Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Teoria Sistemelor
Încărcat de
poparamonaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Teoria Sistemelor
Încărcat de
poparamonaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1
Seminar 3
Discretizarea funciilor continue
Problema 1
Se d funcia f : R R,
f ( t ) = ( 4 e
-t
+ t e
-2t
) 1( t )
i h > 0 un pas de discretizare.
S se discretizeze funcia folosind transformata Laplace.
Rezolvare
Se va face trecerea:
f ( t )
transIormata LapIacc
-- f ( s)
dIscrctIzarc
--f
d
( z) = r ez jf ( s)
z
z e
sh
[
poIII I( s)
Se aplica transformata Laplace i se obine:
f ( s) =
4
s + 1
+
1
( s + 2)
2
=
4s
2
+ 17s + 17
( s + 1) ( s + 2)
2
Acum se poate calcula f
d
( z) :
f
d
( z) = r ez jf ( s)
z
z e
sh
[
poIII I( s)
f
d
( z) = r ez _
4s
2
+ 17s + 17
( s + 1) ( s + 2)
2
z
z e
sh
_
p1= -1, m1=1
p2=-2, m2=2
Se calculeaz separat r ez
1
[ ] i r ez
2
[ ] :
r ez
1
[ ] = l i m
s-1
1
0!
_( s + 1)
4s
2
+ 17s + 17
( s + 1) ( s + 2)
2
z
z e
sh
_
r ez
1
[ ] =
4 17 + 17
1
z
z e
-h
= 4
z
z e
-h
r ez
2
[ ] = l i m
s-2
1
1!
d
ds
_( s + 2)
2
4s
2
+ 17s + 17
( s + 1) ( s + 2)
2
z
z e
sh
_
r ez
2
[ ] = l i m
s-2
1
1!
d
ds
_
z( 4s
2
+ 17s + 17)
( s + 1) ( z e
sh
)
_
2
r ez
2
[ ] = l i m
s-2
1
1!
_
z( 8s + 17) ( s + 1) (z e
sh
) z( 4s
2
+ 17s + 17) (z e
sh
h( s + 1) e
sh
)
( s + 1)
2
( z e
sh
)
2
_
r ez
2
[ ] =
z( 16 + 17) ( 1) (z e
-2h
) z( 16 17) (z e
-2h
h( 1) e
-2h
)
( z e
-2h
)
2
r ez
2
[ ] =
z(z e
-2h
) + z(z e
-2h
+ he
-2h
)
( z e
-2h
)
2
r ez
2
[ ] = h
z
( z e
-2h
)
2
e
-2h
f
d
( z) = r ez
1
[ ] + r ez
2
[ ] = 4
z
z e
-h
+ h
z
( z e
-2h
)
2
e
-2h
Problema 2
Se d funcia f : R R,
f ( t ) = ( 4 e
-t
+ t e
-2t
) 1( t )
i h > 0 un pas de discretizare.
S se calculeze transformata Z a funciei discretizate.
Indicaie: Trebuie s se obin acelai rezultat ca n problema 1, avnd n vedere faptul c se
dorete discretizarea aceleeai funcii.
Rezolvare
Se va face trecerea:
f ( t )
dIscrctIzarc
-- f
d
( k ) = f ( k h)
tranIormata Z
-- f
d
( z)
Funcia discretizat cu pasul h > 0 este f
d
: N R, avnd forma:
f
d
( k ) = f ( k h) = 4 e
-kh
+ k h e
-2kh
, k N
f
d
( k ) = 4 (e
-h
)
k
+ C
k
1
h (e
-2h
)
k
f
d
( k ) = 4 (e
-h
)
k
+ h C
k
1
(e
-2h
)
k-1
e
-2h
Acum se poate calcula direct f
d
( z) cu ajutorul transformatei Z:
f
d
( z) = Z[ f
d
( k ) ] = 4
z
z e
-h
+ h
z
( z e
-2h
)
2
e
-2h
3
Problema 3
Se d funcia f : R R,
f ( t ) = e
2t
( 3 si n 2t cos 2t ) 1( t )
i h > 0 un pas de discretizare.
