Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapter 11
Încărcat de
api-3807704Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 11
Încărcat de
api-3807704Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 11
Managing Basic Remuneration
Human Resource Management, 5E 1
Learning Objectives
• Identify the different components of
remuneration
• Describe the theories of wage and salary
payments
• Identify the variables that influence employee
remuneration
• Point out the wage policy of Government
• Explain the wage concepts
• Explain how special groups can be
compensated
Human Resource Management, 5E 2
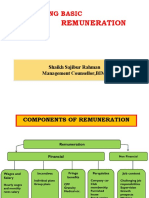
Components of Employee Remuneration
Environment
Remuneration
Financial Non-financial
Job Context
Fringe Benefits Perquisites Challenging job
PF Company car Responsibilities
Hourly and
Incentives Gratuity Club membership Recognition
Monthly rated
Individual plans Medical Care Paid holidays Growth prospects
Wages
Group plans Accident Relief Furnished house Supervision
Salaries
Health and Group Stock option Working
Insurance, etc. Schemes, etc. conditions
Job sharing, etc.
Direct Indirect
Human Resource Management, 5E 3
Theories of Remuneration
• Reinforcement theory
• Expectancy theory
• Equity theory
• Agency theory
Human Resource Management, 5E 4
Consequences of Pay Dissatisfaction
Performance
Strikes
Desire for More
Pay
Grievances
Absenteeism
Search for Higher
Paying Jobs
Turnover
Pay Lower Attractiveness
Dissatisfaction of Job Job Psychological
Dissatisfaction Withdrawal
Absenteeism Visits to the
Doctor
Poor Mental
Health
Human Resource Management, 5E 5
Influencing Factors of Remuneration
Human Resource Management, 5E 6
Linkage of Remuneration Strategy to
Business Strategy
Market Position and Remuneration Blend of
Business Strategy
Maturity Strategy Remuneration
High cash with above
Merging or growth Stimulate average incentive for
Invest to grow
rapidity entrepreneurialism individual performance.
Modest benefits,
Average cash with
moderate incentives on
Manage earnings- Normal growth to Reward management
individual, unit, or
protect markets maturity skills
corporate performance.
Standard benefits.
Below-average cash
Harvest earnings- No real growth or with small incentive tied
Stress
reinvest elsewhere decline to cost control.
Standard benefits.
Source: Wayne F. Cascio, Managing Human Resources, McGraw-Hill, 1995, p.352.
Human Resource Management, 5E 7
Remuneration Model
Job Description
Job Evaluation
Job Hierarchy
Pay Survey
Pricing Jobs
Human Resource Management, 5E 8
Raising Salaries
2003 2004
(Increase in percent)
IT 15 17
ITES 23 25
Telecom (Services) 10 12
Insurance 23 25
Banking (Retail) 12 15
Manufacturing 6 7
Pharma 20 22
Source: Business Today, September 12, 2004. p.46
Human Resource Management, 5E 9
Challenges of Remuneration
Skill-based
Pay
Monetary
vs. Non- Salary
Monetary Reviews
Rewards
Employee Pay
Participation
Remuneration Secrecy
Below Market
Eliticism or
or Above
Egalitarianism
Market Rates
Comparable
Worth
Human Resource Management, 5E 10
Skill-based Pay and Job-based Pay
Compared
Factors Job-based Skill-based
Pay structure Based on job performance Based on ability to perform
Job carries wage; Employee Employee carries wage;
Employer’s focus
linked to job Employee linked to skills.
Job promotion to earn greater Skill acquisition to earn greater
Employee focus
pay pay.
Pay based on value of work
Advantages Flexibility; Reduced workforce.
performed
Potential personnel Potential personnel
Disadvantages
bureaucracy; Inflexibility bureaucracies; Cost controls.
Source: Raymond A. Stone, Human Resource Management, John Wiley & Sons, 1995, p.324.
Human Resource Management, 5E 11
Wage Concepts
• Minimum wage
– provides for sustenance of life but also for
preserving efficiency
• Fair wage
– comparable with standard wages elsewhere
• Living wage
– providing essentials plus certain comforts
Human Resource Management, 5E 12
Reality Check
• Do you think that people work mainly for
pay? Ascertain views of your classmates.
Presentation and discussion can follow in
this class.
