Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Evolution of Computer Cooling Systems FINAL
Încărcat de
Avinash MenonDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Evolution of Computer Cooling Systems FINAL
Încărcat de
Avinash MenonDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
The process of removing heat from computer components.
Excess heat must be dissipated in order to keep the components within their safe operating temperatures.
Varied cooling methods are also used to achieve greater performance such as overclocking.
Excessive heat can cause all sorts of problems. Overheated parts generally exhibit a shorter maximum life-span and may give problems resulting in system freezes or crashes.
Manufacturers have given very close tolerances for operating temperature and humidity.
Using vacuum tubes Using transistors Using integrated circuits Using microprocessors
Vacuum tubes produce heat while operating.
This waste heat is one of the principal factors that affect tube life.
UNIVAC - I
Method of anode cooling. Radiates the heat by black body radiation from the anode to the glass envelope.
Natural air circulation, convection, then removes the heat from the envelope.
forced air cooling adding fins to the anode. operating the anode at red hot temperatures. Tubes with external anodes may be cooled using forced air, water, vapor, and multiphase.
There was less heat generated per circuit.
There was only narrow tolerances to temperature variations.
A transistor, also normally used as a switch, could turn on accidently, when overheated, causing chaos
AKAT - 1
in the system.
Room air conditioning became very important.
Most systems were installed on false floors, with a space of about 1 meter or 3ft below the floor.
This allowed the air conditioning to be supplied
A typical Air conditioning unit for cooling server racks.
under the floor, and exhausted through the false ceiling
Tape drives(storage device) were particularly large producers of heat.
Tapes produce a lot of heat due to the powerful motors they use.
tapes and disks to be installed in a separate room, or partitioned off from the mainframe, so that air conditioning requirements could be better controlled.
Amount of heat generated by an integrated circuit is the prime cause of heat build up in modern computers.
It is a function of the efficiency of its design, the technology used in its construction and the frequency and voltage at which it operates.
In operation, the temperature levels of a computer's components will rise until the temperature gradient between the computer parts and their surroundings is such that the rate at which heat is lost to the surroundings is equal to the rate at which heat is being produced by the electronic component, and thus the temperature of the component reaches equilibrium.
For reliable operation, the equilibrium temperature must be sufficiently low for the structure of the computer's circuits to survive.
Air Cooling Liquid Cooling Heat Sinks
The term computer fan usually refers to fans attached to a computer.
Most common are CPU fan, GPU fan, Chipset fan, PSU fan, HDD fan & PCI slot fans.
It basically allows airflow that will help cooling.
Size varies from 40mm 240mm dia.
Sufficient number of fans will create a neutral airflow that will keep the temperature inside the cabin under control. Positions of fans is important.
Air is drawn in at the front of the rack and exhausted at the rear
blade chassis - In contrast to the horizontal orientation of flat servers, blade chassis are often oriented vertically. This vertical orientation facilitates convection.
When the air is heated by the hot components, it tends to flow to the top on its own, creating a natural air flow along the boards.
Submerse the computer's components in a thermally conductive liquid. Does not require any fans or pumps. cooled exclusively by passive heat exchange between the computer's parts, the cooling fluid and the ambient air.
Water has the ability to dissipate more heat from the parts being cooled than the various types of metals used in heatsinks. Can be set up to cool the CPU, GPU, and other components at the same time with the same system.
Involves attaching a block of machined or extruded metal to the part that needs cooling.
This block usually has fins and ridges to increase its surface area.
The heat conductivity of metal is much better than that of air.
Its ability to radiate heat is better than that of the component part it is protecting.
Same principle as passive, with the addition of a fan that is directed to blow over or through the heat sink.
The moving air increases the rate at which the heat sink can exchange heat with the ambient air.
Primary method of cooling a modern processor or graphics card.
A hollow tube containing a heat transfer liquid.
As the liquid evaporates, it carries heat to the cool end, where it condenses and then returns to the hot end.
Heat pipes thus have a much higher effective thermal conductivity than solid materials.
In computers, the heat sink on the CPU is attached to a larger radiator heat sink by a large heat pipe.
Dust acting as a thermal insulator and impeding airflow, thereby reducing heat sink and fan performance.
Poor airflow including turbulence due to friction against impeding components, or improper orientation of fans, can reduce the amount of air flowing through a case and even create localised whirlpools of hot air in the case
Poor heat transfer due to a lack of, or poor application of thermal compounds.