S se discretizeze funcia folosind transformarea Laplace.
Rezolvare
Se va face trecerea:
f ( t )
transIormata LapIacc
-- f ( s)
dIscrctIzarc
--f
d
( z) = r ez jf ( s)
z
z-c
sh
[
poIII I( s)
Se aplica transformata Laplace i se obine:
f ( s) =
6
( s 2)
2
+ 4
s 2
( s 2)
2
+ 4
=
8 s
s
2
4s + 8
Acum se poate calcula f
d
( z) :
f
d
( z) = r ez jf ( s)
z
z e
sh
[
poIII I( s)
f
d
( z) = r ez _
8 s
s
2
4s + 8
z
z e
sh
_
p1= 2+2j, m1=1
p2=2-2j, m2=1
Se calculeaz separat r ez
1
[ ] i r ez
2
[ ] :
r ez
1
[ ] = l i m
s2+2j
1
0!
_( s 2 2j )
8 s
( s 2 2j ) ( s 2 + 2j )
z
z e
sh
_
r ez
1
[ ] =
( 3j + 1) z
2( z e
2h
cos2h j e
2h
si n2h)
r ez
2
[ ] = l i m
s2-2j
1
0!
_( s 2 + 2j )
8 s
( s 2 2j ) ( s 2 + 2j )
z
z e
sh
_
r ez
2
[ ] =
( 3j 1) z
2( z e
2h
cos2h + j e
2h
si n2h)
Sau se poate calcula direct:
r ez
1
[ ] + r ez
2
[ ] = 2Re [ r ez
1
] =
(6 e
2h
si n2h 2z + 2 e
2h
cos2h)z
2 ( z
2
2z cos2h e
2h
+ e
4h
)
4
f
d
( z) = r ez
1
[ ] + r ez
2
[ ] =
z [z + e
2h
( 3 si n2h + cos2h)
z
2
2z cos2h e
2h
+ e
4h
Problema 4
Se d funcia f : R R,
f ( t ) = e
2t
( 3 si n 2t cos 2t ) 1( t )
i h > 0 un pas de discretizare.
S se calculeze transformata Z a funciei discretizate.
Indicaie: Trebuie s se obin acelai rezultat ca n problema 1, avnd n vedere faptul c se
dorete discretizarea aceleeai funcii.
Rezolvare
Se va face trecerea:
f ( t )
dIscrctIzarc
-- f
d
( k ) = f ( k h)
tranIormata Z
-- f
d
( z)
Funcia discretizat cu pasul h > 0 este f
d
: N R, avnd forma:
f
d
( k ) = f ( k h) = e
2kh
( 3si n2k h cos2k h) , k N
Se poate calcula direct f
d
( z) cu ajutorul transformatei Z:
f
d
( z) = Z[ f
d
( k ) ] = 3
z e
2h
si n2h
z
2
2z cos2h e
2h
+ e
4h
z(z e
2h
cos2h)
z
2
2z cos2h e
2h
+ e
4h
f
d
( z) = Z[ f
d
( k ) ] =
3 z e
2h
si n2h z
2
+ z e
2h
cos2h
z
2
2z cos2h e
2h
+ e
4h
5
Probleme propuse
Se d funcia f : R R,
f ( t ) = ( t
2
+ 2t + 3) 1( t )
i h > 0 un pas de discretizare.
S se determine f
d
( z) prin cele dou metode prezentate.
