Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Transformata Fourier
Încărcat de
Florentina PaicaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Transformata Fourier
Încărcat de
Florentina PaicaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Prof. dr. ing.
Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
CAP 4.
TRANSFORMAEA FOURIER N
STUDIUL SEMNALELOR
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
Transformarea Fourier (TF)
Motivaie
- TF reprezint o legtur ntre dou reprezentri diferite ale unui acelai obiect:
Pt. un semnal, TF leag reprezentarea n domeniu timp cu cea n domeniu frecven
Pt. un proces aleator, TF leag densitatea de probabilitate de funcia caracteristic
Pt. o structur repetitiv (de ex punctele dintr-o reea cristalin), TF leag
reprezentarea din spaiul real de cea din spaiul reciproc (spaiu k)
- TF permite descrierea compoziiei spectrale a unui semnal ntr-o astfel de form
nct face posibil att estimarea efectelor aplicrii unui proces selectiv n
frecven (prin intermediul unui filtru)
- TF permite realizarea mai simpl a unor operaii (algebrizeaz derivarea,
integrarea, convoluia, corelaia)
- TF permite vizualizarea direct sau extragerea unor parametri spectrali de
interes (band ocupat, repartiia spectral a energiei, amplitudinea diverselor
componente spectrale, etc)
- TF este legat de unele procese perceptuale (ex. audio)
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
Interpretare: Densitate spectral de amplitudine
4.1 Transformarea Fourier a
semnalelor funcii din L
1
Observaie: Convergena este asigurat
- Definiie: Pentru definim transformata Fourier prin
( )
1
f t L e
( ) ( )
cu e ,
Def
j t
f t t F d
e
e e
= e
}
( )
F e
( ) ( )
F
f t F e
( ) ( ) ( )
1
e ,
f L
j t
f t f t f t dt
e
e
= <
}
( ) { } ( )
f t F e = F
Fie unde ( ) ( ) ( )
2
1
Def
T
t f f t p t = ( )
2
2 2
T
T T
p t t t o o
| | | |
= +
| |
\ . \ .
Construim semnalul ( ) ( )
1
, 0
T
k
f t kT f t T
=
= >
Dar ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
0 0
0 0 0
/ 2
1
/ 2
1
e , e
2
,
SF
n n
n
T
j t j t
T
T
C n C n
T
f t f t dt
T
e e
t
e e e
=
= = =
}
La limit, dac atunci T ( ) ( )
0 1 0
2
, , t d n f f t
T
t
e e e e =
( ) ( )
e
2
j t
d
f dt t C
e
t
e
e
=
}
( ) ( )
2
C
d
F e
t
e
e =
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
Problem: Se poate recupera din ?
Condiii suficiente (A, B sau C)
4.1 Transf.
Fourier n L
1
( )
( ) ( )
0 0
0
0
lim
2
f t f t
f t
c
c c
+ +
=
( ) ( ) ( )
0
a..
sin
0, lim 2 0
u
f t u f t u f t du
u
e
o
o
e
( - > + =
}
Teorema de inversiune
( )
f t
( )
F e
T1 (inversiune): Dac n orice punct de discontinuitate de spea I, se
consider
0
t
i n orice punct dat se satisface condiia
t e
atunci ( ) ( )
VP
1
2
j t
f t F e d
e
e e
t
=
}
( ) ( ) VP lim
f
A
A A
De
g x dx g x dx
=
} }
( ) ( ) ( )
0
0
0
VP lim
D
t
t
ef
g x dx g x dx g x dx
c
c c
+
(
+
(
=
} } }
A) are variaie mrginit pentru
f
| |
, t t t o o e +
B)
( ) ( ) ( |
, 0, 0,1
r
f t f t M cu M r t o t t < + s > e
C) este derivabil n f t
( ) ( )e
j t
F f t dt
e
e
=
}
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
- Obsevaii:
Imaginea Fourier este n general o funcie complex
( ) ( ) ( )
r i
jF F F e e e = +
4.1 Transf.
Fourier n L
1
Teoreme. Proprieti
( ) { } ( )
( ) { } ( )
Re
Im
Not
ot
r
N
i
F
F
F
F
e
e
e
e
( ) ( )
( )
e
j
F M
e
e e
+
=
( ) ( )
( ) { } ( ) arg
Not
Not
M F
F
e
e e
e
+
=
- T2: este funcie continu (Fourier) i
( )
F e
( )
lim 0 F
e
e
=
Obs: Chiar dac nu rezult c
( )
1
f t L e
( )
1
F L e e
Exemplu: Fie
( ) ( )
1
cu e , 0
t
f t t L
o
o o
e = > ( )
1
F
a j
e
e
=
+
1
L e
- T3 (Proprieti asimptotice):
Dac are variaie mrginit n intervalul atunci transformata sa
Fourier tinde la pentru cel puin ca (Riemann)
0
( )
f t ( )
,
e
1/ e
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.1 Transf.
