Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Drug Information Summary
Încărcat de
Mc Crister SilangDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Drug Information Summary
Încărcat de
Mc Crister SilangDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
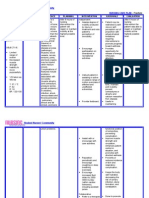
Paracetamol 1 amp Hemostan 500mg Furosemide 20mg Metronidazole 500mg Salbutamol Qualran
Drugs name Classification
Paracetamol 1 amp Non-opiod analgesic and antipyretics
Indication
Acute pain Fever
Action
Through the produce analgesia byblocking pain impulse by inhibitingsynthesis of prostaglandin in cns thatsynthesize pain receptor to stimulation
Contraindication / precautions
Anemia, cardiac & pulmonary disease. Hepatic or severe renal disease. Liver warning & disease. Other medicines containing paracetamol. Concomitant use of warfarin.
Adverse reaction Patient/ family teaching
Allergic skin reactions & gi disturbances. Instruct patient to take with meals Have a plenty of water when taking this drug
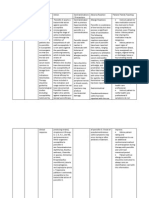
Drugs name Classification Indication
Action
Contraindication / precautions
Adverse reaction
Patient/ family teaching
Hemostan 500mg Antihemophilic agent Antihemorrhagic and antifibrinolytic for effective hem ostasis in varioussurgical and clinical cases, in traumatic injuries, post-tooth extraction and other dental procedures Forms a reversible complex that displaces plasminogen formf i b r i n r e s u l t i n g i n i n h i b i t i o n o f f i b r i n o l y s i s , i t a l s o i n h i b i t s t h e p r o t e o l y t i c activity of plasmin. Not advisable to use for prolonged periods in patients predisposed tothrombosis. Not recommended for prophylaxis during pregnancy and befored e l i v e r y . O p h t h a l m i c e x a m b e f o r e a n d d u r ing therapy required if patient istreated beyond several days; caution in patients with cardiovas c u l a r , r e n a l , cerebrovascular disease Gi disorders: nausea, vomiting. Cns: anorexia, headache may appear,impaired renal insufficiency, hypotension when iv injection is too rapid Dosage modification required in patients with renal impairment Watch out for any signs of bleeding
Drugs name Classification Indication
Furosemide 20mg Electrolytic and water balance agent; loop diuretic Edema: furosemide is indicated in adults and pediatric patients for the treatment of edema associated with congestive heart failure, cirrhosis of the liver, and renal disease, including the nephrotic syndrome. Furosemide is particularly useful when an agent with greater diuretic potential is desired. Furosemide is indicated as adjunctive therapy in acute pulmonary edema. The intravenous administration of furosemide is indicated when a rapid onset of diuresis is desired, e.g., in acute pulmonary edema. If gastrointestinal absorption is impaired or oral medication is not practical for any reason, furosemide is indicated by the intravenous or intramuscular route. Parenteral use should be replaced with oral furosemide as soon as practical. Analgesics reduce natriuretic action of furosemide. Antagonises hypoglycaemic agents and drugs used for gout. Hyperglycaemia with antihypertensive agent diazoxide. Antagonises muscle relaxants. Increased risk of ototoxicity when used with aminoglycosides especially in renal impairment. May enhance nephrotoxicity of cephalosporins. Effects of antihypertensives enhanced. Action antagonised by corticosteroids. Phenytoin and indometacin may reduce effects of furosemide. Severe sodium and water depletion, hypersensitivity to sulphonamides and furosemide, hypokalaemia, hyponatraemia, precomatose states associated with liver cirrhosis, anuria or renal failure. Addison's disease. Prostatic hyperplasia. Hepatic or renal impairment, gout, dm, impaired micturition. Infusion rate should not exceed 4 mg/min to reduce the risk of ototoxicity. Monitor fluid and electrolyte balance and renal function. May lower serum levels of calcium and magnesium, thus serum levels should be monitored. Pregnancy and lactation.