Observaii
n cadrul problemelor, s-au folosit formulele transformatelor Laplace i Z, formula lui Euler
precum i proprietile de paritate/imparitate ale semnalelor armonice sin i cos.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Circuite ElectroniceDocument7 paginiCircuite ElectroniceMonica Cocut100% (1)
- Manual de Programare C++Document180 paginiManual de Programare C++trilulilu8988% (26)
- Subiecte AP RezolvateDocument17 paginiSubiecte AP RezolvatePusca LiviuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caracteristici de FrecvenţăDocument1 paginăCaracteristici de FrecvenţăSorin-Adrian LearschiÎncă nu există evaluări
- .2.8. Elemente de Transfer Liniare Tipizate: MM - II, Expresia Răspunsului IndicialDocument16 pagini.2.8. Elemente de Transfer Liniare Tipizate: MM - II, Expresia Răspunsului IndicialAndreeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AlgoritmicaDocument3 paginiAlgoritmicamasidana100% (1)
- Proiectarea Rețelelor de Rughiniș R.Document227 paginiProiectarea Rețelelor de Rughiniș R.poparamona100% (5)
- TSA GlobalDocument219 paginiTSA GlobalIonutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functia de Transfer - Simplificarea Schemelor BlocDocument13 paginiFunctia de Transfer - Simplificarea Schemelor BlocVladSanduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelarea Unui Sistem de Ordin II RLCDocument6 paginiModelarea Unui Sistem de Ordin II RLCGrindean OvidiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODEL Examen PCLP 2 Sesiunea Iunie 2020Document5 paginiMODEL Examen PCLP 2 Sesiunea Iunie 2020ramsesahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teoria SistemelorDocument160 paginiTeoria SistemelorCătălin VulturÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generarea Semnalelor in MatlabDocument6 paginiGenerarea Semnalelor in MatlabAlex DenisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detectia Prezentei Fetelor Umane in Imagini Folosind Retele Neuronale. Implementare in MatlabDocument21 paginiDetectia Prezentei Fetelor Umane in Imagini Folosind Retele Neuronale. Implementare in MatlabChipaila CiprianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teoria SistemelorDocument51 paginiTeoria SistemelorAlin TicanetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rezolvari Teme de Curs PDFDocument16 paginiRezolvari Teme de Curs PDFPetruta RoxanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 2 Refererat1Document7 paginiCE 2 Refererat1Carmen Mihaela100% (1)
- Fizica Automatica Anul 1Document13 paginiFizica Automatica Anul 1Alex SuciuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teoria Sistemelor MatlabDocument7 paginiTeoria Sistemelor MatlabBarbu MihaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subiecte Teoria SistemelorDocument2 paginiSubiecte Teoria SistemelorDani MoglanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CURS 1 Introducere Sisteme DinamiceDocument22 paginiCURS 1 Introducere Sisteme DinamiceAlessandroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercitii MATLABDocument63 paginiExercitii MATLABJustin PuscasuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metoda Lui EulerDocument4 paginiMetoda Lui Eulercristiionut1234Încă nu există evaluări
- Probleme Ingineria Reglarii AutomateDocument13 paginiProbleme Ingineria Reglarii AutomateBogdan TanasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model Foaie Examen SS+TSDocument1 paginăModel Foaie Examen SS+TSSobolanu AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laborator Metode NumericeDocument4 paginiLaborator Metode NumericeFlorin GheorgheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Programa Seminarii Anul I 2010 2011Document2 paginiPrograma Seminarii Anul I 2010 2011Andreea Bianca AchimescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complexitatea AlgoritmilorDocument47 paginiComplexitatea AlgoritmilorEugenia IvanovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Programarea Paralela Si ConcurentaDocument24 paginiProgramarea Paralela Si ConcurentaBeșliu NicuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calcul NumericDocument9 paginiCalcul NumericandrashikÎncă nu există evaluări