Fourier n L
1
Teoreme. Proprieti
- T4 (Teorema conjugrii):
Dac atunci
( ) ( )
F
f t F e ( ) ( )
* * F
f t F e
Dem: ( ) ( )
1
e
2
j t
f t F d
e
e e
t
=
}
( ) ( )
* *
1
e
2
j t
f t F d
e
e e
t
=
}
( )
*
1
e
2
j t
F d
e
e
e
e e
t
=
}
Observaie: Dac atunci (modul par, arg. impar)
( )
f t e
( ) ( )
*
F F e e =
- T6 (Simetria par pentru semnale reale):
( )
F e e Dac i atunci
( ) ( )
F
f t F e e ( ) ( )
f t f t =
- T5 (Schimbarea de variabil afin):
Dac atunci
( ) ( )
F
f t F e
{ } ( )
1
\ 0 ,
F
a f at F
a a
e
| |
e
|
\ .
Caz particular
( ) ( )
1
F
a f t F e =
( ) ( ) ( )
r i
F F jF e e e = +
- T7 (Simetria impar pentru semnale reale):
( )
F j e e Dac i atunci
( ) ( )
F
f t F e e ( ) ( )
f t f t =
( ) ( ) ( )
r i
F F jF e e e = +
t
e
t
e e
( ) F e
*
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.2 Transformarea Fourier a
semnalelor funcii din L
2
- Definiie: Pentru definim transformata Fourier prin
( )
2
L f t e
( ) ( )
VP cu e ,
Def
j t
f t F dt
e
e e
= e
}
( )
F e
Observaie: Se poate demonstra c dac atunci
( )
2
f t L e
( )
2
F L e e
( ) f t
2
L 2
L
( ) F e
F
Teorema de inversiune: ( ) ( )
VP
1
e
2
j t
d t F f
e
e e
t
=
}
- T8 (Teorema simetriei):
Dac atunci
( ) ( )
F
f t F e
( ) ( )
2
F
F t f t e
Dem: ( ) ( )
1
e
2
j t
f t F d
e
e e
t
=
}
( ) ( ) e 2 c.c.t.d.
t
j t
t
F d f t
e
e
e
e e t
=
}
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.2 Transf.
Fourier n L
2
Teoreme. Proprieti
- T9 (Teorema ntrzierii):
Dac atunci
( ) ( )
F
f t F e ( ) ( )
0
0 0
, e
F j t
t R f t t F
e
e
e
- T10 (Teorema deplasrii):
Dac atunci
( ) ( )
F
f t F e ( ) ( )
0
0 0
, e
j t F
R f t F
e
e e e e
dac derivatele satisfac condiiile de existen pentru transformata Fourier
!! T11 (Teorema derivrii):
Dac atunci
( ) ( )
F
f t F e
( )
( ) ( )
n
n
n
F
d f t
j F
dt
e e
Dac i atunci
( ) ( )
F
f t F e ( ) ( ) ( )
1
De
F
f
t
s t f d F
j
t t e
e
=
}
!! T12 (Teorema integrrii):
( )
0 0 F =
Dem. cond.: Din ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
1,2
0 0 0 s s L s f d F t t
= e = = =
}
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.2 Transf.
Fourier n L
2
Teoreme. Proprieti
( )( ) ( ) ( )
1 2 1 2
* f f t f f t d t t t
=
}
Dem: ( )( ) ( ) ( )
( )
1 2 1 2
1
* e
2
j t
f f t f F d d
e t
t e e t
t
=
} }
- T14 (Comportarea asimptotic):
Dac au variaie mrginit pentru atunci
( )
( )
, 0,1...
k
f t k n =
t e
( )
1
pt.
1
,
n
F O e e
e
+
| |
= |
|
\ .
( ) ( )
2 1
1
e e
2
j t j
F f d d
e et
e t t e
t
=
} }
( ) ( )
2 1
1
e
2
j t
F F d
e
e e e
t
=
}
=
Dac atunci ( ) ( )
1,2 1,2
F
f t F e
( ) ( ) ( )( )
1 2 1 2
1
*
2
F
f t f t F F e
t
!! T16 (Teorema convoluiei n frecven):
Dac atunci ( ) ( )
1,2 1,2
F
f t F e
( )( ) ( ) ( )
1 2 1 2
*
F
f f t F F e e
!! T15 (Algebrizarea convoluiei):
Dac atunci
( ) ( )
F
f t F e
!! T13 (Teorema derivrii n domeniul frecven):
( ) ( )
( )
F
n
n
n
d F
jt f t
d
e
e
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.2 Transf.