Thermoelectric Cooling Liquid Nitrogen Cooling Liquid Helium Cooling Phase-Change Cooling
Run parts of computer (such as the CPU and GPU) at higher voltages and frequencies than manufacturer specifications call for.
This can dramatically increase the performance of the computer.
Results in a greater amount of heat generated and thus increasing the risk of damage to components and/or premature failure.
More advanced and expensive cooling systems are required in these cases.
As liquid nitrogen evaporates at -196 C, far below the freezing point of water, it is valuable as an extreme coolant for short overclocking sessions.
CPU will usually expire within a relatively short period of time due to temperature stress caused by changes in internal temperature.
Liquid helium, colder than liquid nitrogen, has also been used for cooling.
Based on Peltier effect inverse of Seebeck effect. Applying a voltage to a thermocouple creates a temperature difference between two sides. Modern TECs use several stacked units each composed of dozens or hundreds of thermocouples laid out next to each other, which allows for a substantial amount of heat transfer.
Uses a compressor of the same type as in a window air conditioner.
Compressor compresses a gas (or mixture of gases) which condenses it into a liquid.
Liquid evaporates (changing phase), absorbing the heat from the processor.
The evaporation can produce temperatures reaching around 15 to -150 degrees Celsius
Some laptop components, such as hard drives and optical drives, are commonly cooled by having them make contact with the computer's frame, increasing the surface area which can radiate and otherwise exchange heat.
Practice of running the CPU or any other component with voltages below the device specifications.
An undervolted component draws less power and thus produces less heat.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Computer Cooling MethodsDocument11 paginiComputer Cooling Methodssiva0182Încă nu există evaluări
- Computer CoolingDocument35 paginiComputer CoolingMohamed AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functions of Operating SystemDocument6 paginiFunctions of Operating SystemGaurav BishtÎncă nu există evaluări
- # All Words Fullform Related ComputerDocument8 pagini# All Words Fullform Related ComputerPushpa Rani100% (1)
- Use of Raspberry Pi in Operating Systems ClassDocument6 paginiUse of Raspberry Pi in Operating Systems Classgileraz90Încă nu există evaluări
- Networking and TelecommunicationDocument4 paginiNetworking and TelecommunicationfarindraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To ModemDocument1 paginăIntroduction To Modemraghu_534Încă nu există evaluări
- Important Abbreviations - ComputersDocument2 paginiImportant Abbreviations - Computersanilnair88Încă nu există evaluări
- Seminar Topics: Name of The TopicDocument12 paginiSeminar Topics: Name of The TopicRahul NambiarÎncă nu există evaluări
- QuizDocument7 paginiQuizPiyush KhandelwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fedora Operating SystemDocument11 paginiFedora Operating Systemarvi.sardarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generators of Unwanted Heat: Computer Cooling Is Required To Remove TheDocument13 paginiGenerators of Unwanted Heat: Computer Cooling Is Required To Remove TheArun KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Navigation Search: Computer Cooling From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 paginiNavigation Search: Computer Cooling From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJustin CookÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Cooling: Navigation SearchDocument15 paginiComputer Cooling: Navigation SearchPravasini SahooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermoelectric Cooling WhitepaperDocument9 paginiThermoelectric Cooling WhitepaperbitconceptsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report On Thermal Management of Electronic CircuitsDocument12 paginiReport On Thermal Management of Electronic CircuitsSuyash KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- WP-57 Fundamental Principles of Air Conditioners For Information TechnologyDocument10 paginiWP-57 Fundamental Principles of Air Conditioners For Information TechnologyYamaneko ShinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermoelectric Cooling For Industrial EnclosuresDocument6 paginiThermoelectric Cooling For Industrial EnclosuresErdinc KlimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Ventilating and Air Conditioning (Hvac)Document3 paginiHeat Ventilating and Air Conditioning (Hvac)Den Mas DeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cooling SystemDocument10 paginiCooling SystemVenu Gopal VegiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mapua Institute of Technolog1Document15 paginiMapua Institute of Technolog1Ian KasaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Term Paper: Ele102 Topic:: Cooling Methods of TransformersDocument7 paginiTerm Paper: Ele102 Topic:: Cooling Methods of Transformersshailesh singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cooling: Technical