- TS 3. Schema Structurală Și Transf. StructuraleDocument25 paginiTS 3. Schema Structurală Și Transf. Structurale99999999999-971845Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab 5 Met NumDocument35 paginiLab 5 Met NumvvxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verilog HDL CoursesDocument271 paginiVerilog HDL CoursesToderean AlexandruÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Metoda Planului FazelorDocument20 pagini2 Metoda Planului FazelorGold RiverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 1 Teoria SistemelorDocument11 paginiLab 1 Teoria SistemelorAugustina MadoniciÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modele de StareDocument30 paginiModele de StareDemianciuc SebastianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metoda de Selectionare Bazata Pe Fuzzy LogicDocument27 paginiMetoda de Selectionare Bazata Pe Fuzzy LogicRazvan RSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingineria Reglarii AutomateDocument223 paginiIngineria Reglarii AutomateOvidiu CaciulanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SDED Carte PetriDocument145 paginiSDED Carte PetriIonut NeaguÎncă nu există evaluări
- ComputationalMathematics GabrielMos PDFDocument21 paginiComputationalMathematics GabrielMos PDFVasile SentimentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curs Sabloane ProiectareDocument169 paginiCurs Sabloane ProiectarefreestylaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curs Tsra IraDocument371 paginiCurs Tsra IraRobert Allen HarkonennÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tema Proiect Ingineria Reglarii AutomateDocument14 paginiTema Proiect Ingineria Reglarii Automatenumer_nine99Încă nu există evaluări
- Modele Matematice PrezentareDocument26 paginiModele Matematice PrezentareAlex AndruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sisteme DinamiceDocument15 paginiSisteme DinamiceAndrei LaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capitolul 1-1 PDFDocument180 paginiCapitolul 1-1 PDFStelian DraganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formule Si Scheme Clasice de ProbabilitateDocument4 paginiFormule Si Scheme Clasice de ProbabilitateanamariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Separarea RadacinilorDocument4 paginiSepararea RadacinilorMihai NistorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingineria Reglarii Automate PDFDocument27 paginiIngineria Reglarii Automate PDFDorin PleavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algoritmica GrafurilorDocument465 paginiAlgoritmica GrafurilorDragu StelianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curs ASD Format B5 NouDocument164 paginiCurs ASD Format B5 NouPetrascuVladÎncă nu există evaluări
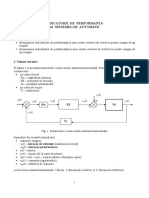
- L2 - Indicatori de Performanta Ai Sistemelor AutomateDocument4 paginiL2 - Indicatori de Performanta Ai Sistemelor Automateangeleyes999Încă nu există evaluări
- Proiectarea Unui Regulator Pentru Controlul Unui ProcesDocument26 paginiProiectarea Unui Regulator Pentru Controlul Unui ProcesVisan Cosmin-GabrielÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 IirDocument34 pagini3 IirMocanu AlinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2010 Serii de Timp-2-1Document16 pagini2010 Serii de Timp-2-1Mihaela CiochinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interpolare Și RegresiaDocument22 paginiInterpolare Și RegresiaСаша Аня КушмаренкоÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subiecte Examen Semnale Si SistemeDocument8 paginiSubiecte Examen Semnale Si SistemeLucian IonutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probleme de Extrem ConditionatDocument4 paginiProbleme de Extrem ConditionatMihaela StancuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Derivate Parţiale, Matrice JacobianăDocument9 paginiDerivate Parţiale, Matrice JacobianăDiana ElenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar NR - 8 - Derivate Partiale - DiferentialeDocument11 paginiSeminar NR - 8 - Derivate Partiale - DiferentialeGeorgiana MargineanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modulul 5Document41 paginiModulul 5fla8991Încă nu există evaluări
- Modulul 3 Procesare de TextDocument47 paginiModulul 3 Procesare de TextElida EliÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECDL Modul 4 Excel Calcul TabelarDocument42 paginiECDL Modul 4 Excel Calcul TabelarpoparamonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PC2008Document202 paginiPC2008smedreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coding StyleDocument3 paginiCoding StyleCristian PopaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rețele Locale de Rughiniș R.-Rughiniș - R. - Deaconescu - R. - Ciorba - A. - Doinea - B.Document360 paginiRețele Locale de Rughiniș R.-Rughiniș - R. - Deaconescu - R. - Ciorba - A. - Doinea - B.poparamona100% (2)