Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
ARITMII Umf Iasi
Încărcat de
Ancuta GaburaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ARITMII Umf Iasi
Încărcat de
Ancuta GaburaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ef Lucrri dr.
Viviana AURSULESEI
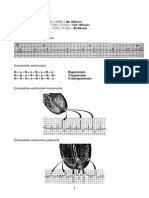
Cea mai frecvent tulburare de ritm
FIBRILAIA ATRIAL: DE CE?
Incidena crete n timp dar i cu vrsta
Prevalen dubl > 50 ani
Asociat cu morbiditate crescut: risc estimat AVC x 5
Asociat cu morbiditate crescut
Predictor independent de mortalitate
Spitalizare prelungit, dependen funcional prin consecine
X 5
ESC Guidelines 2012 on the Management of Atrial Fibrillation
X 2
FIBRILAIA ATRIAL ESTE O CONDIIE FRECVENT SILENIOAS CU
CONSECINE SERIOASE APARIIA AVC
30%
FIBRILAIA ATRIAL ESTE O CONDIIE FRECVENT SILENIOAS CU
CONSECINE SERIOASE APARIIA AVC
30%
FIBRILAIA ATRIAL I CREIERUL: dincolo
de AVC
Studii clinice
Adult Changes in Thought
Study
OnTarget, Transcend
Mecanisme
via AVC ischemic
Embolii silenioase
Hipoperfuzie cerebral
Inflamaie
Disfuncie microvascular
FIBRILAIA ATRIAL: ce factori de risc?
....i nu numai
FIBRILAIA ATRIAL: ce mecanisme?
Factori atriali
Factori
electrofiziologici
Predispoziie
genetic
REMODELARE
ELECTRO
ANATOMC
SDR. CARDIACE
MOTENITE
MECANISM FOCAL
MULTIPLE
WAVELET"
FIBRILAIA ATRIAL: consecine
Conducere atrio-ventricular
Modificri hemodinamice
Tromboembolism
Pacientul tnr cu fibrilaie atrial
M.A., 24 ani
07. 12. 2011
APP: fr
AHC: nesemnificative
Nefumtor, neconsumator de alcool
Istoric: uoar fatigabilitate la efort de aproximativ 3 luni,
palpitaii
Clinic:
FC=120/min, fr sufluri, TA=120/80mmHg
zgomote cardiace aritmice, deficit de puls
Diagnostic clinic: fibrilaie atrial
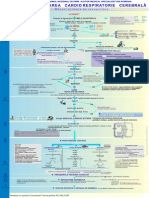
PRIORITATE CHEIE: detecie i diagnostic
Case
detection
Assessment
Rate-
control
Rhythm-
control
Referral
Follow-up
Follow-up
O
R
An ECG should be
performed
in all patients, whether
symptomatic or not, in
whom AF is suspected
because an irregular
pulse has been
detected
Diagnostic clinic: fibrilaie atrial
ECG
Algoritmdiagnostic: ntrebri cheie?
CARACTERIZAREA FIBRILAIEI ATRIALE
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
Algoritmdiagnostic: ntrebri cheie?
CARACTERIZAREA FIBRILAIEI ATRIALE
ETIOLOGIE
VECHIME
SIMPTOME
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
CONDIII PREDISPOZANTE SAU CARE MENIN
FIBRILAIA ATRIAL
European Heart Journal, 2010
FIBRILAIA ATRIAL IDIOPATIC ("lone AF")
I. BILAN ETIOLOGIC
Ex.C-V: normal
Ecocord: normal
colesterol=183mg%
trigliceride=130mg%
glicemie=98mg%
TSH=2,68UI/ml
FT4=16,89pmol/l
FA IDIOPATIC
II. Vechimea fibrilaiei atriale
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
III. FIBRILAIA ATRIAL: SIMPTOMATIC?
SCORUL EHRA
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
DIAGNOSTIC POZITIV
FIBRILATIE ATRIAL IDIOPATIC,
PERSISTENT, CLASA EHRA II
SUMAR DIAGNOSTIC
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
FIBRILAIA ATRIAL: CUM TRATM?
FIBRILAIA ATRIAL: PAI MANAGEMENT
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
FIBRILAIA ATRIAL: PAI DE MANAGEMENT
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
CE CONDUIT LA PACIENT?