Action
Contraindication / precautions
Adverse reaction
Fluid and electrolyte imbalance. Rashes, photosensitivity, nausea, diarrhoea, blurred vision, dizziness, headache, hypotension. Bone marrow depression (rare), hepatic dysfunction. Hyperglycaemia, glycosuria, ototoxicity. Rarely, sudden death and cardiac arrest. Hypokalaemia and magnesium depletion can cause cardiac arrhythmias. Instruct patient to take furosemide as directed. Take missed doses as soon as possible; do not double doses caution patient to change positions slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension. Caution patient that the use of alcohol, exercise during hot weather, or standing for long periods during therapy may enhance orthostatic hypotension instruct patient to consult health care professional regarding a diet high in potassium (see food sources for specific nutrients) advise patient to contact health care professional of weight gain more than 3 lbs in 1 day advise patient to consult health care professional before taking otc medication or herbal products concurrently with this therapy instruct patient to notify health care professional of medication regimen before treatment or surgery caution patient to use sunscreen and protective clothing to prevent photosensitivity reactions advise patient to contact health care professional immediately if muscle weakness, cramps, nausea, dizziness, numbness, or tingling of extremities occurs Emphasize the importance of routine follow-up examinations advise patients on antihypertensive regimen to continue taking medication even if feeling better. Furosemide controls but does not cure hypertension reinforce the need to continue additional therapies for hypertension (weight loss, exercise, restricted sodium intake, stress reduction, regular exercise, moderation of alcohol consumption, cessation of smoking)
Patient/ family teaching
Drugs name
Metronidazole 500mg
Classification Indication
Antimicrobial Treatment of serious abdominal infections due to susceptible anaerobic bacteria Treatment of protozoal infections e.g. Amebiasis, giardiasis, trichomoniasis
Action
Metronidazole is converted to reduction products that interact with dna to cause destruction of helical dna structure and strand leading to a protein synthesis inhibition and cell death in susceptible organisms. It is effective against a wide range of organisms including e. Histolytica, t. Vaginalis, giardia, anaerobes e.g. Bacterioides sp, fusobacterium sp, clostridium sp,peptococcus sp and peptostreptococcus sp, and moderately active against gardnerella sp and campylobacter sp. History of hypersensitivity to metronidazole or other nitroimidazole derivatives. Pregnancy (1st trimester) and lactation. Patients with cns diseases; discontinue iv therapy if abnormal neurologic symptoms occur. History of seizure disorder. Evidence or a history of blood dyscrasias; perform total and differential leukocyte counts before and after treatment. Severe hepatic impairment; monitor plasma levels. Predisposition to oedema (inj contains sodium). Prolonged use may result in fungal or bacterial superinfection.
Contraindication / precautions
Adverse reaction
Gi disturbances e.g. Nausea, unpleasant metallic taste, vomiting, diarrhoea or constipation. Furred tongue, glossitis, and stomatitis due to overgrowth of candida. Rarely, antibioticassociated colitis. Weakness, dizziness, ataxia, headache, drowsiness, insomnia, changes in mood or mental state. Numbness or tingling in the extremities, epileptiform seizures (high doses or prolonged treatment). Transient leucopenia and thrombocytopenia. Hypersensitivity reactions. Urethral discomfort and darkening of urine. Raised liver enzyme values, cholestatic hepatitis, jaundice. Thrombophlebitis (iv). advise patient to take drug with food if it causes gi upset. However, instruct him to take extended-release tablets 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals. tell patient with trichomoniasis to refrain from sexual intercourse or to have male partner wear a condom to prevent reinfection. Explain that asymptomatic sex partners should be treated simultaneously. advise patient to report fever, sore throat, bleeding, or bruising. inform patient that drug may cause metallic taste and may discolor urine deep brownishred. tell patient using topical form to clean area thoroughly with mild cleanser before use and then wait 15 to 20 minutes before applying drug. Tell her she may apply cosmetics to skin after applying drug; with topical lotion, instruct her to let skin dry at least 5 minutes before applying cosmetics. tell female patient to consult prescriber if she is pregnant or plans to become pregnant. as appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, tests, and behaviors mentioned above.
