Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Entomology Lecture
Încărcat de
Sayote BahaghariDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Entomology Lecture
Încărcat de
Sayote BahaghariDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Entomology is the Study of Insects
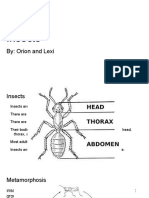
Insects
are the most diverse and abundant forms of life on earth. There are over a million described speciesmore than 2/3 of all known organisms There is more total biomass of insects than of humans. Insects undergo either incomplete or complete metamorphosis (Egg to larva to pupa to insect) Larva have a soft tubular body and look like worms. Fly species larvae are maggots
A single insect bears 3 pairs of legs, 2 pairs of wings, compound and simple eyes, and 2 antennae. The insect exoskeleton provides tremendous strength ... Insects are upside-down ... they have a dorsal heart and a ventral nerve cord. The insect respiratory system is comprised of holes (spiracles) in the abdomen and thorax, and tubes (tracheae) that allow outside air to reach locations next to body organs. Insects smell with antennae and taste with tarsal (foot) pads (and other organs). Their phenomenal features include stalked eyes, brightly colored hairs and spines, large horns, powerful jaws, and ovipositors adapted for spectacular uses.
Respiratory
system (tracheal system): Spiracles: External openings on each side of most body segments Tracheae: large tubes that run the length of the body on each side. Smaller tubes are called tracheal branches and tracheoles. Air sacs that store air (air, not just oxygen) may be located in the abdomen and/or the thorax.
Most insects are oviparous females lay eggs. The act of egg-laying is called oviposition. Eggs may be laid singly or in masses; often they are coated with a sticky substance secreted from the female accessory gland to glue them to each other and a plant surface (or other substrate). In most insect groups, eggs are laid shortly after fertilization; egg development does not occur in the mother.
Exceptions to the general rule include: Ovovivipary: Eggs are incubated in the female until nearly ready to hatch, and hatching occurs almost immediately after oviposition; this occurs in some cockroaches, aphids,scales, beetles, thrips, and flies (but is not the rule in any of these groups). Pseudoplacental vivipary: Egg develops in maternal tissue where nutrients aretransferred to the developing embryo; offspring is born immediately upon hatchingfrom the egg. Common in many aphids; also occurs in some earwigs, Psocoptera, Nad, one family of Hemiptera. In a few fly families, larval development occurs entirely within the mother, and the fully grown larva pupates immediately after birth. This occurs in the tsetse fly, the louse flies or keds, and the bat flies.
Sperm
storage in the spermatheca allows females to store sperm to fertilize eggs later, in the absence of males (sperm remain viable in the spermatheca of queen honey bees for up to 3 years).
Parthenogenesis:
Reproduction via development of unfertilized eggs Eggs may be all female (thelytokous parthenogenesis) aphids Eggs may be all male (arhenotokous parthenogenesis) many Hymenoptera Polyembryony: Two or more embyos develop from one egg; common in Hymenoptera.
Pupae of a Hymenopteran parasite on a hornworm, Manduca sp. An adult wasp inserted one egg into this larva, and multiple embryos developed. Larvae of the wasp fed inside the hornworm and have exited the body and spun cocoons in which they have pupated.
Most
insects are diploid, with one set of chromosomes from each parent. XX individuals usually are female; XO are male. Haploid diploid sex determination occurs when unfertilized eggs develop into haploid individuals and are male; fertilized eggs develop into diploid females occurs in Hymenoptera.
Thoracic tympanae of moths ... for avoiding bats / sometimes they aid in attracting bats Stridulation ... the sound-producing process of crickets Compound eyes ... 30,000 facets in one compound eye in a dragonfly ... they sense movement and some color, but provide poor resolution. Bioluminescence ... In fireflies, flying males flash first; stationary females respond by flashing back. If the flash intervals are correct, the male flies to source to mate.