TRATAMENT
OPTIM?
PACIENT TNR, ACTIV
CONTROLUL SIMPTOMELOR
TRATAMENT
OPTIM?
FR BOAL STRUCTURAL CARDIAC
CONTROLUL FRECVENEI VENTRICULARE?
CONTROLUL RITMULUI CARDIAC?
TRATAMENT
OPTIM?
EVALUARE RISC TROMBOEMBOLIC
CUM?
CONTROLUL FRECVENEI VENTRICULARE
SAU A RITMULUI?
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
FA PAROXISTIC/PERSISTENT
BOAL STRUCTURALCARDIAC
ABSENT/CAUZCORECTAT
PACIENT TNR, ACTIV,
SIMPTOMATIC
CONTROL RITM
CARDIOVERSIE
EEC CARDIOVERSIE
FA PERMANENT
FA SECUNDARUNOR CAUZE CE NU SUNT
CORECTATE /CORECTABILE
VECHIMEA FA
BOALDE NOD SINUSAL/BOALBINODAL
PACIENT VRSTNIC
REFUZ PACIENT PENTRU CARDIOVERSIE
CONTROL FRECVEN
VENTRICULAR
POATE FI I O SITUAIE
TEMPORAR!!
CONTROLUL FRECVENEI VENTRICULARE
SAU A RITMULUI?
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
CONTROLUL RITMULUI N FA
PAROXISTIC: CE OPIUNI?
CONTROLUL RITMULUI N FA PAROXISTIC:
CARDIOVERSIA FARMACOLOGIC
CONTROLUL RITMULUI N FA PAROXISTIC:
CARDIOVERSIA FARMACOLOGIC
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
CONTROLUL RITMULUI N FA PERSISTENT
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
OPIUNE TERAPEUTIC LA PACIENT
07.12.2011: Bisogamma 5mg/zi, Sintrom 2mg/zi
18.01.2012: INR 2,36 Cardioversie electric RS
CE ATITUDINE PENTRU MENINEREA
RITMULUI SINUSAL?
PROFILAXIE
ANTIARITMIC
PRINCIPII DE TERAPIE ANTIARITMIC pentru
MENINEREA RITMULUI SINUSAL (I)
REALITATEA PRACTICVERSUS INDICAII
1. Tratamentul este motivat pentru a reduce simptomele induse de FA
2. Eficiena drogurilor antiaritmice n meninerea RS este modest
3. Terapia antiaritmic de succes mai degrab reduce dect elimin
recurenele FA
4. Dac un drog antiaritmic eueaz, se poate alege un alt drog
5. Proaritmiile induse de droguri sau efectele extracardiace sunt frecvente
6. Alegerea de prim intenie a unui drog antiaritmic trebuie ghidat de
sigurana administrrii i apoi de eficien!
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
PRINCIPII DE TERAPIE ANTIARITMIC pentru
MENINEREA RITMULUI SINUSAL (II)
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
PRINCIPII DE TERAPIE ANTIARITMIC pentru
MENINEREA RITMULUI SINUSAL (III)
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
CONDUITA TERAPEUTIC POSTCARDIOVERSIE LA
PACIENT
PROFILAXIE ANTIARITMIC: PROPAFENON 45O mg/zi
ESTE NECESARTROMBOPROFILAXIE?
CUM DECIDEM INDICAIA DE TROMBOPROFILAXIE?
Stratificare risc AVC
SCOR CHADS
2
Risk factor Points
C Recent Congestive heart failure exacerbation 1
H Hypertension 1
A Age 75 years 1
D Diabetes mellitus 1
S Prior history of Stroke or transient ischemic attack 2
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
SCORUL DE RISC MBUNTIT
CHA
2
DS
2
-VASc
*Prior myocardial infarction, peripheral artery disease, aortic plaque. Actual rates of stroke in contemporary
cohorts may vary from these estimates.
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
ANTIAGREGARE SAU ANTICOAGULARE?
