Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
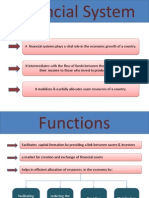
Financial System
Încărcat de
vinit.ambat13510Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Financial System
Încărcat de
vinit.ambat13510Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Financial Intermediary Has Integrated subsystems like
Financial institutions Financial Markets Financial Instruments Financial services
Financial dualism Formal is characterised by
Organised Institutional Regulated
Cater to the financial needs of modern spheres of economy Informal is characterised by
Unorganised Non-institutional Non regulated
Cater to the financial needs of traditional and rural spheres of the economy
Consists of Individual money lenders such as neighbors, relatives, landlords, traders etc Groups of persons operating as funds or associations They have their own rules Partnership firms consisting of local brokers, pawnbrokers, and non-bank financial intermediaries such as finance, investment and chit-fund companies
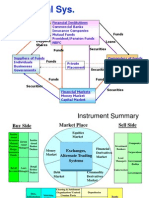
Financial institutions Financial markets Financial instruments Financial services
SEBI RBI IRDA Dept of Financial services (MoF)
Banking institutions Non banking institutions Mutual funds Insurance and Housing finance companies
Scheduled commercial banks Scheduled coop banks Non-scheduled commercial banks Non-scheduled cooperative banks
Public sector banks Private sector banks Foreign banks in India Regional Rural banks
Non banking financial companies DFI Development financial institutions All india FIs- IFCI, IDBI, SIDBI, IDFC, NABARD, EXIM bank, NHB State level FIs- SFCs, SIDCs, etc Other institutions DICGC, ECGC, Stock exchanges
Public sector Private sector
Capital market Money market Fex market GSec market
Equity market Debt market Equity market
Primary
Public issues
Private placement
Secondary Derivatives market
Private corporate debt PSU bond market G sec market Primary dealers (PDs)
Fin instrument is a claim against a person or an institution for payment, at a future date, of a sum of money and / or a periodic payment in the form of interest or dividend Financial securities are financial instruments that are negotiable and tradeable Financial instruments differ in respect of Marketability Liquidity Reversibility/ fungibility Type of options Return Risk Transaction costs
Provides transformation services: Liability, asset and size transformation Maturity transformation Risk transformation
Short term Medium term Long term Primary securities Secondary securities Equity, debentures, mixed, Time deposits, MF units, Insurance policies CPs, CDs,
Depositories Custodial services Credit Rating services Factoring Forfaiting Merchant banking Leasing, HP Guaranteeing PMS Venture capital
Strong legal and regulatory environment Stable money Sound public debt management Strong central bank Sound banking system Transparent information system well functioning securities market
Mobilise and allocate savings Monitor corporate performance Provide payment and settlement system Optimum allocation of risk bearing and reductions Disseminate price related information Offer portfolio adjustment facility Lower the cost of transaction Promote the process of financial deepening and broadening
Bank based Market based Bank based: Few large banks play a dominant role and the financial market is not important eg. India, Germany, Japan, France, Pakistan Market based: Financial markets play an important role while the banking industry is much less concentrated eg. US UK, singapore, Korea
Advantages: Provides attractive terms to both investors and borrowers Facilitates diversification Allows risk sharing Allowing financing of new technologies Drawbacks: Prone to instability Exposure to market risk Free- rider problem
Advantages Close relationship with parties Provides tailor-made contracts Efficient risk sharing No free-rider problem Drawback Retards innovation and growth Impedes competition
Thank
you
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Bull's Eye- A stock market investment guide for beginnersDe la EverandBull's Eye- A stock market investment guide for beginnersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Role of Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument26 paginiRole of Financial Markets and Institutionsshomy02Încă nu există evaluări
- Afm PresentationDocument11 paginiAfm PresentationVipin GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian Financial System: Faculty Facilitator: Rajesh SadhwaniDocument17 paginiIndian Financial System: Faculty Facilitator: Rajesh Sadhwaniparthshah1200Încă nu există evaluări
- FMSDocument12 paginiFMSMahesh SatapathyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session 1: Indian Financial SystemDocument12 paginiSession 1: Indian Financial SystemMahesh SatapathyÎncă nu există evaluări
- L1 PS Indian Financial System Financial InstitutionsDocument61 paginiL1 PS Indian Financial System Financial InstitutionsSanika SankheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial ServicesDocument12 paginiFinancial ServicesarmailgmÎncă nu există evaluări
- FM19 Chap 1Document24 paginiFM19 Chap 1Loui CanamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Markets and Institutions 6Th Edition: Powerpoint Slides ForDocument24 paginiFinancial Markets and Institutions 6Th Edition: Powerpoint Slides Forhappy aminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constituents of Fin SysDocument21 paginiConstituents of Fin Sysakhilindia8Încă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction To Financial System, Its Components: Unit 1Document16 paginiAn Introduction To Financial System, Its Components: Unit 1bhavyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian Financial SystemDocument14 paginiIndian Financial SystemAvinash KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian Debt Market: Presented BY: Sandeep Kr. YadavDocument15 paginiIndian Debt Market: Presented BY: Sandeep Kr. Yadavaksh02007100% (3)