Phylum
(and subphylum) Class (and subclass) Order (and suborder) Superfamily Family (and subfamily) (Tribe) Genus (and subgenus) Species (and subspecies)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Backyard Bugs: An Identification Guide to Common Insects, Spiders, and MoreDe la EverandBackyard Bugs: An Identification Guide to Common Insects, Spiders, and MoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- G-11 PPT P-2Document126 paginiG-11 PPT P-2etsubtarekegn87Încă nu există evaluări
- Animal ReproductionDocument31 paginiAnimal ReproductionAmelda Mira BontilaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproduction SystemDocument38 paginiReproduction SystemNurfatin AdilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insect Reproductive SystemDocument3 paginiInsect Reproductive SystemLiezl Bornales ParreñoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANIMALS Pre 11 (Autosaved)Document124 paginiANIMALS Pre 11 (Autosaved)kiddistnegashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phylum NematodaDocument24 paginiPhylum NematodaKaten KyoukotsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asexual Reproduction in InvertebratesDocument11 paginiAsexual Reproduction in Invertebratesaiman maqsood100% (1)
- How Many Days Does A Butterfly Stay in Its CocoonDocument6 paginiHow Many Days Does A Butterfly Stay in Its CocoonMaricar RaciramÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4Q - Animal Forms Functions 1 - ReproductionDocument41 pagini4Q - Animal Forms Functions 1 - ReproductionMaymayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Morphology and Physiology CompressedDocument54 paginiAnimal Morphology and Physiology CompressedJana Elaine HermosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument15 paginiPerpetuation of LifeMomo Capoquian100% (1)
- EnterobiusDocument11 paginiEnterobiusMayuri VohraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phylum Arthropoda: ReproductionDocument12 paginiPhylum Arthropoda: ReproductionJoshua KennedyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classes of Vertebrates (Comparative Analysis)Document173 paginiClasses of Vertebrates (Comparative Analysis)Vinci EbordeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 46 Animal ReproductionDocument11 paginiChapter 46 Animal ReproductionEmilja ZeneliÎncă nu există evaluări
- The "Nematodes or "Roundworms" (Phylum Nematoda) AreDocument19 paginiThe "Nematodes or "Roundworms" (Phylum Nematoda) AremacybnzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 2Document11 paginiLect 2Sara AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- PlatyhelminthesDocument17 paginiPlatyhelminthesLuisa San SebastianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report in BiologyDocument40 paginiReport in BiologyPanfilo Diaz LacsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modes of ReproductionDocument4 paginiModes of ReproductionSayie GulmaticoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lateral Cephalothorax: Anatomy of An Adult MosquitoDocument5 paginiLateral Cephalothorax: Anatomy of An Adult MosquitoZyrene YanezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insect Reproduction CK Dash SAUDocument3 paginiInsect Reproduction CK Dash SAUChandra Kanta Dash100% (1)
- 04 MetamorphosisDocument15 pagini04 Metamorphosisbrown gondweÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oviparity: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 paginiOviparity: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDhusar RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument69 paginiReproduction in AnimalsAliya CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1Document28 paginiLecture 1Mamun_Abdullah_1612100% (1)
- Reproduction of MosquitoesDocument4 paginiReproduction of MosquitoesJessie MorreÎncă nu există evaluări
- To Study The Development of Cockroach 1.0Document6 paginiTo Study The Development of Cockroach 1.0Utkarsh MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grasshopper InformationDocument7 paginiGrasshopper Informationchopper_hemoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of A ParameciumDocument21 paginiStructure of A ParameciumHwangMiyoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Living Things ReproduceDocument36 paginiHow Living Things Reproduceailynmirano885Încă nu există evaluări