Patient/ family teaching
Drugs name Classificati on
salbutamol Bronchodilator (therapeutic); adrenergics (pharmacologic)
Indication To control and prevent reversible airway obstruction caused by asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) Quick relief for bronchospasm For the prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm Long-term control agent for patients with chronic or persistent bronchospasm Action It relieves nasal congestion and reversible bronchospasm by relaxing the smooth muscles of the bronchioles. The relief from nasal congestion and bronchospasm is made possible by the following mechanism that takes place when Salbutamol is administered. First, it binds to the beta2-adrenergic receptors in the airway of the smooth muscle which then leads to the activation of the adenyl cyclase and increased levels of cyclic- 35-adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). When cAMP increases, kinases are activated. Kinases inhibit the phosphorylation of myosin and decrease intracellular calcium. Decreased in intracellular calcium will result to the relaxation of the smooth muscle airways. Hypersensitivity to adrenergic amines, Hypersensitivity to fluorocarbons, Cardiac disease including coronary insufficiency, a history of stroke, coronary artery diseaseand cardiac arrhythmias, Hypertension ,Hyperthyroidism,Diabetes, Glaucoma, Geriatric patients older individuals are at higher risk for adverse reactions and may require lower dosage, Pregnancy especially near term, Lactation, Children less than 2 years of age because safety of its use has not been established Excess inhaler use which may lead to tolerance and paradoxical bronchospasm Nervousness, Restlessness, Tremor, Headache, Insomnia, Chest pain, Palpitations, Angina, Arrhythmias, Hypertension, Nausea and vomiting, Hyperglycemia, Hypokalemia
Contraindi cation / precaution s
Adverse reaction
Patient / family teachin g
Tell patient to swallow extended-release tablets whole and not to mix them with food. Teach patient signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reaction and paradoxical bronchospasm. Tell him to stop taking drug immediately and contact prescriber if these occur. Instruct patient to notify prescriber immediately if prescribed dosage fails to provide usual relief, because this may indicate seriously worsening asthma. Advise patient to limit intake of caffeine-containing foods and beverages and to avoid herbs unless prescriber approves. Caution patient to avoid driving and other hazardous activities until he knows how drug affects concentration and alertness. Advise patient to establish effective bedtime routine and to take drug well before bedtime to minimize insomnia. As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, foods, and herbs mentioned above.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Dementia (Course Requirement Elective)Document21 paginiDementia (Course Requirement Elective)Mc Crister SilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cholangiocarcinoma, Gallbladder Cancer, Common Bile Duct, Cystic Duct, Intrahepatic, PerihilarDocument25 paginiCholangiocarcinoma, Gallbladder Cancer, Common Bile Duct, Cystic Duct, Intrahepatic, PerihilarMc Crister Silang100% (1)
- Suddural HematomaDocument34 paginiSuddural HematomaMc Crister SilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transition To IndependenceDocument14 paginiTransition To IndependenceMc Crister SilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Document10 paginiSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- Artificial Kidney CareDocument23 paginiArtificial Kidney CareMc Crister SilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan - FractureDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan - Fracturederic95% (19)
- Normal ValuesDocument6 paginiNormal ValuesMc Crister SilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preoperative Skin PreparationDocument5 paginiPreoperative Skin PreparationMc Crister SilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- In The Totality Paradigm Rosemarie ParseDocument2 paginiIn The Totality Paradigm Rosemarie ParseMc Crister Silang43% (7)