- Gau 1Document6 paginiGau 1smittal222Încă nu există evaluări
- Once You Start Working On Something, Don't Be Afraid of Failure and Don't Abandon It. People Who Work Sincerely Are The Happiest. - ChanakyaDocument39 paginiOnce You Start Working On Something, Don't Be Afraid of Failure and Don't Abandon It. People Who Work Sincerely Are The Happiest. - Chanakyasundeepkumar007Încă nu există evaluări
- 1-Indian Financial SystemDocument30 pagini1-Indian Financial SystempallavimakkanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Security Analysis and Portfolio ManagementDocument20 paginiSecurity Analysis and Portfolio ManagementAklas LaskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Primer On Financial Markets & InstitutionsDocument34 paginiA Primer On Financial Markets & InstitutionsRakibul IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fixed Income Securities: A Beginner's Guide to Understand, Invest and Evaluate Fixed Income Securities: Investment series, #2De la EverandFixed Income Securities: A Beginner's Guide to Understand, Invest and Evaluate Fixed Income Securities: Investment series, #2Încă nu există evaluări
- 2.financial ServicesDocument24 pagini2.financial ServicesSwati Jagtap100% (2)
- MBA FM 02 - Security Analysis and Portfolio - IntroductionDocument20 paginiMBA FM 02 - Security Analysis and Portfolio - Introductionraimanish76Încă nu există evaluări
- Financial System - An IntroductionDocument80 paginiFinancial System - An IntroductionAnonymous LUvUBT60pnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bfsi (Banking Financial Services and Insurance)Document21 paginiBfsi (Banking Financial Services and Insurance)india4gÎncă nu există evaluări
- FMI - Chap 3 (24 - 3-2020)Document30 paginiFMI - Chap 3 (24 - 3-2020)alioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Saunders Cornett McGrawDocument58 paginiChapter 1 Saunders Cornett McGrawAlice WenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Financial SystemDocument5 pagini1 Financial SystemRahul AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- NadirSaleem - 56 - 13882 - 3/'financials Market (Capital and Money Market)Document33 paginiNadirSaleem - 56 - 13882 - 3/'financials Market (Capital and Money Market)Maria KhalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Institutions and MarketsDocument84 paginiFinancial Institutions and MarketsShreekumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01-1 Indian Financial SystemDocument160 pagini01-1 Indian Financial Systemanmaya agarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- FM IntroDocument21 paginiFM IntroVinodh Kumar LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial System of IndiaDocument2 paginiFinancial System of IndiaUnni KrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRESENTED TO:Madam Soniya Ismat Presented By: M.Tashfeen Farhad Shafqat Zara BabarDocument20 paginiPRESENTED TO:Madam Soniya Ismat Presented By: M.Tashfeen Farhad Shafqat Zara BabarTashfeen ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retail and Wholesale Banking Session 2Document14 paginiRetail and Wholesale Banking Session 2Rishabh AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial MarketsDocument19 paginiFinancial MarketsRubeenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Financial System: Prepared By:-Pandya Kiran Parmar Ranjit Patel Jignesh Bhayani SanjayDocument18 paginiThe Financial System: Prepared By:-Pandya Kiran Parmar Ranjit Patel Jignesh Bhayani SanjayAbhishek FanseÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRESENTED TO: Mr. Fawad AshrafDocument20 paginiPRESENTED TO: Mr. Fawad AshrafMohsin AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1-Bond MarketDocument85 pagini1-Bond Marketdharmtamanna80% (5)
- Financial Services-1Document11 paginiFinancial Services-1Ranjana PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of Fin SysDocument80 paginiStructure of Fin SysharishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 MBS FIMDocument16 paginiUnit 1 MBS FIMSarun ChhetriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Institutions and Markets: Prof. Manisha SanghviDocument85 paginiFinancial Institutions and Markets: Prof. Manisha SanghviinderpretationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treasury ManagementDocument48 paginiTreasury Managementparthasarathi_inÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Indian Financial SystemDocument31 paginiIntroduction To Indian Financial SystemManoher Reddy100% (2)
- Overview of Indian Financial MARKETSDocument46 paginiOverview of Indian Financial MARKETSGaurav Rathaur100% (2)
- Financial InnovationDocument19 paginiFinancial InnovationSiva ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 8: The Australian Financial Markets: Week 8 NotesDocument3 paginiTopic 8: The Australian Financial Markets: Week 8 NotesJakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finance Vs Financial SystemDocument61 paginiFinance Vs Financial Systempriyasumit100% (1)
- TheoryDocument16 paginiTheoryPhuong ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Financial EnvironmentDocument57 paginiChapter 1 Financial Environmentn nÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investing in Fixed Income Securities: Understanding the Bond MarketDe la EverandInvesting in Fixed Income Securities: Understanding the Bond MarketÎncă nu există evaluări
