Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Health Topic Power Point Inspiration
Încărcat de
TreeLawDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Health Topic Power Point Inspiration
Încărcat de
TreeLawDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Eyes Forward
Eyes Forward
You cant make sense of the world without your sense organs! Start with your eyes. They send tons of information to your brain. So its no surprise that you have built-in structures to protect them! You only see about one sixth of your eyeball on your face. The rest of it is inside your skullsafely protected within a deep bowl of skull bone called your eye socket.
Eyelids protect the eye from bright light
Eyebrows direct sweat away from the eye Eyelashes protect the eye from dust
Tears drain away through ducts in the corner of the eye
Human eye
Moving the Eye
Moving the Eye
Your eyeballs are constantly moving around in their sockets. Sometimes its Turns the a big movement. Other eye toward times, its just a fraction the nose of an inch.
Moves the eye upward
Rotates the eye downward and out, away from the nose
How do your eyes move? Muscles do the job. In fact, eye muscles are the most used muscles in your body. According to some estimates, they move more than 100,000 times a day!
Moves the eye downward
Eyeball with muscles
Moves the eye outward
Rotates the eye upward and outward
Inside the Eye
Inside the Eye
There are some parts of your eye that you can easily see. The clear structure in the middle of the white part of your eye is the cornea. The dark part in the middle of your cornea is the pupil. The iris, or colored part of your eye, controls how much light gets through your pupil.
Cornea
If you could peer inside Pupil to the innermost layer of your eye you would see the retina. The retina contains Iris millions of light-sensitive cells that convert light into electrical impulses that can be sent to the brain. Cross-section of eye
Retina
Forming an Image
Forming an Image
Your eyes collect information. But its your brain that allows you to see! Light refracts (or bends) as it travels through your eye. An upside down image forms on your retina which sends electrical impulses through the optic nerve to your brain.
Light rays sent to the eye pass through the cornea, pupil, and lens
An upside-down image forms on the retina at the back of the eye
Optic nerve
So why dont you see an upside down image? Its because your brain makes sense of it alland you see the image right side up!
Diagram of eye forming an image
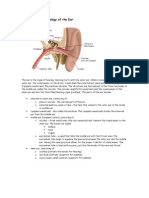
Inside the Ear
Inside the Ear
Just like your eye, most of your ear is actually inside your head. The outer ear collects sound waves. These pass through your eardrum causing it to move, or vibrate. These vibrations move through the tiny bones in your middle ear and are passed on to your inner ear. The snail-shaped cochlea in your inner ear contains nerves that take the information to the brain. And you guessed it! The brain then distinguishes between different kinds of sounds.
Middle ear bones
Cochlea
Eardrum Outer ear canal
Human ear
Smallest Bones
Smallest Bones
The bones in your middle ear are the smallest bones in your body. The three bones get their names from the Latin word for their shapes: malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup). The tiny hammer bone you see in this photo is just inch longyet youll hear no sound (large or small) without it!
Malleus
Tiny hammer bone on finger
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Chapter 8-SPECIAL SENSESDocument5 paginiChapter 8-SPECIAL SENSESrishellemaepilonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Ototoxicity in Adult Rats - Rapid Onset and Massive Destruction of Both Inner and Outer Hair Cells Above a Critical DoseDocument16 pagini2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Ototoxicity in Adult Rats - Rapid Onset and Massive Destruction of Both Inner and Outer Hair Cells Above a Critical DosesovalaxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EarDocument6 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of The EarrizzarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quick Guideto TympanometryDocument6 paginiQuick Guideto TympanometryWilhelm HeinleinÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENT DefinationDocument22 paginiENT Definationيدا واحدةÎncă nu există evaluări
- TF TestDocument23 paginiTF TestFrederick BallesterosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rehabilitacion PlasticidadDocument9 paginiRehabilitacion Plasticidadn_almagroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endoscopic Ear Surgery Course. 4th Edition: Barcelona, April 27, 2022Document1 paginăEndoscopic Ear Surgery Course. 4th Edition: Barcelona, April 27, 2022Luana Maria GherasieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hearing Aid InformationDocument22 paginiHearing Aid InformationDeepakRodeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar Report 2013-14 CyborgsDocument20 paginiSeminar Report 2013-14 CyborgsSafalsha BabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam Additional Sample Questions AudDocument6 paginiExam Additional Sample Questions AudAbouzr Mohammed ElsaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of The Ear and Hearing AcuityDocument3 paginiAssessment of The Ear and Hearing AcuityJay Debby RuizoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch. 15 Sensory SystemDocument23 paginiCh. 15 Sensory SystemJackieFernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deaf CultureDocument17 paginiDeaf Cultureapi-385151452Încă nu există evaluări
- Care of Clients With Sensory Problems Care of Clients With Sensory ProblemsDocument82 paginiCare of Clients With Sensory Problems Care of Clients With Sensory Problemssnpjavier100% (1)
- Tympanoplasty Indications, Types, ProcedureDocument55 paginiTympanoplasty Indications, Types, ProcedurePrasanna DattaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of The Patient With Vertigo - UpToDate PDFDocument29 paginiEvaluation of The Patient With Vertigo - UpToDate PDFDanna GarcíaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BPPV at A GLANCE 2022-Guide Book (Vestibuology) - 230330 - 083425Document56 paginiBPPV at A GLANCE 2022-Guide Book (Vestibuology) - 230330 - 083425EeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Timpanoplastia Tipo IDocument14 paginiTimpanoplastia Tipo ILuis De jesus SolanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neuromuscular Physical TherapyDocument13 paginiNeuromuscular Physical Therapypearl042008100% (3)
- External Ear Anomalies and Hearing Impairment in NoonanDocument17 paginiExternal Ear Anomalies and Hearing Impairment in NoonanPrinksezza LatinnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 Windows of KnowledgeDocument9 paginiUnit 2 Windows of Knowledgesajith kumar VariathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology Foundations For The Health Professions 1st Edition Deborah Roiger Test Bank 1Document56 paginiAnatomy and Physiology Foundations For The Health Professions 1st Edition Deborah Roiger Test Bank 1tabitha100% (30)
- Anatomy EarDocument44 paginiAnatomy Earrinaldy agungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eir SimulatorDocument2 paginiEir SimulatorSophiBelle GamarraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ear WaxDocument7 paginiEar WaxBadeth BustamanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advance Cochlear Physiology-Priagung Hayundoro 2013Document6 paginiAdvance Cochlear Physiology-Priagung Hayundoro 2013priagunghayundoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 075 - Neurology Physiology) Cerebrum - Temporal Lobe Anatomy & FunctionDocument2 pagini075 - Neurology Physiology) Cerebrum - Temporal Lobe Anatomy & Functionzayat13Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - The World Through Our SensesDocument24 paginiChapter 1 - The World Through Our SensesAlice TayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 21 NOTESDocument13 paginiClass 11 Biology Chapter 21 NOTESYashica PradhanÎncă nu există evaluări