Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
f4109 Database System
Încărcat de
CyzuKa JajaDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
f4109 Database System
Încărcat de
CyzuKa JajaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
F4109-DATABASE SYSTEM
ACCESS PROTECTION USER ACCOUNT DATABASE AUDITS
q q q
4/22/12
MOHAMMAD AZMER SULAIMAN NURUL FARHANA SABRI NORSHAHEEZA NORAZIZAN
INTRODUCTION
In a database system management, each DBMS must have its own way management whether using other software or database itself. To make sure data integrity and security in a database, each database must have access protection, user account and also database audits.
4/22/12
WHAT IS ACCESS PROTECTION
Enables an authority to control access to areas and resources. Select the access level, user type, and access level privileges for each user or group in a database. In access protection have identification and authentication.
4/22/12
Principles of Access Protection
Separation of duties
No single individual should be allowed to perform high-value or sensitive tasks on their own
Financial transactions User account creation / changes
4/22/12
Least privilege
Persons
should have access to only the functions or data that they require to perform their stated duties File Servers
Don't give access to others' files
on
Workstations
User Account Control
4/22/12
Defense in depth
Use
of multiple controls to protect an asset controls preferred
Heterogeneous
If one type fails, the other remains If one type is attacked, the other remains
4/22/12
Types of Protection
Technical
Authentication,
encryption, firewalls, anti-virus
Physical
Key
card entry, fingerprints.
Administrative
Policy,
procedures, standards
4/22/12
What is User Account
Allows a user toauthenticate to system services and be grantedauthorizationtoaccess them. Resource owners have classified data according to its need for protective controls, entities should develop procedures to identify all functions of user management.
4/22/12
Managing User Accounts
The everyday users of a database need to be able access & manipulate various database objects in a safe and controlled manner. The DBA creates a USER ACCOUNT for each user by following these basic steps:
Create a username/password protected account and assign the
user to a table space.
Allocate the user limited disk storage space (quota) within the
table space
Grant the user limited privileges to log in/out of the account,
create/destroy and manipulate database objects within the account.
4/22/12
Creating User Accounts
The CREATE USER command (Create a user account)
CREATE USER username IDENTIFIED BY password
Example : create user jaja identified by 123
4/22/12
Changing a password for A user
ALTER USER username identified by newpassword ;
Example:
Alter user jaja identified by genie123
4/22/12
Managing User Accounts
Removing a user account
DROP USER username CASCADE; The cascade option drops all objects in the users schema before dropping the user. If the user owns objects you must specify this parameter to drop the user.
4/22/12
What is Database Audit
Observing a database so as to be aware of the actions of database users. It can be based on individual actions, such as the type of SQL statement executed, or on combinations of factors that can include user name, application, time, and so on.
4/22/12
Principle of database audits
Evaluate your purpose for auditing. Audit knowledgeably. Audit only pertinent actions. Archive audit records and purge the audit trail.
4/22/12
Types of Auditing
Statement Auditing
The selective auditing of related groups of statements regarding a particular type of database structure or schema object. Have two categories:-
-DDL statements -DML statements
4/22/12
Privilege Auditing
Use a system privilege, such asSELECTANYTABLE Privilege auditing can audit the activities of all database users or of only a specified list.
Schema Object Auditing
Can audit allSELECTand DML statements permitted by schema object privileges, such asSELECTorDELETEstatements on a given table.
4/22/12
Summary
The conclusion is all these 3 methods or topics are important in DBMS. Access protection useful for database security and only authorized person can access the database. User account is needed for every user to access data in database. It also important for a database to identify authorized user. Database auditing is needed to figure out all the actions that happened in database.
4/22/12
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Yamaha RX-V677 ManualDocument146 paginiYamaha RX-V677 ManualepascaruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Omneon SystemManagerDocument47 paginiOmneon SystemManagerRobertÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Ult Studio Config 71Document18 paginiUlt Studio Config 71JoséGuedesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Xiseries: High Performance Bar Code PrintersDocument4 paginiXiseries: High Performance Bar Code Printersrodrigogar27Încă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- Fx2n Function Expansion Memory Hardware ManualDocument8 paginiFx2n Function Expansion Memory Hardware ManualsunhuynhÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 9 EditionDocument28 paginiWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 9 EditionMamta BorleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To HCIDocument47 paginiIntroduction To HCICHaz LinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Orientation Tracking Using OS5000-S Digital Compass On FireDocument7 paginiOrientation Tracking Using OS5000-S Digital Compass On FirePriyanshu GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
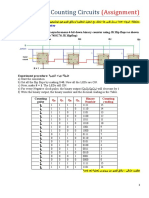
- Experiment 8: Counting Circuits: (Assignment)Document3 paginiExperiment 8: Counting Circuits: (Assignment)AL Asmr YamakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- CSC 5301 - Paper - DB & DW SecurityDocument17 paginiCSC 5301 - Paper - DB & DW SecurityMohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- Alonex Special Amp Industrial Electronic Equipment PDFDocument342 paginiAlonex Special Amp Industrial Electronic Equipment PDFthanh vanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nec Alarm DetailDocument1 paginăNec Alarm DetailPulkit Tyagi100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Code Blocks SourceForgeDocument2 paginiCode Blocks SourceForgesabar5Încă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- FusionCompute V100R005C10 Product Description 01Document61 paginiFusionCompute V100R005C10 Product Description 01Artur KopylovÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- English VSAT PresentationDocument54 paginiEnglish VSAT PresentationcheiksoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Solus Corporate ProfileDocument20 paginiSolus Corporate ProfilesahilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Corrige 2Document3 paginiCorrige 2Sergio FernandesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- Chapter 1 DBMSDocument32 paginiChapter 1 DBMSAishwarya Pandey100% (1)
- Chapter 2 - TCP/IP ArchitectureDocument22 paginiChapter 2 - TCP/IP ArchitectureJuan SantiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- An82156 001-82156 0F VDocument115 paginiAn82156 001-82156 0F Vandrej2112Încă nu există evaluări
- ARM Based Development Course by Mouli SankaranDocument1.027 paginiARM Based Development Course by Mouli SankaranChandramouleeswaran Sankaran100% (7)
- hw2 AnsDocument5 paginihw2 AnsJIBRAN AHMEDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Arm Processors: Ch. S. V. Maruthi Rao Associate Professor Department of ECE, S. I. E. TDocument27 paginiAdvanced Arm Processors: Ch. S. V. Maruthi Rao Associate Professor Department of ECE, S. I. E. TMaruthi RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Access 2013 Beginner Level 1 Adc PDFDocument99 paginiAccess 2013 Beginner Level 1 Adc PDFsanjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8.1.4.4 Lab - Troubleshooting DHCPv4Document9 pagini8.1.4.4 Lab - Troubleshooting DHCPv4Andres CriolloÎncă nu există evaluări
- DS-2DE5225IW-AE 2MP 25× Network IR Speed Dome: Key FeaturesDocument5 paginiDS-2DE5225IW-AE 2MP 25× Network IR Speed Dome: Key FeaturesHarshÎncă nu există evaluări
- MS Project 2007 Torrent - KickassTorrentsDocument2 paginiMS Project 2007 Torrent - KickassTorrentsanadinath sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEAKED_RECEIVERSDocument5 paginiLEAKED_RECEIVERSMg Soe KyannÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Clarion Dxz615 ManualDocument30 paginiClarion Dxz615 ManualmilosgtaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A1800 Meter - Modbus MapDocument48 paginiA1800 Meter - Modbus MaphazimeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)