Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Barrier Free Architecture
Încărcat de
Kuldeep Panchal0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
394 vizualizări10 paginiThe document discusses considerations for barrier-free and universal design. It covers definitions of barrier-free environments and outlines key architectural design elements to ensure accessibility, including parking, entrances, ramps, dropped kerbs, doors, and corridors. The goal is to allow free and safe movement for all people regardless of ability. Dimensions and design features are provided to make spaces accessible to people with disabilities including wheelchair users.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
BARRIER FREE ARCHITECTURE
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThe document discusses considerations for barrier-free and universal design. It covers definitions of barrier-free environments and outlines key architectural design elements to ensure accessibility, including parking, entrances, ramps, dropped kerbs, doors, and corridors. The goal is to allow free and safe movement for all people regardless of ability. Dimensions and design features are provided to make spaces accessible to people with disabilities including wheelchair users.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
394 vizualizări10 paginiBarrier Free Architecture
Încărcat de
Kuldeep PanchalThe document discusses considerations for barrier-free and universal design. It covers definitions of barrier-free environments and outlines key architectural design elements to ensure accessibility, including parking, entrances, ramps, dropped kerbs, doors, and corridors. The goal is to allow free and safe movement for all people regardless of ability. Dimensions and design features are provided to make spaces accessible to people with disabilities including wheelchair users.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 10
BARRIER FREE
ARCHITECTURE
TSHERING YANGDEN BHUTIA
A8304015032
BARRIER-FREE DESIGN
Design for those with
physical or other
disabilities, involving the
provision of
alternative means of
access to steps (e.g.
ramps and lifts
(elevators) for those with
mobility problems). It is
also called universal
or barrier-free design
What is a Barrier-Free
Environment?
A barrier-free environment is a space
that allows for free and safe movement,
function and access for all, regardless of
age, sex or condition. A space or a set of
services that can be accessed by all,
without obstacles, with dignity and with
as much independence as possible. The
environment means buildings, roads,
parks, gardens and other places,
services, modes of transportation,
products of daily use, etc. It must be
clearly understood that barrier–free goes
far beyond just a ramp and has many
other necessary aspects. These range
from door and passage widths to flooring
surfaces, from counter heights to door
handles and railings, from signage and
auditory signals to tactile guides.
Architectural Design
Considerations:
This section deals with the design requirements of vertical and
horizontal access in both new and existing constructions. It is
subdivided into following headings:
Ramps
Elevators/Lifts
Stairs
Railings and Handrails
Entrances
Reception
Doors
Corridors
Toilets
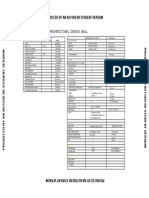
PARKING:
Standard car parking spaces are
typically 3500mm wide x
5000mm long should be
allocated at a convenient place
near the office entrance or
reception with international
symbols of accessibility.
The parking spaces reserved for
persons with a disability shall be
located in proximity and with an
accessible route to entrance.
Ensure the route between the
car park and the entrance to the
building or facility is accessible
and easy to understand
ENTRANCE:
Design Consideration:
For new accessible constructions, all main public entrances should be accessible to
an ambulant disabled person. At least one entrance per facility should be accessible
to a wheelchair user. In new buildings, the accessible entrance(s) should be the main
entrance(s) intended for use by the general public.
Each accessible entrance should be connected by accessible pathways to accessible
indoor or outdoor parking areas, local public transit stops and drop-off areas. Glaze
at Entrance: Glazed doors should have glazed panels that extend low enough to
allow persons using mobility aids to see what is on the far side of the door (i.e.
maximum height from grade 900 mm to lower edge of glazing).
RAMPS:
Problem Identification:
Inaccessible building entrances due to
difference between indoor and outdoor levels.
Inaccessible routes due to differences in level.
Lack of or improper design of ramps.
Very steep and/or long ramps with no resting
landings.
Design Considerations:
Where there is a change in level, the provision
of a ramp is an effective method to ensure
largely independent accessibility for persons
with a disability and the elderly. Interior ramp
is preferred as a means of egress to stair as it
accommodates a wider range of building user,
including wheelchair user.
An exterior location is preferred for ramps to
provide wheelchair access to different floors.
Indoor ramps are not recommended because
they take up a great deal of space.
DROPPED KERBS:
A dropped kerb is a ramp built on a footpath or pavement to
accommodate the change in level towards vehicular areas. Dropped
kerb shall be of appropriate design and provided with adequate visual
and tactile warning.
Design Considerations:
The provision of a dropped kerb is overcome potential hazard arising
from change in level for persons with or without a disability.