ViewDocument39 paginiCooling: Technical ViewKevinHuamanDiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Explanation of Cooling and Air Conditioning Terminology For IT ProfessionalsDocument18 paginiExplanation of Cooling and Air Conditioning Terminology For IT ProfessionalsPirozok PirozkovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-3 - Energy Efficiency in BuildingsDocument39 paginiUnit-3 - Energy Efficiency in BuildingsNmg KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC System Design For The Assembly HallDocument16 paginiAC System Design For The Assembly HallAkatew Haile MebrahtuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air ConditioningDocument11 paginiAir ConditioningBrilliantJohnMalandacRubiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Conditioning System: Comfort ConditionsDocument55 paginiAir Conditioning System: Comfort ConditionsTunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Explanation of Cooling and Air Conditioning Terminology For IT ProfessionalsDocument17 paginiExplanation of Cooling and Air Conditioning Terminology For IT Professionalsamey8231Încă nu există evaluări
- Air Conditioning Thesis StatementDocument7 paginiAir Conditioning Thesis Statementewdgbnief100% (2)
- Calculating Heat Loads and Computer Room Cooling RequirementsDocument5 paginiCalculating Heat Loads and Computer Room Cooling RequirementsAlvin ZetoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Trends in Cooling of BladesDocument8 paginiCurrent Trends in Cooling of BladesPRAVEENÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nanotechnology For Better Efficiency in Computer Chips: Kalasalingam Institute of Technology Krishnan Koil, VirudhunagarDocument15 paginiNanotechnology For Better Efficiency in Computer Chips: Kalasalingam Institute of Technology Krishnan Koil, VirudhunagarPavithra PappuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Handling UnitDocument15 paginiAir Handling UnitDyadecy AraosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.2 Principles of The CoolingDocument10 pagini4.2 Principles of The CoolingAdam AlexÎncă nu există evaluări
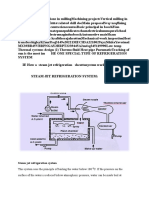
- Shopmillingmsme: Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemDocument7 paginiShopmillingmsme: Steam Jet Refrigeration SystembbaytlÎncă nu există evaluări
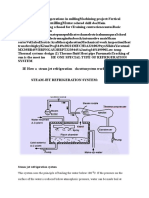
- Shopmillingmsme: Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemDocument7 paginiShopmillingmsme: Steam Jet Refrigeration SystembbaytlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuit DescriptionDocument6 paginiCircuit DescriptionBala MuraliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Fan - WikipediaDocument16 paginiComputer Fan - Wikipediaethan emmanuel clintonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shopmillingmsme: Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemDocument7 paginiShopmillingmsme: Steam Jet Refrigeration SystembbaytlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Conditioning, Nonductable, Ductable-PackagedDocument6 paginiAir Conditioning, Nonductable, Ductable-PackagedRAVIRAJ KARKEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimizing Chiller Tower Systems PDFDocument8 paginiOptimizing Chiller Tower Systems PDFasl91100% (1)
- Thermosyphon EffectDocument10 paginiThermosyphon EffectPit_mkluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Script:-.Air Condition ScriptDocument11 paginiScript:-.Air Condition Scriptaimri_cochinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment # 2: Subject Submitted To Submitted by TopicDocument8 paginiAssignment # 2: Subject Submitted To Submitted by TopicSania SaeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaporative Cooling Technology TodayDocument10 paginiEvaporative Cooling Technology TodayWinwin07Încă nu există evaluări
- Cooling Systems AssignmentDocument14 paginiCooling Systems AssignmentBecky DavisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Square Foot "Rule of Thumb":: How To Estimate A Cooling Load (And Maybe Heating Load)Document7 paginiSquare Foot "Rule of Thumb":: How To Estimate A Cooling Load (And Maybe Heating Load)Arturo Del-RioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disinfection Chamber ProjectDocument21 paginiDisinfection Chamber ProjectKovinraaj ChelathuraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TechCorner 10 - Panel CoolingDocument9 paginiTechCorner 10 - Panel CoolingQuantumAutomationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical SeminarDocument19 paginiTechnical SeminarLibinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction Air ConditionersDocument5 paginiIntroduction Air Conditionersbentarigan77Încă nu există evaluări
- Heat Sinks vs. Liquid CoolingDocument2 paginiHeat Sinks vs. Liquid Coolingrenate_ellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Cooled Heat Exchnger FormatedDocument43 paginiAir Cooled Heat Exchnger FormatedMustafa Anwar50% (2)
- Principle of VRFDocument5 paginiPrinciple of VRFghazanfarhayat456Încă nu există evaluări