Human Resource Management, 5E 13
Reality Check
• How far luck does influence pay? Have
you come across any individual who has
been lucky enough to be more than he or
she deserves?
Human Resource Management, 5E 14
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Bauer2 - 0 PPT Ch05Document31 paginiBauer2 - 0 PPT Ch05Bùi Phan Ý NhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lunenburg, Fred C. Goal-Setting Theoryof Motivation IJMBA V15 N1 2011Document6 paginiLunenburg, Fred C. Goal-Setting Theoryof Motivation IJMBA V15 N1 2011Chirag Sheth0% (1)
- Ebook PDF Canadian Entrepreneurship Small Business Management 9th Canadian Edition PDFDocument42 paginiEbook PDF Canadian Entrepreneurship Small Business Management 9th Canadian Edition PDFdaniel.blakenship8460% (1)
- BEFI 2022-Fall 08c 03 Session Impact-Funding Erkel 2022-11-28Document12 paginiBEFI 2022-Fall 08c 03 Session Impact-Funding Erkel 2022-11-28FounderinstituteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Working Capital Management Case - 1 - Just For Feet, Inc Name - Ashim Kumar KarDocument3 paginiWorking Capital Management Case - 1 - Just For Feet, Inc Name - Ashim Kumar KarAshim KarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Report-IAMAI 40Document60 paginiFinal Report-IAMAI 40ooanalystÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warehouse Delivery Driver Performance Appraisal: Job Performance Evaluation FormDocument19 paginiWarehouse Delivery Driver Performance Appraisal: Job Performance Evaluation FormIrinaGabrielaEnescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compensation ManagementDocument19 paginiCompensation ManagementDushyant Sinha67% (3)
- Business Plan PresentationDocument13 paginiBusiness Plan PresentationCojocaru NicoletaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latest Employment Report: Master of Business Administration (Full-Time MBA)Document2 paginiLatest Employment Report: Master of Business Administration (Full-Time MBA)Gaurav PathakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Training Amd DevelopmentDocument10 paginiChapter 1 Training Amd DevelopmentSumerah Saeed100% (1)
- Six Sigma and Process ImprovementDocument44 paginiSix Sigma and Process ImprovementChristine Viola YongshintingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legal and IP: Workforce Considerations: Founder Institute - Confidential InformationDocument13 paginiLegal and IP: Workforce Considerations: Founder Institute - Confidential InformationFounderinstituteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Three Small Business Environment: Managing External RelationsDocument19 paginiChapter Three Small Business Environment: Managing External Relationscristiana100% (1)
- OPM6090 Final Project - Case For Change Template-1Document8 paginiOPM6090 Final Project - Case For Change Template-1r.olanibi55Încă nu există evaluări
- NWPC FlyersDocument4 paginiNWPC FlyersThoughts and More ThoughtsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gerhart, B. (2017) - Incentives and Pay For Performance in The Workplace. Advances in Motivation Science, 91-140.Document50 paginiGerhart, B. (2017) - Incentives and Pay For Performance in The Workplace. Advances in Motivation Science, 91-140.Charles Manchester100% (1)
- City AgendaDocument17 paginiCity AgendaBen SchachtmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Job Analysis Heneman ChapterDocument56 paginiJob Analysis Heneman ChapterZahra AlhalwachiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Financial Ratios On Firm Performance Study of Selected Brewery Firms in NigeriaDocument8 paginiEffect of Financial Ratios On Firm Performance Study of Selected Brewery Firms in NigeriaEditor IJTSRDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compensation Rewards Trends: and TotalDocument23 paginiCompensation Rewards Trends: and TotalBGMi NubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Auditing Skills On Small Business Performance: A Study of Small Businesses in Anambra State, NigeriaDocument5 paginiEffect of Auditing Skills On Small Business Performance: A Study of Small Businesses in Anambra State, NigeriaIJAR JOURNALÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEFI 2020-Spring 01 01 Orientation Deck 2020-03-11Document61 paginiBEFI 2020-Spring 01 01 Orientation Deck 2020-03-11FounderinstituteÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCS iON NPT - Human Resource Manager Test Syllabus: Level: FoundationalDocument6 paginiTCS iON NPT - Human Resource Manager Test Syllabus: Level: FoundationalSankar EswaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1: What Forces Have Led To The Boom in Entrepreneurship in The U.S. and Across The Globe?Document6 pagini1: What Forces Have Led To The Boom in Entrepreneurship in The U.S. and Across The Globe?Samiir AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Are You Rewarding The Solo Performance at Team's ExpenseDocument5 paginiAre You Rewarding The Solo Performance at Team's ExpenseSuphachittra Thongchavee100% (1)