Fourier n L
2
Teoreme. Proprieti
( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
1 2
1 2 1 2
*
Not Def
f f
f f r f f t d t t t t t
= = +
}
Dem:
( )
( ) ( ) ( )
( )
1 2 1 2
1
* e
2
j t
f f f t F d dt
e t
t e e
t
+
=
} }
( ) ( )
2 1
1
e e
2
j j t
F f t dtd
et e
e e
t
=
} }
( ) ( )
2 1
1
e
2
j
F F d
et
e e e
t
=
}
=
Dac atunci
( ) ( )
F
f t F e ( ) ( ) ( )
sin
*
a
F
at
f t F p
t
e e
t
Dac atunci ( ) ( )
1,2 1,2
F
f t F e
( )
( ) ( ) ( )
1 2 1 2
*
F
f f t F F e e
!! T17 (Algebrizarea corelaiei):
- Corolar:
( ) ( )
2 2
1
2
f t dt F d e e
t
=
} }
( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
* * *
1 2 1 2 1 2
*
F
f f f t f t dt F F t t e e
= +
}
- T18 (Teorema energiei Rayleigh):
Dem: Vezi corolarul pentru i
( ) ( ) ( )
1 2
f t f t f t = = 0 t =
- T19 (Trunchierea unei densiti spectrale):
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.3 Transformarea Fourier a
semnalelor funcii din S
Observaii: Se pot demonstra:
- Problem: Operatorul Fourier transform spaiul n el nsui dar, prin
derivare sau nmulire de polinoame semnale din pot s nu rmn n
2
L
2
L
2
L
- Soluie posibil
Spaiul S Spaiul al funciilor rapid descresctoare la zero
C
( )
( )
( )
de ordin polinom ( ) , ,
m
k
m
m f S t t P P f t k e e < e e e
Transformata Fourier i Teorema de inversiune sunt valabile i pentru semnale din S.
Toate teoremele prezentate anterior rmn valabile
( ) ( )
t F S S f e e e Dac
Spaiul
2
D L S c c
- Dezavantaj: Sunt multe semnale uzuale care nu fac parte din !
S
( ) f t
S
S
( ) F e
F
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.4 Semnale ca distribuii
(temperate) din S
Observaie: Definiia este coerent
- Definiie: Fie funcia temperat
( ) ( ) ( )
*
cu prop a.. fixat . : , 0 1 ,
n
f n f M t M t - e > s +
Definim distribuia temperat regulat (DTR) (asociat funciei temp. ) ' f S e f
( ) ( )
, , =
Def
t f S t dt f | | |
e
}
( )
( )
*
2
a.. , , ' 0 '
1
n
t
S n M M
t
|
|
+
e e - > s
+
( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( )
2 1 2
Atunci
' '
1
1 1
n
n
f t t L
M MM
M t
t t
|
+
s =
+
e +
+
Funcii bune
Distribuii
1
loc
L
' D
Funcii
DR
DS
( ) ( ) , f f t t dt | |
=
}
Funcii bune
Distribuii
temperate
' S
Funcii
DTR
DTS
( ) ( ) , f f t t dt | |
=
}
Funcionalele liniare continue prin iruri definite pe formeaz
spaiul al distribuiilor temperate
S
' S
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.4 Semnale
distribuii n S
Teoreme. Proprieti
Da, dac se ndeplinete una din condiiile:
- T20 (Schwartz): Funciile continue temperate pot fi derivate n sens
distribuional de oricte ori i conduc la distribuii temperate
- Exemplu: Funcia este funcie temperat. Prin derivare distribuional se
obin ( ) ( ) ( ) , , ' , ... t t t o o o
( ) t t o
- T21 (Schwartz): O distribuie temperat rmne n dup:
derivari de orice ordin
nmuliri cu funcii temperate din clasa
schimbri de variabil afin
' S
( ) , , 0, ' a b a f at S b e = + e
C
( )
pt. , ' '
n
f n f S S e e e
- T22 : Dac atunci ? ' , f g S e ' * f g S e
sau au suport compact
iar
i au suport pozitiv
f g
' f S e g S e
f g
- Observaie: Aparin lui
Funciile din , i (ca DTR)
Constantele, , polinoamele (ca DTR)
Orice distribuie din i cu suport compact (ex: )
1
L
( ) t o
2
L
( )
k
P t
' D ( )
( )
( ) ,
k
t t o o
' S
S
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu
Justif.: Fie o funcie temperat, pt. care exist
imaginea sa Fourier, presupus a fi tot o funcie
temperat.
Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.5 Transformarea Fourier a
semnalelor distribuii (temperate) din S
Observaie: Aceast definiie reprezent o
extindere a celei corespunztoare distribuiilor
temperate regulate (DTR)
( ) ( )
?
e
j t
f F t dt
e
e
=
}
- ntrebare: Pentru coerena transformrii Fourier putem accepta ca definiie
(formal), pentru semnale din ?
' S
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) , e
j t
F f d dtd F t
e
| e | e | e e e e e
= =
} } }
f
( ) ( )
?
sau echivalent dei ?? , e , e
j t j t
f F t S
e e
e
= e
- Definiie: Pentru definim a.. ' f S e
( )
' F S e e
pentru orice (pt. care
( )
S t | e
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
, ,
Def
f t F t | e e = u
tim ca exist cu )
( ) ( )
F
t | e u
( )
S e u e s se respecte relaia
( ) ( )
F
f t F e
F
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) , dt t t f t t f
= u = u
}
( ) ( )e
j t
d dt f t
e
e | e
=
} }
=
F
Funcii test
Frecven
u
| f
Timp
Distribuii
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.5 Transformata
Fourier pt. semnale
distribuii n S
Teoreme. Exemple
- Exemplu: ( ) { }
? t o = F
- T23: Pentru rezult . Sunt valabile teoremele prezentate anterior ' f S e ' F S e
Notm i considerm
( ) ( ) ( )
F
f t t F o e =
( ) ( ) .
F
t S S | e e u e Plecnd de la definiie putem scrie
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
0
, , 0 e 1,
Def t
j t
F t t t dt t dt d
e
e | e o | | | e e | e
= u = u = = = =
} } }
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) , ,
Def
f t F t | e e = u
( )
1
F
t o
Observaie: Formal acceptndu-se drept
funcie test (din S).
( ) ( ) ( ) e 1 , e
j t j t
F t dt t
e e
e o o
= = =
}
e
j t e
Explicaie: Distribuia Dirac este cu suport punctual
- ntrebare: Pentru coerena transformrii Fourier putem accepta ca definiie
(formal), pentru semnale din ?
' S
( ) ( )
?
sau echivalent dei ?? , e , e
j t j t
f F t S
e e
e
= e ( ) ( )
?
e
j t
f F t dt
e
e
=
}
- Exemplu: S se demonstreze teorema simetriei
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
2
F
F
f t F
F t f
e
t e
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) , ,
Def
F
f t F F f t t e e | e = u
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
, , ,
,
?
2 2 ,
Def Def t
F
t
F t F t G t F
f t t
G
f
e
e
| e e e e
t| | e
e
t e
=
=
= u = u =
= =
=
- Exemplu:
( )
1 2
F
to e
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.5 Transformata
Fourier pt. semnale
distribuii n S
Teoreme. Exemple
- Exemplu: ( ) { }
sgn ? t = F
Notm
( ) ( ) ( ) sgn
F
f t t F e =
( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( )
in '
in ' in ' in '
0
0
lim sgn 2 lim sin
cos cos
1 2 1
2 lim 2 lim 2
A A
j t
A A A
A
A
S S
A
S
S
F t e dt j t dt
t A
j j jVP VP
j
e
e e
e e
e e e e
= =
| | | |
|
=
= =
|
\ . \
=
.
} }
- T24: Dac este o funcie temperat, atunci f
( ) ( ) ( )
VP n '
j t
F f t e dt S
e
e
=
}
- ntrebare: Pentru coerena transformrii Fourier putem accepta ca definiie
(formal), pentru semnale din ?
' S
( ) ( )
?
sau echivalent dei ?? , e , e
j t j t
f F t S
e e
e
= e ( ) ( )
?
e
j t
f F t dt
e
e
=
}
( )
.
VP
2 1 2
sgn
Not tolerat
F
t
j j e e
| |
=
|
\ .
Observaii: n spaiul (categoria cea mai larg de semnale):
'
S
Se lucreaz cu integrale n sensul valorii principale
Se poate opera formal cu ca funcie de test, n mod deosebit n cazul
distribuiilor cu suport compact
e
j t e
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.5 Transformata
Fourier pt. semnale
distribuii n S
Teoreme. Exemple
- T25 (Teorema integrrii variant cu grad de generalitate mai ridicat) :
- Exemple:
0
?
F j t
e
e
( )
0
cos ?
F
t e
( )
0
sin ?
F
t e
( )
?
F
t o
?
F
t
( )
0
0
2
F j t
e
e
to e e
( ) ( ) ( )
0 0 0
cos
F
t e to e e to e e + +
( ) ( ) ( )
0 0 0
sin
F
t
j j
t t
e o e e o e e +
( ) ( ) ( )
VP
1 1 1
F
t
j j
o to e to e
e e
| |
+ = +
|
\ .