- Rajesh Thesis 03.08.2017Document95 paginiRajesh Thesis 03.08.2017Ajay KumawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shopmillingmsme: Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemDocument7 paginiShopmillingmsme: Steam Jet Refrigeration SystembbaytlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis Cooling TowerDocument8 paginiThesis Cooling Towermmwsmltgg100% (2)
- Electronic Enclosure Cooling Thermoelectric vs. Compressor Based Air Conditioners WhitepaperDocument13 paginiElectronic Enclosure Cooling Thermoelectric vs. Compressor Based Air Conditioners WhitepaperYoussef LandolsiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction of PeltierDocument6 paginiIntroduction of PeltierKazi Moshfiqur Rahman SajalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9a Grundfos 50Hz Catalogue-1322Document48 pagini9a Grundfos 50Hz Catalogue-1322ZainalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impact of Wrongful Termination On EmployeesDocument4 paginiImpact of Wrongful Termination On EmployeesAvil HarshÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS 148 - Introduction To Computer Graphics and ImagingDocument3 paginiCS 148 - Introduction To Computer Graphics and ImagingMurtaza TajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management by ObjectivesDocument30 paginiManagement by ObjectivesJasmandeep brar100% (4)
- Review of Financial Statements and Its Analysis: Rheena B. Delos Santos BSBA-1A (FM2)Document12 paginiReview of Financial Statements and Its Analysis: Rheena B. Delos Santos BSBA-1A (FM2)RHIAN B.Încă nu există evaluări
- ShapiroDocument34 paginiShapiroTanuj ShekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unilever Financial PerformanceDocument9 paginiUnilever Financial PerformanceAbdul QayumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discovering Computers 2016: Operating SystemsDocument34 paginiDiscovering Computers 2016: Operating SystemsAnonymous gNHrb0sVYÎncă nu există evaluări
- (SPN) On J1939 Data LinkDocument107 pagini(SPN) On J1939 Data LinkAM76Încă nu există evaluări
- JKR SPJ 1988 Standard Specification of Road Works - Section 1 - GeneralDocument270 paginiJKR SPJ 1988 Standard Specification of Road Works - Section 1 - GeneralYamie Rozman100% (1)
- Questions & Answers On CountersDocument24 paginiQuestions & Answers On Counterskibrom atsbha100% (2)
- Soal TKM B. Inggris Kls XII Des. 2013Document8 paginiSoal TKM B. Inggris Kls XII Des. 2013Sinta SilviaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fashion Designing Sample Question Paper1Document3 paginiFashion Designing Sample Question Paper1Aditi VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3-Matic 14 - User Manual 15Document169 pagini3-Matic 14 - User Manual 15Oliver RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pivacare Preventive-ServiceDocument1 paginăPivacare Preventive-ServiceSadeq NeiroukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project of Consumer BehaviourDocument28 paginiProject of Consumer BehaviourNaveed JuttÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agenda 9Document46 paginiAgenda 9Bala Gangadhar TilakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class B Digital Device Part 15 of The FCC RulesDocument7 paginiClass B Digital Device Part 15 of The FCC RulesHemantkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Art and Culture KSG IndiaDocument4 paginiArt and Culture KSG IndiaAbhishek SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 SampleDocument12 paginiChapter 3 Samplesyarifah53Încă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines For New Students - 2022Document14 paginiGuidelines For New Students - 2022Ria Faye PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ra 11521 9160 9194 AmlaDocument55 paginiRa 11521 9160 9194 Amlagore.solivenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philippine Multimodal Transportation and Logistics Industry Roadmap - Key Recommendations - 2016.04.14Document89 paginiPhilippine Multimodal Transportation and Logistics Industry Roadmap - Key Recommendations - 2016.04.14PortCalls50% (4)
- HRM Ass1Document3 paginiHRM Ass1asdas asfasfasdÎncă nu există evaluări
- IMO Publication Catalogue List (June 2022)Document17 paginiIMO Publication Catalogue List (June 2022)Seinn NuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Resource Management - Introduction - A Revision Article - A Knol by Narayana RaoDocument7 paginiHuman Resource Management - Introduction - A Revision Article - A Knol by Narayana RaoHimanshu ShuklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beneparts Quotation BYBJ192388 20191024Document1 paginăBeneparts Quotation BYBJ192388 20191024احمد عبدهÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review On A Protective Scheme For Wind Power Plant Using Co-Ordination of Overcurrent Relay-NOTA TECNICADocument5 paginiReview On A Protective Scheme For Wind Power Plant Using Co-Ordination of Overcurrent Relay-NOTA TECNICAEdgardo Kat ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Profile Romblon IslandDocument10 paginiProfile Romblon Islandderella starsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ad CVDocument2 paginiAd CVzahid latifÎncă nu există evaluări