The tactile warning strip should be provided in order to notify the
presence of traffic.
The tactile warning strip should have luminous contrast for the elderly
and persons with visual impairment.
DOORS:
Door Dimension:
For exterior door, minimum width should be 0.90 m
-1.00m • For interior doors, minimum width should be
0.80-0.85 m.
Clear height of 2.10-2.20 m is recommended for all the
doors. Accessible door features finish to ensure clear
visibility for people suffering from visual impairment.
Useful suggestions:
In general, automatic doors are accessible. Automatic
doors are of two types- Swinging door and sliding door.
Sliding door should be preferred over Swinging door.
Revolving doors should not be preferred in any public
building type.
Automatic doors should have an adequate opening
interval to allow people with mobility problems easy
access.
CORRIDORS:
Corridor Dimensions:
Width of corridors- Preferable width
should be in between 1.50 m-1.80
m to allow easy passage of two
wheelchairs without any
obstruction. (1.80 m width is
appropriate for 180* turn inside
corridor)
In a place where traffic is low,
corridors may have width less than
1.50 but not less than 0.90 m.
Water fountain or any other
facilities such as fire hoses should
be located outside the corridor area
and not protrude outside.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- CPWD GuidelinesDocument9 paginiCPWD Guidelinesmanasa manasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Commercial Complex Literature ReviewDocument43 paginiCommercial Complex Literature ReviewRonij Sandha100% (1)
- Wave MallDocument8 paginiWave MallARCHikeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- MLCP PlanningDocument26 paginiMLCP PlanningUsha RaghunandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On On MohaliDocument24 paginiPresentation On On MohaliBabita PilaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic: Landscape of ELANTE MALL, ChandigarhDocument17 paginiTopic: Landscape of ELANTE MALL, ChandigarhNancy BansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Swot AnalysisDocument1 paginăSwot AnalysisSHERAZ BHATTIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis Synopsis - Sijo MonachanDocument20 paginiThesis Synopsis - Sijo MonachanSIJO MONACHANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study Sec-17Document9 paginiCase Study Sec-17anusha8204Încă nu există evaluări
- Literature Study: Shopping MallDocument27 paginiLiterature Study: Shopping MallKhalida ParveenÎncă nu există evaluări
- WTP - Case StudyDocument19 paginiWTP - Case Studyamogh renuseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architectural Internship Work ReportDocument116 paginiArchitectural Internship Work Reportdillishwar bishwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literarure StudyDocument41 paginiLiterarure StudyAmit KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Travelator (Moving Walkway) Escalator Elevator: What Is Shopping Mall?Document4 paginiTravelator (Moving Walkway) Escalator Elevator: What Is Shopping Mall?Rhythm SatyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 Presentation 1 Delhi Urban Art CommisionDocument14 paginiUnit 3 Presentation 1 Delhi Urban Art CommisionAman RanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eight Vehicle Lanes, Two Train Lines, A Footway and A CyclewayDocument9 paginiEight Vehicle Lanes, Two Train Lines, A Footway and A CyclewayAkshara AkileshwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Triveni Kala KendraDocument5 paginiTriveni Kala KendraParthil MajumdarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7d Cinema DetailsDocument4 pagini7d Cinema DetailsmathangghiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synopsis Ncpa ChandigarhDocument10 paginiSynopsis Ncpa ChandigarhSanjiv Aggarwal100% (1)
- Team Orio )Document50 paginiTeam Orio )aarthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Library Study ON Commercial Building: Presented by Aditya Gupta Aryo Das Aman Kumar Sanyam JainDocument36 paginiLibrary Study ON Commercial Building: Presented by Aditya Gupta Aryo Das Aman Kumar Sanyam JainADITYA GUPTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Rise BuildingDocument21 paginiHigh Rise BuildingPavithra.GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architecture Thesis Topic: Hydrabad Habitat CenterDocument13 paginiArchitecture Thesis Topic: Hydrabad Habitat CenterDhoni PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conventional-Center-A1 1Document19 paginiConventional-Center-A1 1Kvm RajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature and Data ThesisDocument7 paginiLiterature and Data ThesisSai CharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- India Habitat Centre - Location PDFDocument2 paginiIndia Habitat Centre - Location PDFRaj AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cultural Centre at Rohtak 2Document17 paginiCultural Centre at Rohtak 2Tabish RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revitalization of Kurupam Market in Visakhapatnam City: Sustainable Urban DesignDocument7 paginiRevitalization of Kurupam Market in Visakhapatnam City: Sustainable Urban DesignMonica GiduturiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mantri Centrium PDFDocument68 paginiMantri Centrium PDFsheenamÎncă nu există evaluări