2
2
F
t
e
Fie i
( ) ( )
F
f t F e ( ) ( ) ( )
F
t
g t f d G t t e
=
}
Se observ c ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) *
t
g t f t f g t d f d o t t t t t
= = =
} }
Rezult dac exist ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) VP VP
1 1 1 1
0
F
g t F F F
j j
e to e e t o e
e e
(
| | | |
+ = +
| | (
\ . \ .
( ) 0 F
( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
VP dac
VP dac
1 1
0 0
1 1
0 0 0
F
t
F F
j
f d
F F F
j
e
e
t t
e t o e
e
| |
=
|
\ .
| |
+ =
|
\ .
}
( )
( )
( )
( )
( ) ( ) ( )
dac
dac
0 0
0 0 0
F
t
F
F
j
f d
F
F F
j
e
e
t t
e
t o e
e
+ =
}
- Observaie: Distribuia Dirac este element neutru pt. convoluie ( )( ) ( )( ) ( )
* * f t f t f t o o = =
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.6 Transformarea Hilbert
( ) ( ) ( )
sgn
F
f t j F e e
( ) Deoarece VP rezult succesiv
2 1
sgn
F
t
j e
| |
|
\ .
- Definiie: Fie semnalul real pentru care .
( )
f t e
( ) ( )
F
f t F e
Definim transformata Hilbert a semnalului i notm cu semnalul care
are transformat Fourier
( )
f t ( )
f t
( )
F
f t ( ) ( )
sgn j F e e
( ) ( )
F
f t F e
( )
sgn j e
?
( ) ( ) VP i respectiv VP
2 1 1 1
2 sgn sgn
F F
j
j t t
t e e
t
| | | |
| |
\ . \ .
( ) ( )
( )
VP VP
1 1 1
*
f
f t f t d
t t
t
t
t t t
| |
= =
|
\ .
}
1
*
t t
Transformarea Hilbert elimin componenta continu i rotete toate celelalte
componentele spectrale cu (defazeaz cu )
90 / 2 t
Observaie:
( ) ( ) ( )
( )
( )
2
2
0
sgn 0 0
0
j
j
F
e F
f t j F
e F
t
t
e e
e e e
e e
>
= =
<
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.7 Semnalul analitic
( ) ( ) ( )
e
a
D f
f t f t j f t = +
( ) ( ) { }
Re
a
f t f t =
- Definiie: Pentru un semnal real , semnalul analitic se definete
ca
( )
a
f t
( )
f t e
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) F 1 sgn =2F
F
a
f t e e e o e ( +
Semnalul analitic are densitatea spectral nul la
frecvene negative
Observaie:
( ) ( )
0
cos f t t e =
- Exemplu: S se determine semnalul analitic pentru
( ) ( )
0
sin f t t e = ( )
0
j t
a
f t e
e
=
t
e
t
e e
( ) F e
t
e
e
( )
a
F e
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.8 Transformata Fourier a semnalelor
periodice (n S)
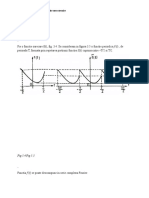
( ) ( ) ( ) | ) , supp 0,
T
k
f t f t kT f t T
=
= c
Fie semnalul periodic
- Exemplu: Imaginea Fourier pentru distribuia Dirac periodic
( ) ( )
0
0 0
2
e , cu
jn t
T
n
C n f t
T
e
t
e e
=
= =
Seria Fourier ataat este
( ) ( ) ( )
0 0
2
T
F
n
f t n C n to e e e
Prin aplicarea transformatei Fourier se obine
( ) ( )
0
2
j F n T
T
n n
t e n
T
e
t
o o e e
= =
=
( ) ( ) ( )
0
1
e
Def
jn t
T
n
S
T
F
n
f t t t nT
T
e
o o
= =
= = =
- T24 (Teorem de calcul pt. coef. seriei Fourier):