- Reptile ReproductionDocument5 paginiReptile ReproductionDiyar Ahmad100% (1)
- InsectsDocument5 paginiInsectsapi-271048363Încă nu există evaluări
- Parthenogenesis (from the Greek παρθένος parthenos, "virgin", + γένεσις genesis, "birth"Document11 paginiParthenogenesis (from the Greek παρθένος parthenos, "virgin", + γένεσις genesis, "birth"Sankalp SahuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skeleton Endoskeleton Human Tortoise: ExoskeletonDocument5 paginiSkeleton Endoskeleton Human Tortoise: ExoskeletonMohd Khairul Azwan SirajudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module in Science 5 3rd Quarter Week 3Document5 paginiModule in Science 5 3rd Quarter Week 3Ronalyn RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q2 W3 SCI 5-Methods of Reproduction (ANIMALs)Document32 paginiQ2 W3 SCI 5-Methods of Reproduction (ANIMALs)Buena Rosario100% (1)
- Lesson 3 ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Students NotesDocument6 paginiLesson 3 ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Students NotesrasingtanyaroseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kingdom Animalia: Clade Ecdysozoa Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms)Document18 paginiKingdom Animalia: Clade Ecdysozoa Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms)draykidÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Characteristics: NematodesDocument27 paginiGeneral Characteristics: NematodesJaica Mangurali Tumulak100% (1)
- ButterflyDocument13 paginiButterflyashisb444Încă nu există evaluări
- Butterfly: New Messages Last Change Navigation SearchDocument16 paginiButterfly: New Messages Last Change Navigation SearchhotchickenwingsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Reproduction Not SummarizeDocument4 paginiAnimal Reproduction Not SummarizeKim KardashianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beige Vintage Insects Nature PresentationDocument47 paginiBeige Vintage Insects Nature PresentationAl Francis MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class InsectaDocument30 paginiClass InsectaEdz SeletariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10. Edited ReproductionJ Growth and DevelopmentDocument10 paginiChapter 10. Edited ReproductionJ Growth and Development5pn4x4czxnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproductive SystemDocument19 paginiReproductive SystemJoan GalarceÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnimalsDocument9 paginiAnimalssolomon MekonninÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entomology Laboratory ExcerciseDocument13 paginiEntomology Laboratory ExcerciseKhimmie PalzÎncă nu există evaluări
- AHMADDocument7 paginiAHMADSUNDAY MUSAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fish Reproduction: 1 AnatomyDocument11 paginiFish Reproduction: 1 Anatomysksingl350Încă nu există evaluări
- F0rensics sCiEncE!!! @un!Document8 paginiF0rensics sCiEncE!!! @un!Noraidah AbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.1.1 Mosquito Life Cycle: Culex Mosquitoes Lay Them Together in The Form of A Raft. Many Aedes Species Lay Their Eggs OnDocument4 pagini4.1.1 Mosquito Life Cycle: Culex Mosquitoes Lay Them Together in The Form of A Raft. Many Aedes Species Lay Their Eggs OnAtrizha MWÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch. 15 Nematoda (Web Version)Document35 paginiCh. 15 Nematoda (Web Version)bewildered-escapist-4301Încă nu există evaluări
- Major V Sem PracticalDocument12 paginiMajor V Sem Practicalmohitpatel18032003Încă nu există evaluări
- Reproductive System Etc.Document29 paginiReproductive System Etc.Shadab HanafiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bab Pembahasan EntomologiDocument11 paginiBab Pembahasan EntomologiRahmayulis 123Încă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge ReviewDocument81 paginiKnowledge ReviewAmr EldemardashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument2 paginiReviewer in BiologyCrisha LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidebook Zoology PDFDocument270 paginiGuidebook Zoology PDFMuhammad Modassir Ali100% (5)
- Activity Sheet in Earth and Life ScienceDocument23 paginiActivity Sheet in Earth and Life ScienceRODEL AZARES0% (1)
- Asexual Reproduction in InvertebratesDocument11 paginiAsexual Reproduction in Invertebratesaiman maqsood100% (1)