- Money and Capital Markets 8526Document11 paginiMoney and Capital Markets 8526mariamehdi22Încă nu există evaluări
- Financial SystemDocument17 paginiFinancial SystemKavita ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 3 AnswersDocument13 paginiWorksheet 3 AnswersKUMARI PUJA-MBAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Environment: Financial Markets of PakistanDocument26 paginiFinancial Environment: Financial Markets of PakistanMuneeb UmairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian Financial Systems: Meaning & ConstituentsDocument7 paginiIndian Financial Systems: Meaning & ConstituentsrishugÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial System& RBI SEBI FINALDocument31 paginiFinancial System& RBI SEBI FINALvrushkopÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Financial Markets "Final Project": Submitted byDocument16 paginiIntroduction To Financial Markets "Final Project": Submitted byHafsa ZulfiqarÎncă nu există evaluări
- The psychology of investment: Educating the Financial Mind to Invest ConsciouslyDe la EverandThe psychology of investment: Educating the Financial Mind to Invest ConsciouslyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equity Investment for CFA level 1: CFA level 1, #2De la EverandEquity Investment for CFA level 1: CFA level 1, #2Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Master in Finance LBSDocument24 paginiMaster in Finance LBSarmandete22Încă nu există evaluări
- Leveraging Region With Economy, Social and Technology CollaborationDocument270 paginiLeveraging Region With Economy, Social and Technology CollaborationGatotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For The Economics of Money Banking and Financial Markets 6th Canadian Edition MishkinDocument36 paginiTest Bank For The Economics of Money Banking and Financial Markets 6th Canadian Edition Mishkinordainer.cerule2q8q5g100% (35)
- "A Study of Online Trading and Stock Broking": A Project Report OnDocument85 pagini"A Study of Online Trading and Stock Broking": A Project Report OnShubha DevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Market & Institution WorksheetDocument5 paginiFinancial Market & Institution WorksheetBobasa S Ahmed100% (1)
- Gagan Singh Pal STRDocument63 paginiGagan Singh Pal STRABHISHEK GUPTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- GRP 1 Financial-Market-Intro-TypesDocument34 paginiGRP 1 Financial-Market-Intro-TypesXander C. PasionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Sector Development and Economic Growth in EthiopiaDocument11 paginiFinancial Sector Development and Economic Growth in EthiopiaAbdi ÀgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- FM - Angel BrokingDocument137 paginiFM - Angel Brokingjagrutisolanki01Încă nu există evaluări
- Code For Instagram HackDocument1.766 paginiCode For Instagram HackBishop Ojonuguwa Ameh100% (1)
- Institutional Investor - 07 JUL 2009Document72 paginiInstitutional Investor - 07 JUL 2009jumanleeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intraday Trading Using Camarilla and Advanced CamarillaDocument12 paginiIntraday Trading Using Camarilla and Advanced Camarillawierdooo69% (16)
- REVIEWER - Business Finance Q3 TQDocument3 paginiREVIEWER - Business Finance Q3 TQCharry BaidiangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 2 Financial Market EnvironmentDocument17 paginiCH 2 Financial Market EnvironmentAkash KarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Analysis of The Financial MarketsDocument27 paginiTechnical Analysis of The Financial Marketsgavin henning100% (1)
- Financial Sector Reforms in IndiaDocument5 paginiFinancial Sector Reforms in Indiasindhu_penugondaa0% (1)
- CrisisDocument11 paginiCrisisShabeer AlikakathÎncă nu există evaluări
- (ECO) Chapter 9 Money Market and Capital MarketDocument12 pagini(ECO) Chapter 9 Money Market and Capital MarketMehfooz PathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recent Development in Global Financial MarketDocument8 paginiRecent Development in Global Financial MarketBini MathewÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On Investor Attitude Towards Primary MarketDocument63 paginiA Study On Investor Attitude Towards Primary MarketAnkit BissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch. 4 Securities Market and Trading Part 1 & 2Document35 paginiCh. 4 Securities Market and Trading Part 1 & 2teshome dagneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internship Report On HSBCDocument78 paginiInternship Report On HSBCM I HASSANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Credit Risk Management at Icici BankDocument128 paginiCredit Risk Management at Icici Bankyash gupta83% (6)
- Financial Market ReviewerDocument9 paginiFinancial Market ReviewerBryan NograÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Economics - III - TYBCOMDocument5 paginiBusiness Economics - III - TYBCOMDarshit V VoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corporate BondDocument14 paginiCorporate BondRavi WadherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finansering GuldnoterDocument140 paginiFinansering GuldnoterSebastian Manfred StreyffertÎncă nu există evaluări
- EQUITY ANALYSIS WITH REPECT TO Automobile SectorDocument83 paginiEQUITY ANALYSIS WITH REPECT TO Automobile SectorSuraj DubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sandhani Life UF GrowthDocument12 paginiSandhani Life UF Growthnahid250Încă nu există evaluări
- Corporate Finance B40.2302 Lecture Notes: Packet 1: Aswath DamodaranDocument332 paginiCorporate Finance B40.2302 Lecture Notes: Packet 1: Aswath Damodaranset_hitÎncă nu există evaluări