary and secondary current
• Summarizing
• Phase angle of VP and VS and IP and IS are same
Ideal Transformer
Ideal Transformer
• Dot Convention
• VP positive at the dotted end w.r.t undotted end, VS to be
positive at dotted end
• IP flowing into the dotted end of primary windings, IS to flow out
of the dotted end at the secondary windings
Ideal Transformer
• Power
• For an ideal transformer
• (Same power factor for primary and secondary windings)
QUIZ
Ideal Transformer
•
• Same for reactive power and apparent power
• Impedance Transformation
• Changing voltage and current also changes apparent impedance
• Possibility to match a load impedance to a source impedance by
picking proper turns ratio
Example
• Ex 2.1
• Find line current, load voltage, line losses for both circuits
Example
Example
• Ex 2.1
• Find line current, load voltage, line losses for both circuits
Example
• For circuit 2
Example
Example
Thank You
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Practical Transformer Handbook: for Electronics, Radio and Communications EngineersDe la EverandPractical Transformer Handbook: for Electronics, Radio and Communications EngineersEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (16)
- Surge Control (Op)Document58 paginiSurge Control (Op)ahmed messallam100% (1)
- Piston Engine FundamentalDocument62 paginiPiston Engine Fundamentalkp subedi100% (1)
- Power TransformersDocument357 paginiPower TransformersRK K100% (1)
- Types of TransformersDocument27 paginiTypes of Transformerskyaw winÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE 322 TransformersDocument73 paginiEE 322 TransformersCedric BernardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Scope Statement For Wilmonts CaseDocument4 paginiProject Scope Statement For Wilmonts CaseSyed Haider88% (8)
- Routine Maintenance Schedule Switchboard PDFDocument1 paginăRoutine Maintenance Schedule Switchboard PDFAzman HanafiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Static Relays: Prepared byDocument56 paginiStatic Relays: Prepared byLavanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work Breakdown StructureDocument5 paginiWork Breakdown StructureSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- X-Ray Generator ComponentsDocument39 paginiX-Ray Generator ComponentsPRAFULL RAIÎncă nu există evaluări
- TransformerDocument235 paginiTransformerRK K100% (1)
- Bayer CLINITEC 500 Urine Chemistry Analyzer Service ManualDocument322 paginiBayer CLINITEC 500 Urine Chemistry Analyzer Service Manualtunet1106Încă nu există evaluări
- Scope Management Plan Group 1Document6 paginiScope Management Plan Group 1Syed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daihatsu Type K3 Engine Service Manual No.9737 No.9332 No. 9237 Emission Control System PDFDocument11 paginiDaihatsu Type K3 Engine Service Manual No.9737 No.9332 No. 9237 Emission Control System PDFMozes SimataaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bremse GsDocument3 paginiBremse GsХелфор УкраинаÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformers & Electrical Distribution Systems: HSC Module 9.3 Motors & GeneratorsDocument45 paginiTransformers & Electrical Distribution Systems: HSC Module 9.3 Motors & GeneratorsBALACHITRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISO Standards ListDocument13 paginiISO Standards ListviahulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformers & MachinesDocument100 paginiTransformers & MachinesAmeerUlHaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 Ee336Document31 paginiUnit 4 Ee336Satya Sudhakar RasamsettiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2Document40 paginiUnit 2SindhujaSindhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- AGK - Electrics 23 Power Conversion 24 S8 PDFDocument24 paginiAGK - Electrics 23 Power Conversion 24 S8 PDFCemalettin öztoprakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materi Fisika Semerter 1Document25 paginiMateri Fisika Semerter 1Adi SetiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformers: How They Work and Their TypesDocument13 paginiTransformers: How They Work and Their TypesVishnuraj R100% (2)
- Final TransformersDocument21 paginiFinal TransformersZahira JavedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sarthak Physics 2Document21 paginiSarthak Physics 2Priyanshu GautamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lectures 1&2Document53 paginiLectures 1&2Yong Jian RongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.2 Power GenerationDocument31 pagini1.2 Power GenerationLeojhun PalisocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - TransformerDocument40 paginiChapter 2 - Transformerarokia samyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1transformer NotesDocument74 paginiUnit 1transformer NotesLokesh .cÎncă nu există evaluări
- TransformersDocument23 paginiTransformersAarush PitlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transf ReactorDocument46 paginiTransf ReactorNaga BinduÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Transformers": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument25 pagini"Transformers": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 TransformerDocument33 pagini7 TransformerMd. Sojib KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power DevicesDocument28 paginiPower DevicesAnnas QureshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TransformerDocument22 paginiTransformerIF21 Minit ChitrodaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Physics 3.1Document16 paginiBio Physics 3.1reza dehghaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical System (CB Bank)Document48 paginiElectrical System (CB Bank)chanÎncă nu există evaluări