- Gallbladder Cancer MedscapeDocument7 paginiGallbladder Cancer MedscapeMc Crister SilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- of UrinaryDocument42 paginiof UrinaryMc Crister SilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gallbladder CancerDocument4 paginiGallbladder CancerMc Crister SilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amikacin antibiotic for urinary tract infectionsDocument17 paginiAmikacin antibiotic for urinary tract infectionsMc Crister SilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan To The Client With Fractures of The Extremities and Extremities SurgeryDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan To The Client With Fractures of The Extremities and Extremities SurgeryMaria MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument36 paginiDrug StudyMc Crister SilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Same Sex MarriageDocument1 paginăSame Sex MarriageMc Crister SilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Recommendation Letter - BeverlyDocument2 paginiRecommendation Letter - Beverlyapi-355180754100% (2)
- Thesis TitlesDocument25 paginiThesis TitlesMicah Dianne DizonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group Leukemia ProjectDocument12 paginiGroup Leukemia Projectapi-194733693100% (1)
- Physician'S Order Sheet: Part of The Medical RecordDocument2 paginiPhysician'S Order Sheet: Part of The Medical RecordJewenson SalvadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breast LumpsDocument77 paginiBreast LumpsAliyah Tofani PawelloiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Halcion WebDocument125 paginiHalcion WebdrkameshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellulitis: Clinical Review: Be The First To CommentDocument9 paginiCellulitis: Clinical Review: Be The First To CommentAnonymous 1nMTZWmzÎncă nu există evaluări
- HYPERBILIRUBINEMIADocument30 paginiHYPERBILIRUBINEMIAAlexisRoyE100% (1)
- FCRSDocument13 paginiFCRSDr FPÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Prime PPPDocument17 paginiLiver Prime PPPParimal P. DubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mini Mental State Examination Cognitive FIM Instrument and The Loewenstein Occupational Therapy Cognitive Assessment Relation To Functional Outco PDFDocument4 paginiMini Mental State Examination Cognitive FIM Instrument and The Loewenstein Occupational Therapy Cognitive Assessment Relation To Functional Outco PDFDamira HalilovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventilator Draeger Evita V300 - Spesifikasi Teknis PDFDocument4 paginiVentilator Draeger Evita V300 - Spesifikasi Teknis PDFArifyadin SudonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensory Integration Therapy ExplainedDocument15 paginiSensory Integration Therapy Explainedakanksha nagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regen EndoDocument88 paginiRegen EndoJitender ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sirosis HepatisDocument65 paginiSirosis HepatisIntania Fadilla100% (1)
- SRBIJA BANJE-Spas and Health ResortsDocument30 paginiSRBIJA BANJE-Spas and Health ResortsandrejnigelÎncă nu există evaluări
- SYNOPSISDocument13 paginiSYNOPSISJoseph KuruvilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PitocinDocument5 paginiPitocinWilliam BrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crohn's Disease and TPNDocument13 paginiCrohn's Disease and TPNAira Vida TesoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attachment ReportDocument23 paginiAttachment Reportalex Villnet96% (24)
- Body Image Disturbance NCPDocument2 paginiBody Image Disturbance NCPPaulo de JesusÎncă nu există evaluări
- First International congress on clinical Hypnosis & Related Sciences programDocument91 paginiFirst International congress on clinical Hypnosis & Related Sciences programGolnaz BaghdadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABG EquipmentDocument43 paginiABG EquipmentMohammed NaguibÎncă nu există evaluări
- HematologyDocument100 paginiHematologyerzaraptorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Purpose, Problem StatementsDocument4 paginiResearch Purpose, Problem StatementsManish Kohli100% (1)
- Cer 212 Urinary Incontinence Updated 1Document643 paginiCer 212 Urinary Incontinence Updated 1rahmat_husein1Încă nu există evaluări
- Common drugs in the labor roomDocument4 paginiCommon drugs in the labor roomBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Meta Analysis of Play Therapy Outcomes PDFDocument16 paginiA Meta Analysis of Play Therapy Outcomes PDFAron MautnerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rsemue Video IsiDocument5 paginiRsemue Video IsiPuvaan RaajÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Person Environment Occupation (PEO) Model of Occupational TherapyDocument15 paginiThe Person Environment Occupation (PEO) Model of Occupational TherapyAlice GiffordÎncă nu există evaluări