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
CONDUITA TROMBOPROFILACTIC:
ntre beneficiu i risc
Scorul de risc HAS-BLED
SCOR 3 = RISC NALT DE SNGERARE
CONDUITA TERAPEUTIC POSTCARDIOVERSIE
LA PACIENT
PROFILAXIE ANTIARITMIC: PROPAFENON 45O mg/zi
TROMBOPROFILAXIE CU ASPENTER 75 mg/zi
EVOLUIE SUB TRATAMENT
Recurena fibrilaiei atriale, asimptomatice
Bisoprolol 5 mg/zi, Aspenter 75mg/zi (CHADS=0)
CE OPIUNI N CAZ DE RECUREN?
2011 ACCF/AHA/HRS Focused Update on the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation (Updating the 2006 Guideline)
2006 Recommendations
2011 Focused Update Recommendations
Class I
Before initiating antiarrhythmic drug
therapy, treatment of precipitating or
reversible causes of AF is recommended.
(Level of Evidence: C)
1. Before initiating antiarrhythmic drug therapy,
treatment of precipitating or reversible causes of AF is
recommended. (Level of Evidence: C)
2. Catheter ablation performed in experienced centers* is
useful in maintaining sinus rhythm in selected patients
with significantly symptomatic, paroxysmal AF who have
failed treatment with an antiarrhythmic drug and have
normal or mildly dilated left atria, normal or mildly
reduced LV function, and no severe pulmonary disease.38
51 (Level of evidence:A)
Class IIa
In patients with lone AF without structural
heart disease, initiation of propafenone or
flecainide can be beneficial on an outpatient basis in
patients with paroxysmal AF who are in sinus rhythm
at the time of drug initiation. (Level of Evidence B )
In patients with AF without structural or
coronary heart disease, initiation of
propafenone or flecainide can be beneficial
on an outpatient basis in patients with
paroxysmal AF who are in sinus rhythm at
the time of drug initiation.5254 (Level of Evidence B )
CE OPIUNI N CAZ DE RECUREN?
NLOCUIREA CU UN ALT DROG
2011 ACCF/AHA/HRS Focused Update on the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation (Updating the 2006 Guideline)
CE OPIUNI N CAZ DE RECUREN?
ESC Guidelines 2012 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
DRONEDARONE N FIBRILAIA ATRIAL: CND?
2011 Focused Update Recommendations Comments
Class IIa
1. Dronedarone is reasonable to decrease the need for
hospitalization for cardiovascular events in patients with
paroxysmal AF or after conversion of persistent AF.
Dronedarone can be
initiated during outpatient therapy
Class IIIHarm
1. Dronedarone should not be administered to patients
with class IV heart failure or patients who have had an
episode of decompensated heart
failure in the past 4 weeks, especially if they have
depressed left ventricular function (left ventricular
ejection fraction 35%)
New recommendation
New recommendation
2011 ACCF/AHA/HRS Focused Update on the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation (Updating the 2006 Guideline)
DRONEDARONE N FIBRILAIA ATRIAL
CE ALTE OPIUNI N CAZ DE RECUREN:
INDICAIA DE RADIOABLAIE
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
CE ALTE OPIUNI N CAZ DE RECUREN:
INDICAIA DE RADIOABLAIE
ESC Guidelines 2010 on the management of Atrial Fibrillation
STADIUL
AFECTRII
ATRIALE
BOAL
STRUCTURAL
CARDIAC
OPIUNI
ALTERNATIVE
TIP FA
ISTORICUL FA
MRIME ATRIU STNG
PREZENT
ABSENT
MEDICAIE ANTIARITMIC
CONTROLUL FC
ALEGEREA PACIENTULUI
CONDUIT LA CAZ: opiunea
pacientului este un factor cheie!
Consult specialist electrofiziologie
Se poate tenta ablaia fibrilaiei atriale (izolare de vene pulmonare)
Cost 6000 euro
Rata de succes 70% 1 an; 50% 5 ani
O nou cardioversie electric +
FLECAINID
ABLAIA PE CATETER: opiune la
pacient?