- Class Actvity 1 AnswersDocument10 paginiClass Actvity 1 AnswersSue AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- PWC Actuarial Services India - Vacancy DescriptionDocument14 paginiPWC Actuarial Services India - Vacancy DescriptionMohit Kohli100% (1)
- HH Poll 2009Document6 paginiHH Poll 2009Venky VenkateshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Resource Policies and ProcedureDocument119 paginiHuman Resource Policies and ProcedurekrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aon Salary Increase and Turnover Survey India 2023-24 - Phase II - Detailed ReportDocument108 paginiAon Salary Increase and Turnover Survey India 2023-24 - Phase II - Detailed ReportbhanuprakashbadriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Employee RetentionDocument7 paginiEmployee Retentionswirvve18Încă nu există evaluări
- Rudri PathDocument3 paginiRudri PathDeepakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Joel Nickelsen - Growing LeanDocument21 paginiJoel Nickelsen - Growing LeanJose ComorelÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRMnext Interview Questions in Noida - Glassdoor - Com.au PDFDocument9 paginiCRMnext Interview Questions in Noida - Glassdoor - Com.au PDFSuneelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapters To Be Covered: BITS PilaniDocument47 paginiChapters To Be Covered: BITS PilaniSita RamachandranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2Document16 paginiModule 2Sonam GondlekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- MM ZC441: Human Resource ManagementDocument43 paginiMM ZC441: Human Resource ManagementPankaj VishwakarmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 17Document20 paginiLecture 17Aman ManshahianÎncă nu există evaluări
- CompensationDocument23 paginiCompensationabeer rajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2.5 Compensation-ManagmentDocument17 pagini2.2.5 Compensation-ManagmenthayelomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic RemunerationDocument24 paginiBasic RemunerationIstiak RashedÎncă nu există evaluări
- of Wages and Salaries AdmDocument12 paginiof Wages and Salaries Admshiiba2294% (17)
- Reality Based Pay StructuresDocument14 paginiReality Based Pay StructuresShiji SjÎncă nu există evaluări
- of Wages and Salaries AdmDocument12 paginiof Wages and Salaries AdmRavindra ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compensation & BenefitsDocument30 paginiCompensation & BenefitsSeema SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9Document16 paginiChapter 9Palompo Angela CrisvyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On: Compensation ManagementDocument29 paginiPresentation On: Compensation Managementarun_aglÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wages and Salaries Presented by Mr. Ramesh Kumar NehraDocument12 paginiWages and Salaries Presented by Mr. Ramesh Kumar Nehranehraramesh6984100% (1)
- Final Compensation PPT 2Document18 paginiFinal Compensation PPT 2parakhsÎncă nu există evaluări
- CompensationDocument12 paginiCompensationgeachew mihiretuÎncă nu există evaluări
- HRM - Total RewardsDocument50 paginiHRM - Total RewardsRavi Kumar Anand0% (1)
- A Presentation ON Compensation & Benefits: BY: Nikita Dhoot Nikita BumbDocument18 paginiA Presentation ON Compensation & Benefits: BY: Nikita Dhoot Nikita BumbNikita BumbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Employee RemunerationDocument22 paginiEmployee RemunerationJagruti Bhansali100% (3)
- CompensationDocument31 paginiCompensationFaysalAminTamimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compensation MGTDocument36 paginiCompensation MGTJivanjot SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wage and SalaryDocument8 paginiWage and SalaryParvathi Babu100% (1)
- Pay ManagementDocument3 paginiPay ManagementAshfaak MahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compensation ManagementDocument56 paginiCompensation ManagementShubham SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mind MapDocument6 paginiMind MapSyaz Amri100% (1)
- Chapter 13Document10 paginiChapter 13api-3807704Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10Document19 paginiChapter 10api-3807704Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 09Document12 paginiChapter 09api-3807704Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 08Document5 paginiChapter 08api-3807704Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 06Document9 paginiChapter 06api-3807704Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 05Document17 paginiChapter 05api-3807704Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 04Document11 paginiChapter 04api-3807704100% (1)