- OATDocument16 paginiOATprarthumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elanta MallDocument16 paginiElanta Mallmanya khaddar100% (1)
- Circulation: Architectural Design 4 StageDocument76 paginiCirculation: Architectural Design 4 StageHemn Shex SdeeqÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 - Chennai Metro Station - ST - Thomas Mount-Chennai Access Audit Report AICDocument42 pagini15 - Chennai Metro Station - ST - Thomas Mount-Chennai Access Audit Report AICDisability Rights AllianceÎncă nu există evaluări
- IndianhabitatcenterDocument29 paginiIndianhabitatcentercoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature Study Office: Linked in Office, DLF Cyber City, GurgaonDocument11 paginiLiterature Study Office: Linked in Office, DLF Cyber City, GurgaonMaya Dang100% (2)
- Regulations Goa Site - FAR, Height, SetbackDocument5 paginiRegulations Goa Site - FAR, Height, SetbackBhavika Dabhi100% (1)
- Mall Case StudyDocument7 paginiMall Case StudyTanujaa HemakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accoustic Case StudyDocument25 paginiAccoustic Case StudyLogesh WaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- IHC ParkingDocument4 paginiIHC ParkinganimeshoctÎncă nu există evaluări
- Housing Society Case Study: Presented By: Jagtap ShatikshaDocument11 paginiHousing Society Case Study: Presented By: Jagtap ShatikshaBhakti MantriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kashmeregateisbt 140914100001 Phpapp01Document8 paginiKashmeregateisbt 140914100001 Phpapp01Iqra QaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- MR Guruprakash Sastry - InfosysDocument6 paginiMR Guruprakash Sastry - Infosyssahil mouryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anand Agricultureu Case StudyDocument9 paginiAnand Agricultureu Case StudyNimesh Ranpara100% (1)
- Area Statements MallDocument1 paginăArea Statements MallVishnu ThipparthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oakwood, Ub CityDocument18 paginiOakwood, Ub CityAfreen BandayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study ShravyaDocument3 paginiCase Study ShravyasuniiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ArchitectsAct 1972Document12 paginiArchitectsAct 1972sunil kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- M.G.University SEM-10 THESIS AND VIVA VOCEDocument4 paginiM.G.University SEM-10 THESIS AND VIVA VOCELivya RobyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study of Hvac System in A Sustainable Building PDFDocument70 paginiCase Study of Hvac System in A Sustainable Building PDFguru jiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis Report 1Document41 paginiThesis Report 1Jasim QamarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLF Mall of India - Nodia: Lower Ground Floor PlanDocument4 paginiDLF Mall of India - Nodia: Lower Ground Floor PlanKavit BhatiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Isbt Kashmere Gate: Isbt Inter State Bus Terminals Haryana Jammu & KashmirDocument28 paginiIsbt Kashmere Gate: Isbt Inter State Bus Terminals Haryana Jammu & KashmirHiteshi BhardwajjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature StudyDocument4 paginiLiterature StudyNandhini Nagarajan0% (1)
- OlmolmDocument4 paginiOlmolmvikas kashyapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Audi Case StudyDocument8 paginiAudi Case Studydhanaraj100% (1)
- Venice MallDocument13 paginiVenice MallGeeta ShariyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datacollection 180415025345 PDFDocument7 paginiDatacollection 180415025345 PDFTarun Tango100% (1)
- City Centre (Siliguri)Document20 paginiCity Centre (Siliguri)Harshit KhandelwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Location:: Basant Lok Community Centre, New DelhiDocument3 paginiLocation:: Basant Lok Community Centre, New DelhiKartik KhannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Improving Interchanges: Toward Better Multimodal Railway Hubs in the People's Republic of ChinaDe la EverandImproving Interchanges: Toward Better Multimodal Railway Hubs in the People's Republic of ChinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aged&disabledDocument85 paginiAged&disabledKuldeep PanchalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Barrier-Free ConceptDocument80 paginiBarrier-Free ConceptKuldeep PanchalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Barrier Free Architecture - TsheringDocument11 paginiBarrier Free Architecture - TsheringKuldeep PanchalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Barrier-Free-Development A3Document14 paginiBarrier-Free-Development A3Kuldeep PanchalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planning TheoryDocument25 paginiPlanning TheoryKuldeep PanchalÎncă nu există evaluări