Da, numai dac:
exist recuren dup toate
antiaritmicele
acceptat de pacient
Este opiunea de preferat la
tnr vs amiodaron
critical fibres
microcircuits
of reentry
focal triggers
ABLAIA PE CATETER
ABLAIA PE CATETER:
sumar practic
UTILDOAR DAC:
este practicat n centre
specializate!
s-a epuizat eficiena
antiaritmicelor
este preferat de pacient de
prim intenie
pe termen lung nu a aprut
recuren n primele 6
sptmni
Antiaritmicele ntre beneficiu i risc
M.E.,73 ani, 02. 12. 2010
MI: palpitaii
APP :
1980: HTA
18.XI.2010: FA paroxistic (monitorizare ECG Holter)
tratat cu:
Cordarone 400mg/zi, 14 zile, ulterior 600mg/zi
anticoagulare oral
QT=480 msec(+20%)
QT=520msec(+40%)
EVOLUIE N SPITAL
Episoade de palpitaii
Repetate episoade de convulsii, cianoz,
pierderea strii de contien
CAUZA?
EPISOADE SUBINTRANTE DE
TORSADA VRFURILOR
III
MONITORIZARE ECG n evoluie
II
CARDIOSTIMULARE ELECTRIC
TEMPORAR
PACING ANTI-TAHICARDIC
I
EE (repetate) MgSO
4
, xilin p.i.v.
GENERATOR PENTRU
STIMULARE TEMPORAR
PRINCIPIU:
STIMULARE CU FRECVEN
VENTRICULAR
SUPERIOAR FRECVENEI DE
BAZ
Regresia intervalului QT
Monitorizarea ECG Holter 10.12.2010
un episod de fibrilaie atrial paroxistic
Atitudine terapeutic
betablocant
anticoagulare oral permanent
controlul valorilor TA
B.E., 73 ani, 16. 01. 2012
MI: palpitaii, ameeli, dispnee
APP:
HTA
DZ tip 2
Dislipidemie
Obezitate (IMC=42 Kg/m
2
)
AVC (infarct occipital stng) - 2005
FA persistent (redus cu Cordarone) - 2010
Antiaritmic :Cordarone
200mg/zi
Anticoagulant
Antihipertensive:diuretic +
inhibitor ACE
Hipolipemiant: statin
COMPLICAIE EXTREM DE RAR LA CORDARONE
Uree=65mg%
Creatinina=0,73mg%
Glicemie=148-128mg%
Na=141mEq/l K=4,6mEq/l
RA=25mEq/l
TSH=67,41ui/ml; FT4=11,53pmol/l
QT= 440msec
AMIODARONA: ce alte efecte adverse?
Smurf Drug
Tratament antihipertensiv
Tratament anticoagulant
Tratament de substituie tiroidian
Meninerea RS fr tratament antiaritmic
Exist riscuri? Da:
nou episod de FA
risc crescut de AVC
CE ATITUDINE DUP CONTROLUL
HIPOTIROIDIEI?
Anticoagulare strict
Controlul frecvenei ventriculare:
60-80/min n repaus
90-115/min la efort
Ce medicaie?
CE ATITUDINE ESTE DE PREFERAT?
Unpredictable
response
Routine coagulation
monitoring
Slow onset/offset
of action
Risk of Bleeding
Complications
Anticoagulation
therapy has
several
limitations that
make it difficult
to use in
practice
Numerous drug-drug
interactions
Numerous food-drug
interactions
Frequent dose
adjustments
Narrow therapeutic
window
(INR range 2-3)
Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation
Limitations of Anticoagulation Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation
OAC was #1 in 2003 and 2004 in the number of mentions of deaths for
drugs causing adverse effects in therapeutic use
OAC caused 6% of the 702,000 ADEs treated in the ED/year; 17% required
hospitalization
J Thromb Thrombolysis 2008; 25: 52-60
New antithrombotic treatments in Phase III trials
for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
Tissue Factor
Plasma Clotting
Cascade
Prothrombin
Thrombin
Fibrinogen Fibrin
Thrombus
Platelet Aggregation
Conformational
Activation of GPIIb/IIIa
Collagen
Thromboxane A
2
ADP
AT
Aspirin
Clopidogrel
Prasugrel
AZD6140
Dabigatran
Ximelagatran
Factor
Xa
Idraparinux
Apixaban
Rivaroxaban
Edoxaban
Dabigatran
Rivaroxaban
Nu sunt inferiori n prevenia
AVC/embolii n FA
Risc redus de hemoragii fatale,
inclusiv intracerebrale
Risc crescut de HDS
Nu necesit monitorizarea
coagulrii
Dabigatran
Rivaroxaban
Features Warfarin New agents
Onset Slow Rapid
Dosing Variable Fixed
Food/drug interactions Many None or very few
Monitoring Yes No
Half life Long Short
Antidote Yes No
Recommendation for Combining Anticoagulant
With Antiplatelet Therapy
2011 Focused Update Recommendation
Comments
Class IIb
1. The addition of clopidogrel to aspirin
(ASA) to reduce the risk of major
vascular events, including stroke, might
be considered in patients with AF in
whom oral anticoagulation with warfarin
is considered unsuitable due to patient
preference or the physicians assessment
of the patients ability to safely sustain