( ) ( ) ( )
0
0
e
SFC
jn t
T
k n
C n f t f t kT
e
e
= =
= =
Fie semnalul periodic
Dac atunci ( ) ( )
F
f t F e
( ) ( )
0
0
1
F
n
n
T
C e
e e
e
=
=
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( )
*
T
T
n
n
f t nT
f t n
f t t
f t T
o t o
=
=
= = -
= =
( ) ( ) ( )
0
2
T
F
n
f t F n
T
t
e o e e
( ) ( )
0 0
2
n
F n n
T
t
o e e e
=
=
( ) ( )
0 0
2
n
C n n t o e e e
=
=
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu
s
T
t
T t
( ) f t
2
s
T 2
t
T
0
f
1
f
2
f
1
f
2
f
Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.9 Teorema eantionrii
pe care l eantionam cu perioada , pt. care
s
T
( ) ( )
sinc
2
s
n
n s
t nT f f t
e
=
(
=
(
( ) ( ) ( )
cu , 0,
M
F
F f t F e e e e = >
Dem.: Periodizm spectrul semnalului obinnd
( ) f t
- Formulare: Fie un semnal de band limitat la ( )
f t
M
e
2
2
s
s M
T
e e
t
> =
t
( ) f t
M
e
M
e e
( ) F e
F
Atunci
( ) ( )
s
n
G F n e e e
=
=
unde
2
s
jn
n
S
n
F
e
t
e
e
=
= I
( )
2
1 M
s
M
Def jn
n
s
F e d
t
e
e
e
e
e e
e
I =
}
( )
2
s
s
f nT
t
e
=
( ) e
s
jnT
SF
s
n
n
f G T
e
e
=
=
e
s
n n
jnT
n
n s
f T
e
=
=
period. 2
s M
e e =
M
e
M
e e
( ) G e
s
e
M s
e e
s
e
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu
M
e
M
e e
( ) G e
s
e
M s
e e
s
e
( )
1
p
e
e
1
e
s
T
t
T t
( ) f t
2
s
T 2
t
T
0
f
1
f
2
f
1
f
2
f
Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.9 Teorema eantionrii
pe care l eantionam cu perioada , pt. care
s
T
( ) ( )
sinc
2
s
n
n s
t nT f f t
e
=
(
=
(
( ) ( ) ( )
cu , 0,
M
F
F f t F e e e e = >
Dem.: Periodizm spectrul semnalului obinnd
( ) f t
- Formulare: Fie un semnal de band limitat la ( )
f t
M
e
2
2
s
s
M
T
e e
t
> =
t
( ) f t
M
e
M
e e
( ) F e
F
Atunci
1
2
s
e
e =
( ) e
s
jn
s
n
n
T
f G T
e
e
=
=
period. 2
s M
e e >
Cum putem recupera semnalul iniial ?
( ) ( ) ( )
1
filtrare F G p
e
e e e =
FTJ cu
1 M s M
e e e e s s
M
e
M
e e
( ) F e 1
F
t
( ) f t
( ) ( )
1
e
s
j T
s n
n
n
p T f F
e
e
e e
=
=
( )
1
1
sin
F
t
p
t
e
e
e
t
( )
1
1 1
1
sin
F
t
p
t
e
e e
e
t e
( )
1
1
1
sinc
F
t p
e
e
e e
t
( ) ( )
1
1
sinc
s s
n
n
T t nT f f t
e
e
t
=
( =
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu
s
T
t
T t
( ) f t
2
s
T 2
t
T
0
f
1
f
2
f
1
f
2
f
t
( ) f t
Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
4.9 Teorema eantionrii
pe care l eantionam cu perioada , pt. care
s
T
( ) ( )
sinc
2
s
n
n s
t nT f f t
e
=
(
=
(
( ) ( ) ( )
cu , 0,
M
F
F f t F e e e e = >
Dem.: Periodizm spectrul semnalului obinnd
( ) f t
- Formulare: Fie un semnal de band limitat la ( )
f t
M
e
2
2
s
s
M
T
e e
t
> =
M
e
M
e e
( ) F e
F
Atunci
M
e
M
e e
( ) G e
s
e
M s
e e
s
e
1
2
s
e
e =
( ) e
s
jn
s
n
n
T
f G T
e
e
=
=
period. 2
s M
e e >
Cum putem recupera semnalul iniial ?