- TransformerDocument9 paginiTransformerVeankatapathy 613 Xl group BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presented By:-Borse RishikeshDocument15 paginiPresented By:-Borse Rishikeshjitu borgohainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electricity Transmission: Bhagwan Mahavir College of ArchitectureDocument25 paginiElectricity Transmission: Bhagwan Mahavir College of ArchitectureVala Vraj M.Încă nu există evaluări
- DAM 1213 Topic 1-2Document46 paginiDAM 1213 Topic 1-2Nur FizriyanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Passive Components: Resistors Capacitors Inductors Diodes Interface ComponentsDocument186 paginiPassive Components: Resistors Capacitors Inductors Diodes Interface ComponentsyokeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rad T 290: X-Ray Generators and TransformersDocument29 paginiRad T 290: X-Ray Generators and Transformersomad pendaftaranPPDSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 Transformer StudentDocument53 paginiUnit 2 Transformer StudentJeet DoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bem I Elect JPDocument122 paginiBem I Elect JPdaminipatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Energy System - Energy - 3Document48 paginiElectric Energy System - Energy - 3Agent SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2-1 - TransformerDocument44 paginiChapter 2-1 - TransformerHanis SyafiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification and Design AspectsDocument45 paginiClassification and Design AspectsNandiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Variable Digital Transformer: Submitted byDocument14 paginiLinear Variable Digital Transformer: Submitted byAnonymous SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- TransformersDocument124 paginiTransformersRohini MukunthanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformers Explained: Types, Construction, Working PrinciplesDocument52 paginiTransformers Explained: Types, Construction, Working PrinciplesNIHAL GUPTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1337683650.628lecture 5 - TransformersDocument25 pagini1337683650.628lecture 5 - TransformersgnathblÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes Week13Document74 paginiLecture Notes Week13Sezer CeyhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd LectureDocument50 pagini3rd LectureSafdar HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complex Engineering Problem (CEP) EE-311 DesignDocument4 paginiComplex Engineering Problem (CEP) EE-311 Designlaksh rathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jeje's Presentation1Document22 paginiJeje's Presentation1Tomola JejeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer SheetDocument4 paginiTransformer SheetDalia SaqqaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-4 Single Phase Transformer - NewDocument50 paginiUnit-4 Single Phase Transformer - NewSneha GadgilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xmer (Small)Document11 paginiXmer (Small)VivekÎncă nu există evaluări
- RT 102 Self InducDocument16 paginiRT 102 Self InducdvdmegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformers Basic and TypesDocument11 paginiTransformers Basic and Typesismail hashimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machines I - TransformersDocument31 paginiElectrical Machines I - TransformersOneil Prettyboyswagg LeitchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer: 3612C Haralambie Cristian Frangu Alin Cantabine IonutDocument8 paginiTransformer: 3612C Haralambie Cristian Frangu Alin Cantabine Ionutlowder -CristiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Switching DC Power SupplyDocument64 paginiSwitching DC Power SupplyJavez DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machines 1 Chapter 3 Transformers (ECL 302Document21 paginiElectrical Machines 1 Chapter 3 Transformers (ECL 302pawan fartyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit:2: 1. Transformers and Its Operation 2Document64 paginiUnit:2: 1. Transformers and Its Operation 2Agent SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer - Types & ApplicationsDocument38 paginiTransformer - Types & ApplicationsBenish CmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motor Transformers and Distribution Systems LectureDocument44 paginiMotor Transformers and Distribution Systems LectureShahab HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- E. WORKSHOP II by SemereDocument93 paginiE. WORKSHOP II by SemereSami Ye KiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase TransformerDocument15 paginiSingle Phase TransformerAgnivesh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Synchronous Motors": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument22 pagini"Synchronous Motors": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Transformers": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument25 pagini"Transformers": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- AV-222 Electromechanical Systems: Text Book: Chapter 3Document17 paginiAV-222 Electromechanical Systems: Text Book: Chapter 3Syed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Rectifier Circuits: AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument12 paginiBasic Rectifier Circuits: AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Introduction": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument14 