- Nature and Scope of HRMDocument18 paginiNature and Scope of HRMHemang LimbachiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 28Document25 paginiChapter 28api-3807704Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 02Document8 paginiChapter 02api-3807704Încă nu există evaluări
- Kodai Gosse - Careers Exploration Part 1 2Document12 paginiKodai Gosse - Careers Exploration Part 1 2api-552654464Încă nu există evaluări
- Certified Compensation and Benefits Manager - Middle Earth HRDocument3 paginiCertified Compensation and Benefits Manager - Middle Earth HREdward Ebb BonnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Staffing: Dickson Johan Jay B. LlemaDocument51 paginiStaffing: Dickson Johan Jay B. LlemaDickson LlemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SplicingDocument111 paginiSplicingamiya001100% (1)
- Study of Compensation Management in HDFC BankDocument40 paginiStudy of Compensation Management in HDFC BankTusharr Ahuja0% (1)
- 1.7 08reso Temporary Special Permit Foreign ArchsDocument17 pagini1.7 08reso Temporary Special Permit Foreign ArchsKYRA TIQUIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategic Human Resource Management - MBADocument11 paginiStrategic Human Resource Management - MBAShagufta ShowkatÎncă nu există evaluări
- HRM Sem IV Full NotesDocument54 paginiHRM Sem IV Full NotesNeha GodsoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labor Law GuideDocument14 paginiLabor Law GuideMan2x SalomonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fitter 2nd Year (Volume I of II) TPDocument154 paginiFitter 2nd Year (Volume I of II) TPpradeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- UAE Labour LawDocument23 paginiUAE Labour LawKhuram MunibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combining Social Insurance Contributions From AbroadDocument5 paginiCombining Social Insurance Contributions From Abroadsoltero2Încă nu există evaluări
- 08 - ESOL Teacher Notes Entry 2 Unit 8Document11 pagini08 - ESOL Teacher Notes Entry 2 Unit 8WayneÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3879 SITI AISHAH BINTI ADNAN s253721 Comparative Individual Assignment 73526 315203905Document14 pagini3879 SITI AISHAH BINTI ADNAN s253721 Comparative Individual Assignment 73526 315203905aton hudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Resources: Business English UnitDocument8 paginiHuman Resources: Business English UnitMist TwimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proposal For Conducting AMCAT: Aspiring Minds Assessment Pvt. LTDDocument10 paginiProposal For Conducting AMCAT: Aspiring Minds Assessment Pvt. LTDRashmi AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Labour in IndiaDocument12 paginiChild Labour in IndiaDUKI BANAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education Problems in India - Problems of Education System in India - Current Educational Problems in IndiaDocument8 paginiEducation Problems in India - Problems of Education System in India - Current Educational Problems in IndiaSourabh AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Four Reasons Behind Maruti SuzukiDocument13 paginiFour Reasons Behind Maruti SuzukiSaurabh PrabhakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ramesh Singh Eco Notes On e SurveyDocument43 paginiRamesh Singh Eco Notes On e SurveyAbhijeet ArvindÎncă nu există evaluări
- ALINDDocument67 paginiALINDDaniel GainesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mercertrs SamplecontentDocument27 paginiMercertrs Samplecontentönay akgünÎncă nu există evaluări
- WNS Global Services - CasestudyDocument2 paginiWNS Global Services - CasestudyManoj G ShekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Job Application and Cover LettersDocument1 paginăJob Application and Cover LettersDyah AgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application LetterDocument1 paginăApplication LetterWV Gamiz Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- HRM Activity, Session 2Document1 paginăHRM Activity, Session 2Sio-Ann TapilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Company Profile of Ambit ProjectsDocument43 paginiCompany Profile of Ambit ProjectsSaurav Gautam100% (1)
- Redevelopment Strategies For The Bloomington Hospital SiteDocument44 paginiRedevelopment Strategies For The Bloomington Hospital SiteIndiana Public Media NewsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dominic BuchananDocument1 paginăDominic BuchananJames BoydÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mckinsey & Co.Document12 paginiMckinsey & Co.AbhimanyuBhardwajÎncă nu există evaluări