- Frontier Explorer 020Document41 paginiFrontier Explorer 020lowtech4100% (2)
- Earth and Life Science Week 11-12Document14 paginiEarth and Life Science Week 11-12Aleli Joy Profugo DalisayÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Reproduction in Organisms: SolutionsDocument10 pagini11 Reproduction in Organisms: SolutionsPugalmeena PugalmeenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perpetuation of Life Animal ReproductionDocument23 paginiPerpetuation of Life Animal ReproductionKyla Heart ZaragozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Advanced GeneticsDocument31 paginiChapter 6 Advanced GeneticsRochelleCasador180Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2. Introduction To Daphnia BiologyDocument21 paginiChapter 2. Introduction To Daphnia BiologyMohamad QinaoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Organ System and Their FunctionsDocument39 paginiAnimal Organ System and Their FunctionsMa Cristina VelascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gametogénesis GeckosDocument16 paginiGametogénesis GeckosIsabella ValenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FibonacciDocument45 paginiFibonacciChristelle Joy EusebioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal RepdoductionDocument24 paginiAnimal RepdoductionSichayra GamotiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fish Reproduction: 1 AnatomyDocument11 paginiFish Reproduction: 1 Anatomysksingl350Încă nu există evaluări
- Earth-and-Life-Science Q2 Mod11 Animal-Reproduction Version1Document15 paginiEarth-and-Life-Science Q2 Mod11 Animal-Reproduction Version1ivanjade627Încă nu există evaluări
- Class 12 Bio Zoology TM Chapter-1 Full GuideDocument7 paginiClass 12 Bio Zoology TM Chapter-1 Full GuidemakeshwaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAS GenBio2 MELC 1 Week 1Document14 paginiLAS GenBio2 MELC 1 Week 1Roland Jacques AlconisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Namma Kalvi 12th Zoology Reduced Syllabus Study Material EM 220454Document32 paginiNamma Kalvi 12th Zoology Reduced Syllabus Study Material EM 220454Anitha SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals: Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument64 paginiCompare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals: Reproduction and DevelopmentMarites PacañaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TMA Journal Volume6Document52 paginiTMA Journal Volume6Transverse Myelitis AssociationÎncă nu există evaluări
- ALPH by Charles Eric Maine gnv64 PDFDocument232 paginiALPH by Charles Eric Maine gnv64 PDFPrlilisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parthenogenesis by Joanna Azaniah WadeDocument13 paginiParthenogenesis by Joanna Azaniah WadeJaden Azareah WadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fission: Molds, Lichens, Many Plants, and Animals Such As Sponges, Acoel Flatworms, Some Annelid Worms and Sea StarsDocument2 paginiFission: Molds, Lichens, Many Plants, and Animals Such As Sponges, Acoel Flatworms, Some Annelid Worms and Sea StarsKARENÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Biology of Reproduction - Bio565: WelcomeDocument47 paginiComparative Biology of Reproduction - Bio565: WelcomehuddaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vajiram CSP20 CA Test 1Document71 paginiVajiram CSP20 CA Test 1annushaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Namma Kalvi 12th Bio-Zoology Full Study Material em 219472Document284 paginiNamma Kalvi 12th Bio-Zoology Full Study Material em 219472gokul ganesh DÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth and Life Sci QRTR 2 Module 5 Perpetuation of Life Student Edition Grade 11 DescartesDocument46 paginiEarth and Life Sci QRTR 2 Module 5 Perpetuation of Life Student Edition Grade 11 Descartesmelvin madronal100% (1)
- Definitions of Parasitism Considering Its Potentially Opposing Effects at Different Levels of Hierarchical OrganizationDocument8 paginiDefinitions of Parasitism Considering Its Potentially Opposing Effects at Different Levels of Hierarchical OrganizationwellingtonlimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Vs External DevelopmentDocument13 paginiInternal Vs External Developmentapi-299996815Încă nu există evaluări
- Asexual ReproductionDocument12 paginiAsexual ReproductionROWELL LEGASÎncă nu există evaluări