pagini"Introduction": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Series DC Motor/ Motor Efficiency": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument12 pagini"Series DC Motor/ Motor Efficiency": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Ac Machine Fundamentals: AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument13 pagini"Ac Machine Fundamentals: AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Synchronous Generators": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument10 pagini"Synchronous Generators": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Ac Machine Fundamentals": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument13 pagini"Ac Machine Fundamentals": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Real Machines: AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument18 pagini"Real Machines: AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- "DC Generators": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument15 pagini"DC Generators": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- "DC Motors": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument23 pagini"DC Motors": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- "DC Machine Fundamentals: AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument22 pagini"DC Machine Fundamentals: AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Transformers" Voltage Regulation and Efficiency: AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument22 pagini"Transformers" Voltage Regulation and Efficiency: AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- AbdullahDocument1 paginăAbdullahSyed HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Mechanics 4 Force System ResultantDocument24 paginiEngineering Mechanics 4 Force System Resultantanil3091Încă nu există evaluări
- Date: Project Manager: Karrar Haider: Role Stakeholder NameDocument14 paginiDate: Project Manager: Karrar Haider: Role Stakeholder NameSyed Haider50% (2)
- Listening Sample Task - Matching Example 1Document4 paginiListening Sample Task - Matching Example 1Cristiane SerbanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Listening Sample Task - Plan Map Diagram LabellingDocument3 paginiListening Sample Task - Plan Map Diagram LabellingAdhi ThyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Listening - Sample - Task - Matching - Example - 2 - PDFDocument3 paginiListening - Sample - Task - Matching - Example - 2 - PDFSVS SudheerÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPU - Organisation - Sir NotesDocument8 paginiCPU - Organisation - Sir Notes69Sutanu MukherjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- B&S 161400-161499Document22 paginiB&S 161400-161499Bruno MarianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schematic Diagrams For Philips CD753Document12 paginiSchematic Diagrams For Philips CD753knightmare88100% (1)
- Outdoor Vacuum Circuit Breaker 12/36kVDocument4 paginiOutdoor Vacuum Circuit Breaker 12/36kVEnergy TecÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4090-9002 Control ModuleDocument2 pagini4090-9002 Control ModuleMahmoud Abdul Wahed Radi100% (1)
- Intelligent Electromagnetic Braking for 4-Wheel VehiclesDocument4 paginiIntelligent Electromagnetic Braking for 4-Wheel VehiclesSkive FabsysÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dobrica PavlinuÅ¡iÄ 's random unstructured stuff on meanIT tablet Q70Document3 paginiDobrica PavlinuÅ¡iÄ 's random unstructured stuff on meanIT tablet Q70Cassio Jose FonsecaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fan Drive System: Systems OperationDocument5 paginiFan Drive System: Systems Operationallan lariosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BRC 300 and PBA 200 User ManualDocument112 paginiBRC 300 and PBA 200 User ManualAtreyo SahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ca1000 CN235Document3 paginiCa1000 CN235indra pratamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MY19 Mattoc Comp Service Guide and Travel Change 1Document31 paginiMY19 Mattoc Comp Service Guide and Travel Change 1Anonymous DabMRntnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microcontroller configuration options guideDocument12 paginiMicrocontroller configuration options guidewesker2010Încă nu există evaluări
- Berger Lahr ServomotorsDocument32 paginiBerger Lahr ServomotorsAlvaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF N Fcom Gia TF N Eu 20121113 DSC 21Document116 paginiPDF N Fcom Gia TF N Eu 20121113 DSC 21Nigel AmartaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6e Engine Start BatteryDocument6 pagini6e Engine Start BatteryJegadeshwaran RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelling of SOI-LDMOS TransistorDocument13 paginiModelling of SOI-LDMOS TransistorchaitudscÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Service Information System (ERWIN - ERWIN) 5Document7 paginiElectronic Service Information System (ERWIN - ERWIN) 5Marius PopÎncă nu există evaluări
- CV FormatDocument2 paginiCV FormatTehmas KamranÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATV600 Getting Started Annex EAV64300 12Document8 paginiATV600 Getting Started Annex EAV64300 12rabia akramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Playstation 2 SCPH-90001Document118 paginiPlaystation 2 SCPH-90001ZohiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wire Size Chart NEC 2011Document1 paginăWire Size Chart NEC 2011Ali AkbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Five PDFDocument32 paginiChapter Five PDFAdelu BelleteÎncă nu există evaluări