( )
1
p
e
e
1
e
( ) ( ) ( )
1
filtrare F G p
e
e e e =
FTJ cu
1 M s M
e e e e s s
M
e
M
e e
( ) F e 1
F
t
( ) f t
Varianta alternativ
1
F
( ) ( )
s s
n
n
g t T t f nT o
=
=
s
T
t
T t 2
s
T 2
t
T
( ) ( )
s s
n
n
f g t T t nT o =
( ) ( ) ( )
1
1
filtrare * sinc g t f t t
e
e
t
=
( )
1
1
1
sinc
F
t p
e
e
e e
t
( ) ( )
1
1
sinc
s s
n
n
T t nT f f t
e
e
t
=
( =
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu
s
T
t
T t
( ) f t
2
s
T 2
t
T
0
f
1
f
2
f
1
f
2
f
s
T
t
T t
( ) f t
2
s
T 2
t
T
0
f
1
f
2
f
1
f
2
f
t
( ) f t
Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
pe care l eantionam cu perioada , pt. care
s
T
( ) ( )
sinc
2
s
n
n s
t nT f f t
e
=
(
=
(
( ) ( ) ( )
cu , 0,
M
F
F f t F e e e e = >
Observaie: La limit, pt. evitarea alierii spectrale 2
s M
e e =
- Formulare: Fie un semnal de band limitat la ( )
f t
M
e
2
2
s
s
M
T
e e
t
> =
M
e
M
e e
( ) F e
F
Atunci
M
e
M
e e
( ) G e
s
e
M s
e e
s
e
1
2
s
e
e =
period. 2
s M
e e >
( )
1
p
e
e
1
e
( ) ( ) ( )
1
filtrare F G p
e
e e e =
M
e
M
e e
( ) F e 1
F
t
( ) f t
1
F
s
T
t
T t 2
s
T 2
t
T
( ) ( )
s s
n
n
f g t T t nT o =
( ) ( ) ( )
1
1
filtrare * sinc g t f t t
e
e
t
=
4.9 Teorema
eantionrii
Comentarii privind frecvena de
eantionare
M
e
M
e e
( ) G e
s
e s
e
s
T
t
T t
( ) f t
2
s
T 2
t
T
0
f
1
f
2
f
1
f
2
f
( )
1
p
e
e
period. 2
s M
e e =
Prof. dr. ing. Cristian Negrescu
M
e M
e e
( ) G e
s
e
s
e
M
e
M
e e
( ) G e
s
e s
e
s
T
t
T t
( ) f t
2
s
T 2
t
T
0
f
1
f
2
f
1
f
2
f
s
T
t
T t
( ) f t
2
s
T 2
t
T
0
f
1
f
2
f
1
f
2
f
s
T
s
T t
( ) f t
2
s
T 2
s
T
0
f
1
f
2
f 1
f
2
f
t
( ) f t
Universitatea Politehnica din Bucureti
pe care l eantionam cu perioada , pt. care
s
T
( ) ( )
sinc
2
s
n
n s
t nT f f t
e
=
(
=
(
( ) ( ) ( )
cu , 0,
M
F
F f t F e e e e = >
Observaie: Ce se ntmpl dac !?! 2
s M
e e <
- Formulare: Fie un semnal de band limitat la ( )
f t
M
e
2
2
s
s
M
T
e e
t
> =
M
e
M
e e
( ) F e
F
Atunci 1
2
s
e
e =
period. 2
s M
e e =
( ) ( ) ( )
1
filtrare F G p
e
e e e =
1
e
1
e e
( ) F e 1
F
t
( ) f t
( ) f t
1
F
( ) ( ) ( )
1
1
filtrare * sinc g t f t t
t
e
e
=
4.9 Teorema
eantionrii
Comentarii privind frecvena de
eantionare
( )
1
p
e
e
period. 2
s M
e e <
s
T
s
T t
( ) f t
2
s
T 2
s
T
0
f
1
f
2
f 1
f
2
f
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
1
1
* sinc g t t f f t t
e
e
t
= =
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
1
F p G F
e
e e e e = =
Aliere spectral !
(ntoarcerea spectrului)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 2 Analiza Armonica - Serii FurierDocument2 pagini2 Analiza Armonica - Serii Furieradrianmarian1994Încă nu există evaluări
- Analiza Semnalelor in Domeniul Frecventa PDFDocument41 paginiAnaliza Semnalelor in Domeniul Frecventa PDFMoti PuturosulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cap5 Transformata LaplaceDocument27 paginiCap5 Transformata LaplaceKta Cata100% (1)
- Serii Fourier TrigonometriceDocument39 paginiSerii Fourier TrigonometriceIL Kook SongÎncă nu există evaluări
- ModulatiaDocument45 paginiModulatiaOana ArisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matematica DiscretaDocument3 paginiMatematica DiscretaVasile MunteanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cartea Lui HALANAYDocument252 paginiCartea Lui HALANAYAlexandraAndreea100% (1)
- Curbe În Spațiu Si Reprezentările Lor-TeoriaDocument8 paginiCurbe În Spațiu Si Reprezentările Lor-TeoriaPetrica MarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Serii Taylor+ExtremeDocument7 paginiSerii Taylor+ExtremeMadalina PătruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semnale Si SistemeDocument100 paginiSemnale Si SistemefasolăiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformata LaplaceDocument28 paginiTransformata LaplaceKis ZsomborÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scs2 1Document8 paginiScs2 1Sebastian NicolaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esantionare DiscretizareDocument31 paginiEsantionare DiscretizareLeulinaripatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformata LaplaceDocument11 paginiTransformata LaplaceDaniela DraganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cursul Meu 6 .Transformata FourierDocument37 paginiCursul Meu 6 .Transformata FourierVadim EriomencoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformata FourierDocument5 paginiTransformata Fourieradi10kÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elemente de Procesare Digitala A Semnalelor: A) Aplicaţii SpaţialeDocument41 paginiElemente de Procesare Digitala A Semnalelor: A) Aplicaţii Spaţialeoni_centÎncă nu există evaluări