- SITE Study Page 1Document1 paginăSITE Study Page 1Kuldeep PanchalÎncă nu există evaluări
- LDA Building Bye-LawsDocument103 paginiLDA Building Bye-Lawsrizvi_amir199080% (35)
- Garden Cities & Their LegaciesDocument26 paginiGarden Cities & Their LegaciesDevika Hemalatha DeviÎncă nu există evaluări
- NBC 2016-Vol.2Document1.026 paginiNBC 2016-Vol.2Madhavpokale90% (30)
- Case Study-Taj and GemniDocument31 paginiCase Study-Taj and GemniKuldeep PanchalÎncă nu există evaluări
- PVC & UpvcDocument46 paginiPVC & UpvcKuldeep PanchalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building For The Performing ArtsDocument28 paginiBuilding For The Performing ArtsKuldeep PanchalÎncă nu există evaluări
- I Reliable/Durable I Ease I - I T - : Motor BuiltDocument16 paginiI Reliable/Durable I Ease I - I T - : Motor Builtjose miguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Higway Capacity ManualDocument2.257 pagini8 Higway Capacity ManualTIGESTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalogo de Partes UM Fastwind 220Document33 paginiCatalogo de Partes UM Fastwind 220lainer chaux100% (3)
- Cessna172RG Checklist Revised 11-6-12Document24 paginiCessna172RG Checklist Revised 11-6-12alphaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traffic Volume StudyDocument60 paginiTraffic Volume StudyShafiul Islam ArnobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Johnson Outboard Gasket SetsDocument15 paginiJohnson Outboard Gasket SetsMarine Parts ChinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chat GPT Math WorkDocument4 paginiChat GPT Math WorkSarthak SinglaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bus ID No.: E-3070: Passenger InformationDocument1 paginăBus ID No.: E-3070: Passenger InformationAnand SankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internship Final ReportDocument35 paginiInternship Final Reportlalu kalu100% (4)
- Ficha Tecnica Cat Cs-433eDocument16 paginiFicha Tecnica Cat Cs-433eJavier Hernandez AbrilÎncă nu există evaluări
- (TM) Ssangyong Manual de Taller Ssangyong Actyon 2013 en Ingles (1) - 101-200Document100 pagini(TM) Ssangyong Manual de Taller Ssangyong Actyon 2013 en Ingles (1) - 101-200LUIS HERNANDO100% (1)
- XCMG XR240E - Technical Specification - IsuzuDocument24 paginiXCMG XR240E - Technical Specification - IsuzuDaryono100% (1)
- Blue Med SurgicalsDocument6 paginiBlue Med SurgicalsRetteri KUMARANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geo StormDocument5 paginiGeo StormRoberto Ortega MicalizziÎncă nu există evaluări
- The BMW X5 M and X6 M.: Price List. From August 2016Document20 paginiThe BMW X5 M and X6 M.: Price List. From August 2016Wrestling Reality IIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irca Part 4Document6 paginiIrca Part 4Vikash100% (2)
- Factual Report Text KD 3.21 & 4.21Document2 paginiFactual Report Text KD 3.21 & 4.21Medika Dwi Putriaa50% (2)
- Wiring PDFDocument488 paginiWiring PDFManny AybarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aw 03 72le Aw0373leDocument195 paginiAw 03 72le Aw0373leBrian AqifÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Implementation of API RP 1102 Code To Evaluate Gas Pipeline Road CrossingDocument10 paginiThe Implementation of API RP 1102 Code To Evaluate Gas Pipeline Road CrossingRagil Siswo UtomoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research and Development of Hydrogen-Fueled InternDocument23 paginiResearch and Development of Hydrogen-Fueled InternSriramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Danymics - Homeworks - Chapter 2 Newton - S Second LawDocument3 paginiDanymics - Homeworks - Chapter 2 Newton - S Second LawRed DemonsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proposal EVRDocument2 paginiProposal EVRpahmi.ltfxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hot WheelsDocument36 paginiHot WheelsCedric DranrebÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2016 SunnySedan Owner ManualDocument386 pagini2016 SunnySedan Owner ManualA QanasÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASK Brake Lining CatalogueDocument9 paginiASK Brake Lining CatalogueBalaji vÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volvo 9500 Euro6 Brochure ENDocument13 paginiVolvo 9500 Euro6 Brochure ENAaron Hevia MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison UR ACDocument19 paginiComparison UR ACTewodros TadesseÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS PD Final 3 SPREAD HD 2018-2020Document75 paginiBS PD Final 3 SPREAD HD 2018-2020JAVIER BERMUDEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- C1AC1Document5 paginiC1AC1Mohammad HafizÎncă nu există evaluări