anticoagulation.10 (Level of Evidence: B)
New recommendation
2011 ACCF/AHA/HRS Focused Update on the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation (Updating the 2006 Guideline)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- EKG Tulburari de Ritm Si de ConducereDocument8 paginiEKG Tulburari de Ritm Si de ConducereConsuela BarsanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumologie PDFDocument25 paginiPneumologie PDFCristina ChiruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abordarea Pacientului IntoxicatDocument38 paginiAbordarea Pacientului Intoxicatcasyopa100% (1)
- 11 Ginecologie Si ObstetricaDocument90 pagini11 Ginecologie Si ObstetricaSERGIU TUDOSEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valvulopatii. Elaborare MetodicăDocument71 paginiValvulopatii. Elaborare MetodicăFlorina Oane100% (1)
- Afectiunile OsteoarticulareDocument2 paginiAfectiunile Osteoarticulareionica964Încă nu există evaluări
- Penumo PDFDocument884 paginiPenumo PDFAlin NeataÎncă nu există evaluări
- SDA Curs PDFDocument79 paginiSDA Curs PDFAlexandra OanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curs Aritmii 2019Document70 paginiCurs Aritmii 2019Sandu AlexandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caz Clinic - Nefropatia LupicăDocument40 paginiCaz Clinic - Nefropatia LupicăDan NechitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carte Curs Stafie PDFDocument424 paginiCarte Curs Stafie PDFIoana IsbindaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boala Coronariana IschemicaDocument6 paginiBoala Coronariana IschemicaAndreea Mihaela OpreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LP 5 - Intoxicatii Cu Alcooli ToxiciDocument17 paginiLP 5 - Intoxicatii Cu Alcooli ToxiciOlimpia RusuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urgente Medicale 2004Document136 paginiUrgente Medicale 2004Andrei Ghiderman100% (1)
- Solutii PerfuzabileDocument25 paginiSolutii PerfuzabileBorbely ErwinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tratament Anticolici SugariDocument4 paginiTratament Anticolici SugariRaluca ToiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perfuzia Cerebrala in Chirurgia Crosei AorteiDocument21 paginiPerfuzia Cerebrala in Chirurgia Crosei AorteiRaluca LÎncă nu există evaluări
- SincopăDocument6 paginiSincopăGeorgiana DÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cateterismul Cardiac Diagnostic Si Terapeutic La NNDocument39 paginiCateterismul Cardiac Diagnostic Si Terapeutic La NNClaudia KosztelnikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pulsul ArterialDocument3 paginiPulsul ArterialkereklovagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Life SupportDocument1 paginăBasic Life SupportOana TănaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curs Medicina Conditiilor ExtremeDocument67 paginiCurs Medicina Conditiilor ExtremeParvu Delia IrinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Programa SemiologieDocument8 paginiPrograma SemiologieDaniel AfloareiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curs 2 ATLSDocument101 paginiCurs 2 ATLSAdriana VickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tulburarile de Ritm Si de ConducereDocument24 paginiTulburarile de Ritm Si de Conduceremarilena0danielaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curs - Tulb - Acido - BaziceDocument47 paginiCurs - Tulb - Acido - BaziceAndrei BarbuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curs 3Document34 paginiCurs 3Alexandra RărișÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZdrengheaDocument265 paginiZdrengheaAciobăniței TeodoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 Maladii Sexual-Transmisibile MSTDocument199 pagini7 Maladii Sexual-Transmisibile MSTChiriţoiu AnamariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tumori HipofizareDocument42 paginiTumori HipofizareAndrei ParaschivÎncă nu există evaluări
- ComaDocument39 paginiComaCosmina Alina MoscuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curs Investigatii in PediatrieDocument51 paginiCurs Investigatii in PediatrieTiberiu-o CodrinÎncă nu există evaluări