- Convolutie Si CorelatieDocument9 paginiConvolutie Si CorelatieFlorentina PaicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cap6 6.2.transformata FourierDocument6 paginiCap6 6.2.transformata FourierKta Cata100% (2)
- TAPDS Curs 1 IntroducereDocument48 paginiTAPDS Curs 1 IntroducereMarius FerdyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Captiol 1 Semnale PeriodiceDocument23 paginiCaptiol 1 Semnale PeriodiceAndrei Cristian LeonteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semnale Si Sisteme DiscreteDocument34 paginiSemnale Si Sisteme DiscreteAndreea OrbanÎncă nu există evaluări
- UlarucondescuDocument6 paginiUlarucondescuContoloru CostinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cap6 6.1.serii FourierDocument10 paginiCap6 6.1.serii FourierKta CataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Serii Fourier, MatematicaDocument5 paginiSerii Fourier, MatematicaAngela MateescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformata LaplaceDocument6 paginiTransformata LaplaceHinda RazvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1109 Polinoame TaylorDocument9 pagini1109 Polinoame TaylorCrina LazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cap 7Document20 paginiCap 7ionita_02Încă nu există evaluări
- Serii Fourier. Transformata FourierDocument4 paginiSerii Fourier. Transformata FourierBogdan AlexandruÎncă nu există evaluări
- TSRA Curs2Document8 paginiTSRA Curs2Alexandru BocoșÎncă nu există evaluări
- TScurs 14Document14 paginiTScurs 14Crismada DanÎncă nu există evaluări
- L4 - Laborator - Semnale v2Document8 paginiL4 - Laborator - Semnale v2Ionut AndreiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminarul 1Document9 paginiSeminarul 1Tatarus Marius Marian100% (1)
- Saapi 2 Imagini FFTDocument79 paginiSaapi 2 Imagini FFTNTRBTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regimul Periodic Nesinusoidal (Deformant)Document17 paginiRegimul Periodic Nesinusoidal (Deformant)emilfrancuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 STMM Imagini FFT1Document51 pagini03 STMM Imagini FFT1Emi CocanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrotehnica Si Masini Electrice Power Point 3 4Document41 paginiElectrotehnica Si Masini Electrice Power Point 3 4Sebi NegruţÎncă nu există evaluări
- Referat MA MaddyDocument13 paginiReferat MA MaddyMadalina MaddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examen PSDocument9 paginiExamen PSRadu MarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probabilitati Curs 9-IIDocument6 paginiProbabilitati Curs 9-IIDan GhimpuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probleme Semnale Si SistemeDocument7 paginiProbleme Semnale Si SistemeAndreea ElenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAIMDocument14 paginiSAIMMirelusha MirelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar 1: Introducere in Teoria Semnalelor: I - Transformări Elementare Ale Semnalelor În Domeniul TimpDocument2 paginiSeminar 1: Introducere in Teoria Semnalelor: I - Transformări Elementare Ale Semnalelor În Domeniul TimpAnca FagetanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marimi Alternative: Marime Alternativa Marime Variabila, A Carei Valoare Medie Este Egala Cu ZeroDocument41 paginiMarimi Alternative: Marime Alternativa Marime Variabila, A Carei Valoare Medie Este Egala Cu ZeroValiMorarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curs5 - Masurari Acustice Si de VibratiiDocument28 paginiCurs5 - Masurari Acustice Si de VibratiiDiaconu NicoletaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TAPDS Curs 2 SISTEME MULTIRATĂ PDFDocument67 paginiTAPDS Curs 2 SISTEME MULTIRATĂ PDFMarius FerdyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Filtre AnalogiceDocument4 paginiFiltre AnalogiceFlorin BranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curs 5Document6 paginiCurs 5Mihai NastaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elemente Din Teoria SelectieiDocument7 paginiElemente Din Teoria SelectieiTiffyyyyyyyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curent AlternativDocument41 paginiCurent AlternativBotis IoanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CURS 7 - RezumatDocument59 paginiCURS 7 - RezumatDC1234Încă nu există evaluări
- Tcai Seminar Analiza FourierDocument11 paginiTcai Seminar Analiza FourierOvidiu ManolescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar 1Document23 paginiSeminar 1Lavinia CiubotariuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculul Operational (Transf.L+F)Document24 paginiCalculul Operational (Transf.L+F)Mocanu BiancaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecuatii DiferentialeDocument281 paginiEcuatii Diferentialematei5homeÎncă nu există evaluări