- R2 2004Document88 paginiR2 2004Zupcu MarcelÎncă nu există evaluări
- AritmogenezaDocument135 paginiAritmogenezaClaudia IrinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- POTENTIALE TARDIVE VENTRICULARE EbookDocument134 paginiPOTENTIALE TARDIVE VENTRICULARE EbookAlex MircescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paeds Basic Manual 2015 - Ro - FormatatDocument229 paginiPaeds Basic Manual 2015 - Ro - FormatatMelinda BorobarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protocol Terapeutic in BPOCDocument9 paginiProtocol Terapeutic in BPOCChiriac AdinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prof. Univ - DR - Egidia Miftode Tranzitia de La Terapia Antimicrobiana Intravenoasa La Cea OralaDocument21 paginiProf. Univ - DR - Egidia Miftode Tranzitia de La Terapia Antimicrobiana Intravenoasa La Cea OralapaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prezentare de Caz (Semiologie Generala Anul III)Document3 paginiPrezentare de Caz (Semiologie Generala Anul III)Alex SeiceanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BPOCDocument1.176 paginiBPOCAnnaMincaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supliment Cardiologie in Medicina de FamilieDocument32 paginiSupliment Cardiologie in Medicina de FamilieGessyca JeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- VALORI NORMALE Anul I PDFDocument2 paginiVALORI NORMALE Anul I PDFClara ZuzyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2016 Basic 4 Nurses Manual ROMANA 02 02 2017 Corectata MuresDocument175 pagini2016 Basic 4 Nurses Manual ROMANA 02 02 2017 Corectata MuresLoredana CenuseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aritmii Cardiace - Fibrilatia Atriala PDFDocument0 paginiAritmii Cardiace - Fibrilatia Atriala PDFAlecsandra MunteanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fibrilatie Atriala PDFDocument4 paginiFibrilatie Atriala PDFleturaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complicatiile CoronaroangiografieiDocument62 paginiComplicatiile Coronaroangiografieimedic_brinza100% (1)
- Kinetoterapia C3aen Patologia Cardiovascularc483Document9 paginiKinetoterapia C3aen Patologia Cardiovascularc483donceaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinetoterapia În Fibrilația AtrialăDocument4 paginiKinetoterapia În Fibrilația AtrialăVlad PadinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FISA DE LUCRU Socul A.T.I. MG 3 BDocument3 paginiFISA DE LUCRU Socul A.T.I. MG 3 BCatalinaAndreeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiologie, Fibrilatii AtrialeDocument14 paginiCardiologie, Fibrilatii Atrialesacha.basistii32Încă nu există evaluări
- Cardiologie, Fibrilatii AtrialeDocument14 paginiCardiologie, Fibrilatii Atrialesacha.basistii32Încă nu există evaluări
- 2.examinarea Clinica Si Paraclinica A Pacientului in ChirurgiaDocument96 pagini2.examinarea Clinica Si Paraclinica A Pacientului in ChirurgiaLoredana Ivanov100% (1)
- Defectele Septale Atriale Și Riscurile Pentru Chirugia Dento AlveolarăDocument18 paginiDefectele Septale Atriale Și Riscurile Pentru Chirugia Dento AlveolarăDoroş DorinÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCP 4333 21.02.12Document9 paginiRCP 4333 21.02.12COSMIN-MARIUS OLARIUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accidentul Vascular Cerebral La Vârstnici ShortDocument34 paginiAccidentul Vascular Cerebral La Vârstnici ShortAntonia100% (1)
- IECDocument42 paginiIECZamfirescu Mihaela-ElenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insuficiența Cardiacă CronicăDocument17 paginiInsuficiența Cardiacă CronicăGiulia BanciuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Terenul La BătrâniDocument14 paginiTerenul La BătrâniCostea VladÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fibrilatiile AtrialeDocument11 paginiFibrilatiile AtrialeSchuldesz PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tulburari de Ritm Si de ConducereDocument18 paginiTulburari de Ritm Si de ConducereBianca AndreiÎncă nu există evaluări